Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Electrochemistry. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic Electrochemistry.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: Electrochemistry
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry.
Electrochemistry is that branch of chemistry which deals with the study of production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electrical energy to bring about non-spontaneous chemical transformations.
Importance of Electrochemistry
- Production of metals like Na, Mg. Ca and Al.
- Electroplating.
- Purification of metals.
- Batteries and cells used in various instruments.
Conductors
Substances that allow electric current to pass through them are known as conductors.
Metallic Conductors or Electronic Conductors
Substances which allow the electric current to pass through them by the movement of electrons are called metallic conductors, e.g.. metals.
Electrolytic Conductors or Electrolytes
Substances which allow the passage of electricity through their fused state or aqueous solution and undergo chemical decomposition are called electrolytic conductors, e.g., aqueous solution of acids. bases and salts.
Electrolytes are of two types:
- Strong electrolytes The electrolytes that completely dissociate or ionise into ions are called strong electrolytes. e.g., HCl, NaOH, K2SO4
- Weak electrolytes The electrolytes that dissociate partially (ex < 1) are called weak electrolytes, e.g., CH3COOH, H2CO3, NH4OHH2S, etc.
Electrochemical Cell and Electrolytic

A cell of almost constant emf is called standard cell. The most common is Weston standard cell.
Galvanic cell is also called voltaic cell.
General Representation of an Electrochemical Cell

Other features of the electrochemical cell are
- There is no evolution of heat.
- The solution remains neutral on both sides.
- The reaction and now of electrons stops after sometime.
Daniell Cell
An electrochemical cell of zinc and copper metals is known as Daniell cell. It is represented as

By convention cathode is represented on the RHS and anode on the LHS.
Function of salt bridge
- It completes the circuit and allows the flow of current.
- It maintains the electrical neutrality on both sides. Salt-bridge generally contains solution of strong electrolyte such as KNO3, KCL etc. KCI is preferred because the transport numbers of K+ and Cl– are almost same.
Transport number or Transference number The current flowing through an electrolytic solution is carried by the ions. The fraction of the current carried by an ion is called its transport number or transference number. Thus.
Transport number of cation. nc = (current carried by cation/total current)
Transport number of cation. na = (current carried by anion/total current)
Evidently nc + na = 1
Electrode Potential
When an electrode is in contact with the solution of its ions in a half-cell, it has a tendency to lose or gain electrons which is known as electrode potential. It is expressed in volts. It is an intensive property, i.e., independent of the amount of species in the reaction.
Oxidation potential The tendency to lose electrons in the above case is known as oxidation potential. Oxidation potential of a half-cell is inversely proportional to the concentration of ions in the solution.
Reduction potential The tendency to gain electrons in the above case is known as reduction potential. According to IUPAC convention, the reduction potential alone be called as the electrode potential unless it is specifically mentioned.
E°red = – E°oxidalion
It is not possible to determine the absolute value of electrode potential. For this a reference electrode [NHE or SHE] is required. The electrode potential is only the difference of potentials between two electrodes that we can measure by combining them to give a complete cell.
Standard electrode potential The potential difference developed between metal electrode and solution of ions of unit molarity (1M) at 1 atm pressure and 25°C (298 K) is called standard electrode potential.
It is denoted by E°.
Reference Electrode
The electrode of known potential is called reference electrode. It may be primary reference electrode like hydrogen electrode or secondary reference electrode like calomel electrode.
Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). also known as normal hydrogen electrode (NHE), consists of platinum wire, carrying platinum foil coated with finely divided platinum black. The wire is sealed into a glass tube. placed in beaker containing 1 M HCl. The hydrogen gas at 1 atm pressure is bubbled through the solution at 298K. Half-cell is pt H2 (1 atm) H+ (1 M)

In SHE. at the surface of plantinum, either of (he following reaction can take place
2H+(ag) + 2e– → H2G Reduction
H2(g) → 2H+(ag) + 2e– Oxidation
The electrode potential of SHE has been fixed as zero at all temperatures.
Its main drawbacks are
- It is difficult to maintain 1 atm pressure of H2 gas.
- It is difficult to maintain H+ ion concentration 1 M.
- The platinum electrode is easily poisoned by traces of impurities.
Hence, calomel electrodes are conveniently used as reference electrodes, It consists of mercury in contact with Hg2 Cl2 (calomel) paste in a solution of KCl.
Electromotive Force (emf) of a Cell
It is the difference between the electrode potentials of two half-cells and cause flow of current from electrode at higher potential to electrode at lower potential. It is also the measure of free energy change. Standard emf of a cell,
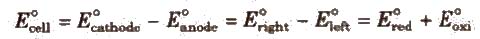

Electrochemical Series
It is the arrangement of electrodes in the increasing order of their standard reduction potentials.
Standard Electrode Potential at 298 K


Appications of Electrochemical Series (ECS)
1. The lower the value of E°, the greater the tendency to form cation.
M → Mn+ + ne–
Metals placed below hydrogen in ECS replace hydrogen from di1 acids but metals placed above hydrogen cannot replace hydrogen from dil acids.

3. Oxides of metals placed below hydrogen are not reduced by H2 but oxides of iron and metals placed above iron are reduced by H2·
- SnO, PbO, CuO are reduced by H2
- CaO, K2O are not reduced by H2·
4. Reducing character increases down the series.
5. Reactivity increases down the series.
6. Determination of emf; emf is the difference of reduction potentials of two half-cells.
- Eemf = ERHS – ELHS
If the value of emf is positive. then reaction take place spontaneously, otherwise not.
7. Greater the reduction potential of a substance, oxidising power. (e.g.. F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2)
8. A negative value of standard reduction potential shows that it is the site of oxidation.
9. Oxides of metals having E°red ≥ 0.79 will be decomposed by heating to form O2 and metal.
HgO (s) → Hg(l)(1/2)O2(g)
(E°Hg2+/Hg = 0.79V)
Nernst Equation
The relationship between the concentration of ions and electrode potential is given by Nernst equation.
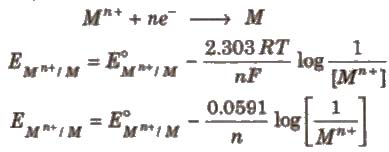
For a electrochemical cell,
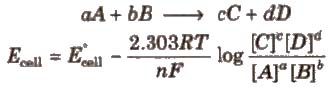
Concentration of pure solids and liquids is taken as unity.
Nernst equation and Kc
At equilibrium

Here, ΔG° is the standard Gibbs free energy change.
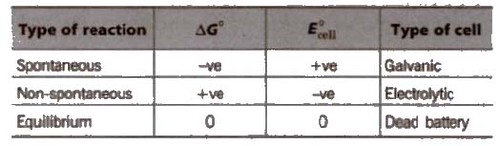
Relationship between free energy change and equilibrium constant
ΔG° = – 2.303RT log Kc
Concentration Cells
(i) Electrode concentration cells Two hydrogen electrodes or different pressures are dipped In the same solution of electrolyte,
e.g..

(ii) Electrolyte concentration cells Electrodes are the same but electrolyte solutions have different concentrations, e.g..

Conductance (G)
It is the ease of flow of electric current through the conductor. It is reciprocal of resistance (R).
G = (1/R), units ohm-1 mhos or Ω-1
Specific Conductivity (K)
It is the reciprocal of specific resistance.

Unit of cell constant is cm-1 or m-1.
Specific conductivity decreases on dilution. This is because concentration of ions per cc decreases upon dilution.
Molar Conductivity (Λm)
The conductivity of all the ions produced when 1 mole of an electrolyte is dissolved in V mL of solution is known as molar conductivity.
It is related to specific conductance as
Λm = (k x 1000/M)
where. M = molarity.
It units are Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 or S cm2 mol-1.
Equivalent conductivity (Λm)
The conducting power of all the ions produced when 1 g-equivalent of an electrolyte is dissolved in V mL of solution, is called equivalent conductivity. It is related to specific conductance as
Λm = (k x 1000/N)
where. N = normality.
Its units are ohm-1 cm2 (equiv-1) or mho cm2 (equiv-1) or S cm2 (g-equiv-1).
Debye-Huckel Onsagar equation It gives a relation between molar conductivity, Λm at a particular concentration and molar conductivity Λm at infinite dilution.
Λm = Λ0m – √C
where, b is a constant. It depends upon the nature of solvent and temperature.
Factors Affecting Conductivity
(i) Nature of electrolyte The strong electrolytes like KNO3 KCl. NaOH. etc. are completely ionised in aqueous solution and have high values of conductivity (molar as well as equivalent).
The weak electrolytes are ionised to a lesser extent in aqueous solution and have lower values of conductivity (molar as well as equivalent) .
ii) Concentration of the solution The concentrated solutions of strong electrolytes have SIgnificant interionic attractions. which reduce the speed of ions and lower the value of Λm. and Λeq.
The dilution decreases such attractions and increase the value of Λm and Λeq.

The limiting value, Λ0m or Λ∞m. (the molar conductivity at zero concentration (or at infinite dilution) can be obtained extrapolating the graph.
In case of weak electrolytes, the degree of ionisation increases dilution which increases the value of Λm and Λeq. The liminting value Λ0m cannot be obtained by extrapolating the graph. ~
limiting value, Λ0m, for weak electrolytes is obtained by Kohlrausch law.
(iii) Temperature The increase of temperature decreases inter-ionic attractions and increases kinetic energy of ions and their speed. Thus, Λm and Λeq increase with temperature.
Kohlrausch’s Law
At infinite dilution, the molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the ionic conductivities of the cations and anions, e.g., for AxBy.
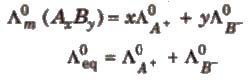
Applications
(i) Determination of equivalent/molar conductivities of weak electrolytes at infinite dilution, e.g.,

(ii) Determination of degree of dissociation (α) of an electrolyte at a given dilution.

The dissociation constant (K) of the weak electrolyte at concentration C of the solution can be calculated by using the formula
kc = (Cα2/1 – α)
where, α is the degree of dissociation of the electrolyte.
(iii) Salts like BaSO4 .., PbSO4‘ AgCl, AgBr and AgI which do not dissolve to a large extent in water are called sparingly soluble salts.
The solubility of a sparingly soluble salt can be calculated as

Electrolysis
It is the process of decomposition of an electrolyte when electric current is passed through either its aqueous solution or molten state,
- In electrolytic cell both oxidation and reduction takes place in the same cell.
- Anode is positively charged and cathode is negatively charged, In electrolytic cell.
- During electrolysis of molten electrolyte, cations are liberated at cathode. while anions at the anode.
- When two or more ions compete at the electrodes. the ion with higher reduction potential gets liberated at the cathode while the ion with lower reduction potential at the anode.
For metals to be deposited on the cathode during electrolysis, the voltage required is almost the same as the standard
electrode potential. However for liberation of gases, some extra voltage is required than the theoretical value of the standard electrode potential. The extra voltage thus required is called over voltage or bubble voltage.
How to Predict the Products of Electrolysis?
When an aqueous solution of an electrolyte is electrolysed, if the cation has higher reduction potential than water (-0.83 V), cation is liberated at the cathode (e.g.. in the electrolysis of copper and silver salts) otherwise H2 gas is liberated due to reduction of water (e.g., in the electrolysis of K, Na, Ca salts, etc.) Similarly if anion has higher oxidation potential than water (- 1.23 V), anion is liberated (e.g., Br–), otherwise O2 gas is liberated due to oxidation of water (e.g., in caseof F–, aqueous solution of Na2SO4 as oxidation potential of SO2-4 is – 0.2 V).
Discharge potential is defined as the minimum potential that must be applied acrossthe electrodes to bring about the electrolysis and subsequent discharge of the ion on the electrode.
Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis
1. First law
The amount of the substance deposited or liberated at cathode directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through electrolyte.
W ∝ I x t = I x t x Z = Q x Z
- I current in amp, t = time in sec,
- Q = quantity of charge (coulomb)
- Z is a constant known as electrochemical equivalent.
When I = 1 amp, t = 1 sec then Q = 1 coulomb, then w = Z.
Thus, electrochemical equivalent I” the amount of the substance deposited or liberated by passing 1A current for 1 sec (i.e.. 1 coulomb, I x t = Q)
2. Second law
When the same quantity of electricity is passed through different electrolytes. the amounts of the substance deposited or liberated at the electrodes arc directly proportional to their equivalent weights, Thus,
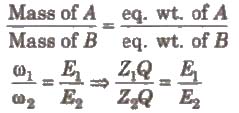
Hence, electrochemical equivalent ∝ equivalent weight.
Batteries
These are source of electrical energy which may have one or more cells connected in series. For a good quality battery it should be reasonably light. compact and its voltage should not vary appreciably during its use.
Primary Batteries
In the primary batteries. the reaction occurs only once and after use over a period of time battery becomes dead and cannot be reused again.
(i) Dry cell or Leclanehe cell
Anode-Zinc container
Cathode-Graphite rod surrounded by MnO2 powder
Electrolyte-Paste of NH4Cl + ZnCl2
Cathode reaction,
2MnO2(s) + 2 NH+4(aq) + 2e– → Mn2O3(s) + 2NH3(g) + H2O(l)
Anode reaction,
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e–
Cell potential 1.25 V to 1.5 V
(ii) Mercury cell
Anode-Zn-Hg amalgam
Cathode-Paste of (HgO + C)
Electrolyte-Moist paste of KOH-ZnO

Secondary Batteries
These cells can be recharged and can be used again and again, e.g.,
(i) Lead Storage battery
Anode-Spongy lead
Cathode-Grid of lead packed with PbO2
Electrolyte-38% H2SO4 by mass

When recharged the cell reactions are reversed.
(ii) Nickel-cadmium storage cell
Anode-Cadmium
Cathode-Metal grid containing NiO2
Electrolyte-KOH solution
Anode reaction,
Cd(s) + 2OH–(aq) → Cd(OH)2(s) + 2e–

Fuel Cells
Galvanic cells which use energy of combustion of fuels like H2, CH4, CH3OH, etc., as the source to produce electrical energy are called fuel cells. The fuel cells are pollution free and have high efficiency.
Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell
Electrodes-Made of porous graphite impregnated with catalyst (Pt, Ag or a metal oxide).
Electrolyte-Aqueous solution of KOH or NaOH
Oxygen and hydrogen are continuously fed into the cell.

Corrosion
Slow formation of undesirable compounds such as oxides, sulphides or carbonates at the surface of metals by reaction with moisture and other atmospheric gases is known as corrosion.
Factors Affecting Corrosion
- Reactivity of metals
- Presence of moisture and atmospheric gases like CO2, SO2, etc.
- Presence of impurities
- Strains in the metal
- Presence of electrolyte
Rusting of Iron-Electrochemical Theory
An electrochemical cell, also known as corrosion cell, is developed at the surface of iron.
Anode- Pure iron
Cathode-Impure surface

Rusting of iron can be prevented by the following methods :
- Barrier protection through coating of paints or electroplating.
- Through galvanisation or coating of surface with tin metal.
- By the use of antirust solutions (bis phenol).
- By cathodic protection in which a metal is protected from corrosion by connecting it to another metal that is more easily oxidised.
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


