Class 12 Maths Probability – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Maths Probability. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Maths study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 12 Maths for topic Probability.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Maths
- Topic: Probability
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Maths Probability
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Maths Probability.
Some Basic Terms
Coin
A coin has two sides, Head and Tail. If an event consists of more than one coins, then coins are considered as. distinct, if not otherwise stated.
Die
A die has six face marked 11, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. If we have more than one dice, then all dice are considered as distinct, if not otherwise stated.
Playing Cards
A pack of playing cards has 52 cards. There are 4 suits (spade, heart, diamond and club) each having 13 cards. There are two colours, red (heart and diamond) and black (spade and club) each having 26 cards.
In 13 cards of each suit, there are 3 face cards namely king, queen and jack so there are in all ’12 face cards. Also, there are 16 honour cards,
4 of each suit namely ace, king, queen and jack.
Types of Experiments
1. Deterministic Experiment
Those experiments, which when repeated under identical conditions produce the same result or outcome are known as deterministic experiment,
2. Probabilistic/Random Experiment
Those experiments, which when repeated under identical conditions, do not produce the same outcome every time but the outcome in a trial is one of the several possible outcomes, called random experiment.
Important Definitions
(i) Trial Let a random experiment, be repeated under identical conditions, then the experiment is called a Trial.
(ii) Sample Space The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space of the experiment and it is denoted by S.
(iii) Event A subset of the sample space associated with a random experiment is called event or case.
(iv) Sample Points The outcomes of an experiment is called the sample point.
(v) Certain Event An event which must occur, whatever be the outcomes, is called a certain or sure event.
(vi) Impossible Event An event which cannot occur in a particular random experiment, is called an impossible event.
(vii) Elementary Event An event certaining only one sample point is called elementary event or indecomposable events.
(viii) Favourable Event Let S be the sample space associated with a random experiment and let E ⊂ S. Then, the elementary events belonging to E are known as the favourable event to E .
(ix) Compound Events An event certaining more than one sample points is called compound events or decomposable events.
Probability
If there are n elementary events associated with a random experiment and m of them are favourable to an event A, then the probability of happening or occurrence of A, denoted by P(A), is given by
P(A) = m / n = Number of favourable cases / Total number of possible cases
Types of Events
(i) Equally Likely Events The given events are said to be equally likely, if none of them is expected to occur in preference to the other.
(ii) Mutually Exclusive Events A set of events is said to be mutually exclusive, if the happening of one excludes the happening of the other.
If A and B are mutually exclusive, then P(A ∩ B) = 0
(iii) Exhaustive Events A set of events is said to be exhaustive, if the performance of the experiment always results in the occurrence of atleast one of them.
If E1, E2, … , En are exhaustive events, then El ∪ E2 ∪ … ∪ En = S i.e., P(E1 ∪ E2 ∪ E3 ∪ … ∪ En) = 1
(iv) Independent Events Two events A and B associated to a random experiment are independent, if the probability of occurrence or non-occurrence of A is not affected by the occurrence or non-occurrence of B.
i.e., P(A ∩ B) = P(A) P(B)
Complement of an Event
Let A be an event in a sample space S~the complement of A is the set of all sample points of the space other than the sample point in A and it is denoted by,
A’ or A = {n : n ∈ S, n ∉ A}
(i) P(A ∪ A’) = S
(ii) P(A ∩ A’) = φ
(iii) P(A’)’ = A
Partition of a Sample Space
The events A1, A2,…., An represent a partition of the sample space S, if they are pairwise disjoint, exhaustive and have non-zero probabilities. i.e.,
(i) Ai ∩ Aj = φ; i ≠ j; i,j= 1,2, …. ,n
(ii) A1 ∪ A2 ∪ … ∪ An = S
(iii) P(Ai) > 0, ∀ i = 1,2, …. ,n
Important Results on Probability
(i) If a set of events A1, A2,…., An are mutually exclusive, then
A1 ∩ A2 ∩ A3 ∩ …∩ An = φ
P(A1 ∪ A2 ∪ A3 ∪… ∪ An) = P(A1) + (A2) + … + P(An)
and A1 ∩ A2 ∩ A3 ∩ …∩ An = 0
(ii) If a set of events A1, A2,…., An are exhaustive, then
P(A1 ∪ A2 ∪ … ∪ An) = 1
(iii) Probability of an impossible event is O. i.e., P(A) = 0, if A is impossible event. ,
(iv) Probability of any event in a sample space is 1. i.e., P(A) = 1
(v) Odds in favour of A = P(A) / P(A)
(v) Odds in Against of A = P(A) / P(A)
(vii) Addition Theorem of Probability
(a) For two events A and B
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
(b) For three events A, Band C
P(A ∪ B ∪ C) = P(A) + P(B) + P(C) -P(A ∩ B) – P(B ∩ C) – P(A ∩ C) + P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
(c) For n events A1, A2,…., An
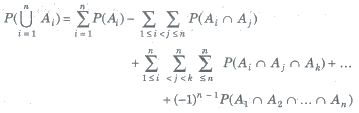
(viii) Booley’s Inequality
If A1, A2,…., An are n events associated with a random experiment, then
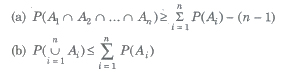
(ix) If A and B are two events, then
P(A ∩ B) ≤ P(A) ≤ P(A ∪ B) ≤ P(A) + P(B)
(x) If A and B are two events associated with a random experiment, then
(a) P(A ∩ B) = P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
(b) P(A ∩ B) = P(A) – P(A ∩ B)
(c)P [(A ∩ B) ∪ (A ∩ B)] = P(A) + P(B) – 2P(A ∩ B)
(d) P(A ∩ B) = 1- P(A ∪ B)
(e) P(A ∪ B) = 1- P(A ∩ B)
(f) P(A) = P(A ∩ B) + P(A ∩ B).
(g) P(B) = P(A ∩ B) + P(B ∩ A)
(xi) (a) P (exactly one of A, B occurs)
= P(A) + P(B) – 2P(A ∩ B) = P(A ∪ B) – P(A ∩ B)
(b) P(neither A nor B) = P(A’ ∩ B’) = 1 – P(A ∪ B)
(xii) If A, Band C are three events, then
(a) P(exactly one of A, B, C occurs)
= P(A) + P(B) + P(C) – 2P(A ∩ B) – 2P(B ∩ C) – 2P(A ∩ C) + 3P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
(b) P (atleast two of A, B, C occurs)
= P(A ∩ B) + P(B ∩ C) + P(C ∩ A) – 2P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
(c) P (exactly two of A, B, C occurs) .
= P(A ∩ B) + P(B ∩ C) + P(A ∩ C) – 3P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
(xiii) (a) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B), if A and B are mutually exclusive events.
(b) P(A ∪ B ∪ C) = P(A) + P(B) + P(C), if A, Band C are mutually exclusive events.
(xiv) P(A) = 1- P(A)
(xv) P(A ∪ B) = P(S) = 1, P(φ) = 0
(xvi) P(A ∩ B) = P(A) x P(B) , if A and B are independent events.
(xvii) If A and B are independent events associated with a random experiment, then
(a) A and B are independent events.
(b) A and B are independent events.
(c) A and B are independent events.
(xviii) If A1, A2,…., An are independent events associated with a random experiment, then probability of occurrence of atleast one
= P(A1 ∪ A2 ∪…. ∪ An) = 1 – P(A1 ∪ A2 ∪…. ∪ An)
= 1 – P(A1)P(A2)…P(An)
(xix) If B ⊆ A, then P(A ∩ B) = P(A) – P(B)
Conditional Probability
Let A and B be two events associated with a random experiment, Then, the probability of occurrence of event A under the condition that B has already occurred and P(B) ≠ 0, is called the conditional probability.
i.e., P(A/B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(B)
If A has already occurred and P (A) ≠ 0, then
P(B/A) = P(A ∩ B) / P(A)
Also, P(A / B) + P (A / B) = 1
Multiplication Theorem on Probability
(i) If A and B are two events associated with a random experiment, then
P(A ∩ B) = P(A)P(B /A), IF P(A) ≠ 0
OR
P(A ∩ B) = P(B)P(A /B), IF P(B) ≠ 0
(ii) If A1, A2,…., An are n events associated with a random experiment, then
P(A1 ∩ A2 ∩…. ∩ An) = P(A1) P(A2 / A1) P(A3 / (A1 ∩ A2)) …P(An / (A1 ∩ A2 ∩ A3 ∩…∩A n – 1))
Total Probability
Let S be the sample space and let E1, E2,…., En be n mutually exclusive and exhaustive events associated with a random experiment. If A is any event which occurs with E1 or E2 or … or En then
P(A) = P(E1)P(A / E1) + P(E2)P(A / E2) + … + P(En) P(A / En)
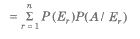
Baye’s Theorem
Let S be the sample space and let E1, E2,…,En, be n mutually exclusive and exhaustive events associated With a random experiment. If A is any event which occurs with E1 or E2 or … or En then probability of occurrence of Ei, when A occurred,
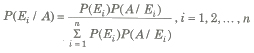
where, P (Ei), i = 1,2, , n are known as the priori probabilities
P (A / Ei), i = 1,2, , n are called the likelyhood probabilities
P (Ei / A), i = 1, 2, … ,n are called the posterior probabilities
Random Variable
Let U or S be a sample space associated with a given random experiment. A real valued function X defined on U or S, i:e.,
X : U → R is called a random variable.
There are two types of random variable.
(i) Discrete Random Variable – If the range of the real function X: U → R is a finite set or an infinite set of real numbers, it is called a discrete random variable.
(ii) Continuous Random Variable – If the range of X is an interval (a, b) of R, then X is called a continuous random variable. e.g., In tossing of two coins S = {HH, HT, TH , TT}, let X denotes number of heads in tossing of two coins, then
X (HH) = 2,X (TH) = 1, X (TT) = 0
Probability Distribution
If a random variable X takes values X1, X2,…., Xn with respective probabilities P1, P2,…., Pn then
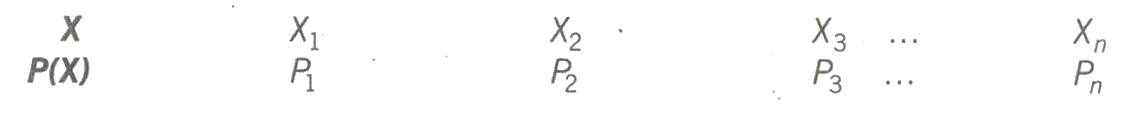
is known as the probability distribution of X.
or
Probability distribution gives the values of the random variable along with the corresponding probabilities.
Mathematical Expectation/Mean
If X is a discrete random variable which assume values X1, X2,…., Xn with respective probabilities P1, P2,…., Pn then the mean x of X is defined as
E(X) = X = P1X1 + P2X2 + … + PnXn = Σni = 1 PiXi
Important Results
(i) Variance V(X) = σ2x = E(X2) – (E(X))2
where, E(X2) = Σni = 1 x2iP(xi)
(ii) Standard Deviation
√V(X) = σx = √E(X2) – (E(X))2
(iii) If Y = a X + b, then
(a) E(Y) = E(aX + b) = aE(X) + b
(b) σ2y = a2V(Y) = a2σ2x
(c) σy = √V(Y) = |a|σx
(iv) If Z = aX2 + bX + c, then
E(Z) = E(aX2 + bX + c)
= aE(X2) + bE(X) + c
Binomial Distribution
Bernaulli Trial
In a random experiment, if there are any two events, “Success and Failure” and the sum of the probabilities of these two events is 1, then any outcome of such experiment is- known as a Bernaulli Trial.
Binomial Distribution
The probability of r successes in n independent Bernaulli Trials is denoted by P(X = r) and is given by
P(X = r) = nCrprqn – r,
where p = probability of success,
q = probability of failure
and p+q=l
Important Results
(i) If P = q, then probability of r successes in n trials is nCrpn
(ii) If the total number of trials is n in any attempt and if there are N such attempts, then the total number of r successes is N(nCrprqn – r)
(iii) Mean = E(X) = x= np
(iv) Variance = σ2x = npq
(v) Standard Deviation = σ2x = √npq
(vi) Mean is always greater than variance
Poisson’s Distribution
It is the limiting case of binomial distribution under the following conditions
(i) Number of trials are very large, i.e., n → ∞
(ii) p → 0
(iii) np → λ, a finite quantity (λ A is called parameter)
The probability of r success for Poisson’s distribution is given by
P(X = r) = e – λλ’ / r!, r = 0, 1, 2,…
For Poisson’s distribution
Mean = Variance = λ = np
Geometrical Probability
If the total number’ of outcomes of a trial in a random experiment is infinite, in such cases, the definitioin, of probability is modified and the
general expression for the probability P of occurrence of an event is given by
p = Measure of the specifie part of the region / Measure of the whole region
where, measure means length or al’~a or volume of the region, if we are dealing with one, two or three dimensional space respectively.
Application Based Result
(i) When two dice are thrown, the number of ways of getting a total r is
(a) (r – 1), if 2 ≤ r ≤ 7 and (b) (13 – r), if 8 ≤ r ≤ 12
(ii) Experiment with insertion of n letters in n addressed envelopes.
(a) Probability of inserting all the n letters in right envelopes
= 1 / n!
(b) Probability that all letters does not in right envelopes
1 – 1 / n!
(c) Probability of keeping al1 the letters in wrong envelope
1 / 2! – 1 / 3!+…+ (-1)n / n!
(d) Probability that exactly letters are in right envelopes
= 1 / r! [1 / 2! – 1 / 3!+ 1 / 4 -…+ (-1)n – r / (n – r)!]
(iii) (a) Selection of shoes from a Cupboard Out of n pair of shoes, if k shoes are selected at random, the probability that there is no pair is
p = nCk2k / 2nCk
(b) The probability that there is atleast one pair is (1- p).
(iv) Selection of Squares from the Chessboard – If r squares are selected from a chessboard, then probability that they lie on a diagonal is
4[7Cr + 6Cr +… + 1Cr] + 2(8Cr) / 64Cr
(v) If A and B are two finite sets and if a mapping is selected at random from the set of all mapping from A into B, then the probability that the mapping is
(a) a one-one function = n(B)Pn(A) / n(B)n(A)
(b) a many-one function = 1 – n(B)Pn(A) / n(B)n(A)
(c) a constant function = n(B) / n(B)n(A)
(d) a one-one onto function = n(A)! / n(B)n(A)
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Maths
Chemistry Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


