Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that, below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids.
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group ( )C=O) is bonded to carbon and hydrogen, while in the ketones, it is bonded to two carbon atoms
Nature of Carbonyl Group
The carbon and oxygen of the carbonyl group are Sp2 hybridised and the carbonyl double bond contains one o-bond and one π-bond.
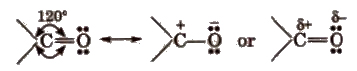
The electronegativity of oxygen is much higher than that of the carbon, so there electron cloud is shifted towards the oxygen. Therefore, C-O bond is polar in nature.
Nomenclature
(i) Nomenclature of aldehydes In IUPAC system, the suffix “e” of alkane is replaced by the suffIX “al”. e.g.,

(ii) Nomenclature of ketones In IUPAC system, the suffix “e” of alkane is replaced by “one”. e.g.,

Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
(i) By oxidation of alcohols Aldehydes and ketones are generally prepared by oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols, respectively.

(ii) By dehydrogenation of alcohols In this method, alcohol vapours are passed over heavy metal catalysts (Ag or Cu). Primary and secondary alcohols give aldehydes and ketones.

(iii) By ozonolysis of alkenes
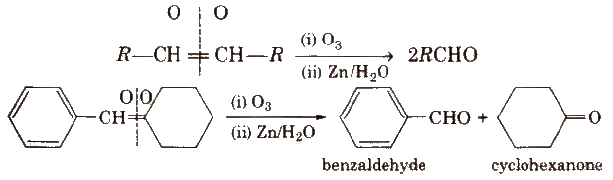
(iv) By hydration of alkynes Acetylene on hydration gives acetaldehyde and other alkynes on hydration give ketones.

Preparation of Aldehydes

Preparation of Ketones
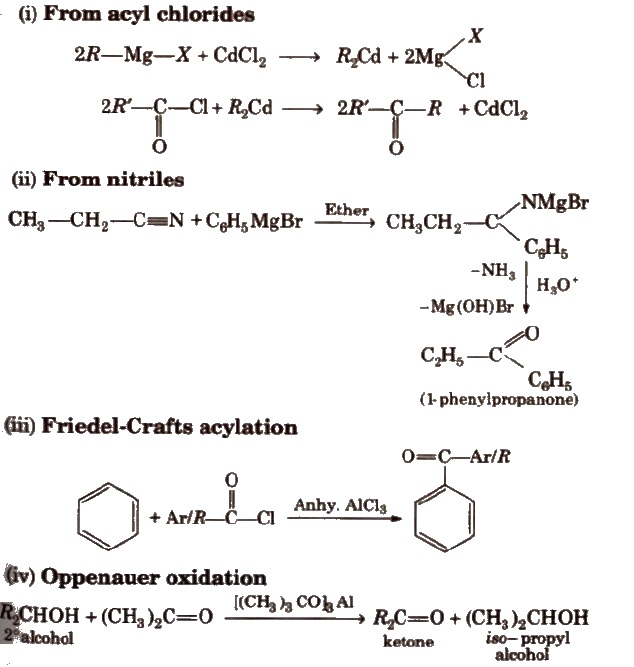
Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
1. Methanal (HCHO) is a gas at room temperature. and its 40% aqueous solution is known as formalin. It is a reducing agent in silvering of mirrors and decolourising vat dyes.
2. Ethanal (CH3CHO) is a volatile liquid. Other aldehydes and ketones are liquid or solid at room temperature.
3. The boiling point of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass due to high magnitude of dipole-dipole interactions.
4. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling point than those of alcohols of similar molecular masses due to absence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
5. The lower members of aldehydes and ketones are miscible with water due to the formation of hydrogen bond with water. However, the solubility decreases with increase in length of alkyl chain.
6. Acetophenone is a hypnotic (sleep producing drug) so used as a medicine under the name hypnone.
Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones


(ii) Addition of ammonia and its derivatives Reaction with ammonia
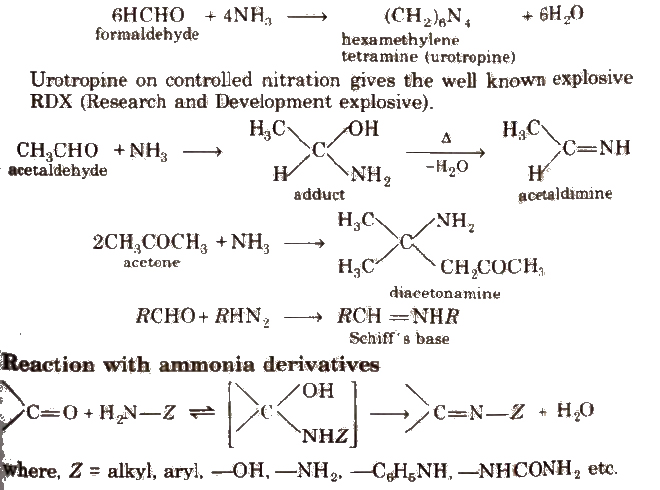
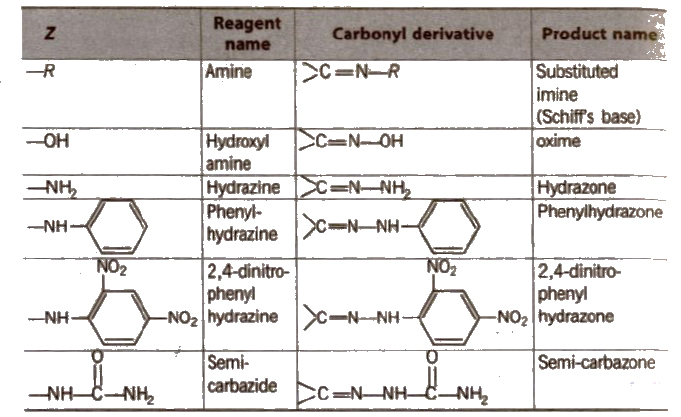
Some N-substituted Derivatives of Aldehydes and Ketones
(iii) Reduction Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols respectively by sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or lithium aluminium hydride [LiAlH4].

(iv) Oxidation Aldehydes get easily oxidised to carboxylic acids by HNO3, KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, etc., or even by mild oxidising agent.

During oxidation of unsymmetrical ketones the point of cleavage is such that keto group stays preferentially with the smaller alkyl group popoff’s rule).

[Fehling solution is a mixture of Fehling solution A and Fehling solution B in 1: 1 ratio. Fehling solution A is aqueous copper sulphate and Fehling solution B is alkaline sodium potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.]
(c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) also give red ppt. of CU2O.
(d) Schiff’s reagent It is an aqueous solution of magenta or pink coloured rosaniline hydrochloride which has been decolourised by passing SO2, Aldehydes give pink colour with this reagent but ketones do not.
Haloform reaction Aldehydes and ketones having at east one methyl group [3-α hydrogen] linked to the carbonyl carbon atom (methyl ketones) are oxidised by sodium hypohalite to sodium salts of corresponding carboxylic acids having one carbon atom less than that of carbonyl compound. The methyl group is converted to haloform.

Iodoform reaction with sodium hypoiodite is also used for the detection of CH3 – group or CH3CH(OH)- group by producing yellow solid CHI3.
(v) Aldol condensation
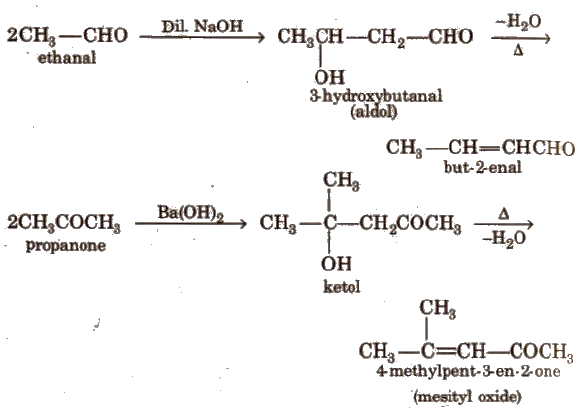
Its further condensation gives phorone,
This reaction is exhibited by those aldehydes and ketones which have at least one a-hydrogen.
(vi) Cross aldol condensation Base catalysed crossed aldol condensation between an aromatic aldehyde and an aliphatic aldehyde or ketone is called Claisen-Schmidt condensation or Claisen reaction.

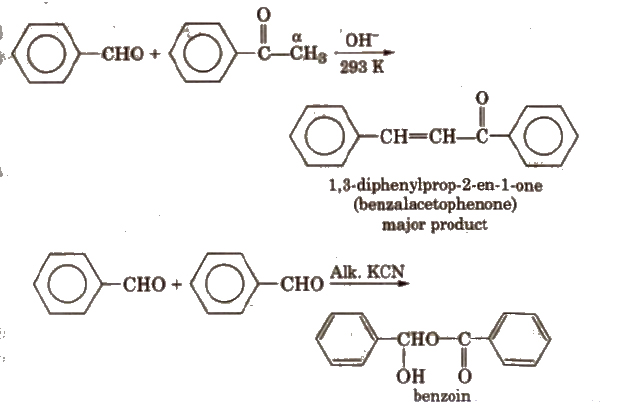
The above reaction is called Benzoin condensation, not the cross aldol condensation.
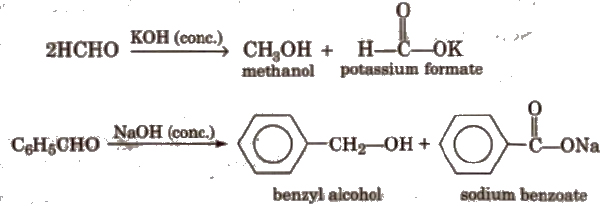
(vii) Cannizzaro reaction Aldehydes which do not have any α – hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali.
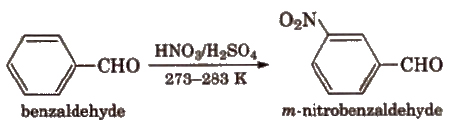
(viii) Electrophilic substitution reaction Aromatic aldehydes and ketones undergo electrophilic substitution. Carbonyl group shows + R effect, therefore acts as a deactivating and meta directing group.
(ix) Baeyer- ViLLiger oxidation With Caro’s acid (H2SO5) or per benzoic acid (C6H5CO3H) or peracetic acid (CH3CO3H) aliphatic ketones give ester.

(xi) Knoevenagel reaction It involves condensation between active methylene group and ,carbonyl groups in the presence of base.


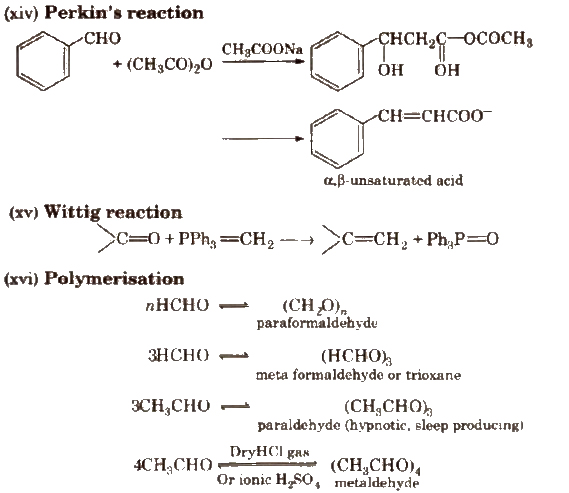
Carboxylic Acids

Classification
Depending upon the number of -COOH groups, they are classified as
(i) monocarboxylic acids; containing one -COOH group
(ii) dicarboxylic acids: containing two -COOH groups.
Sources of carboxylic acids

Nomenclature
Their IUPAC names have been derived from the corresponding alkanes by replacing the letter ‘li of the alkane with ‘oic’ and adding suffix ‘acid’ at the end, Thus, monocarboxylic acids are called alkanoic acids.

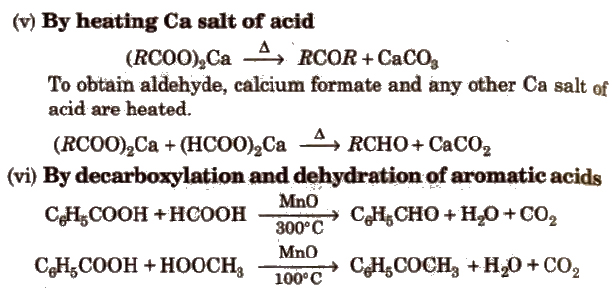
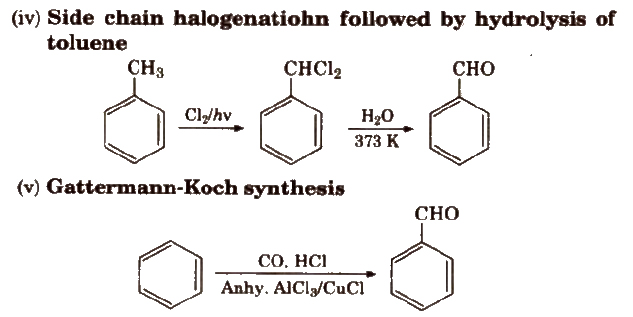
Methods of Preparation of Monocarboxylic Acids
(i) From primary alcohols and aldehydes

(ii) From alkyl benzenes Alkyl benzene when treated with strong oxidising agent like H2CrO4 (chromic acid), acidic or alkaline KMnO4 gives benzoic acid.

(iii) From acid derivatives All acid derivatives like amides (RCONH2), acid halides (RCOCl), esters (RCOOR’), acid anhydrides (RCO-O-COR) on hydrolysis give carboxylic acids. All acid derivatives break from RCO+.
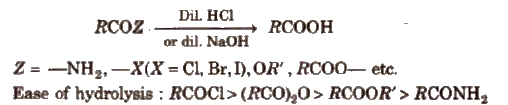
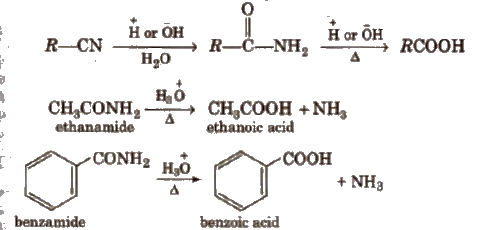
(iv) From nitriles and amides Nitriles are hydrolysed to amides and then to acids in the presence of H+ or OH– as catalyst. Mild reaction conditions are used to stop the reaction at the amide stage.
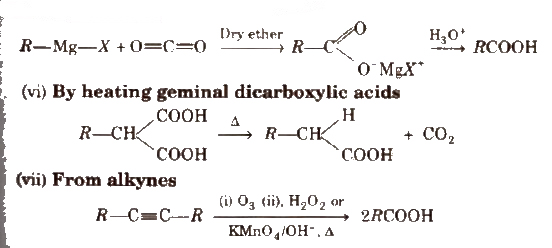
(v) From Grignard reagents Grignard reagents react with carbon dioxide (dry ice) to form salts of carboxylic acids which in turn give corresponding carboxylic acids after acidification with mineral acid
Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
1. Aliphatic carboxylic acids up to nine carbon atoms are colourless liquids at room temperature with unpleasant odours. The higher acids are wax like solids.
2. The lower carboxylic acids are freely miscible with water due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding with H2O molecules. However, the solubility in water decreases gradually due to increase in the size of alkyl group.
3. Monocarboxylic acids have higher boiling points as compared to the alcohols of comparable molecular masses due to the presence of stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonding as shown below.
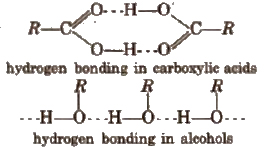
4. Melting points of aliphatic monocarboxylic acids shows alternation or oscillation effect, i.e., the m.p. of an acid with even number of carbon atoms is higher than the next lower and next higher homologue containing odd number of carbon atoms. This is because, in case of acids with even number of carbon atoms, the terminal -CH3 and -COOH groups lie on the opposite sides of the zig-zag chain. As a result, they get closely packed in the crystal lattice.
5. Glacial acetic acid is completely pure acetic acid and represents the solid state of acetic acid. Below 16.6°C temperature pure acetic acid is converted into ice like solid hence it is called glacial acetic acid.
Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl groups as it enters into resonance with lone pair of O of -OH group.
(i) Acidity

Above reactions are used to detect the presence of carboxyl group Ul an organic compound. ,
Carboxylic acids dissociate in water to give resonance stabilised carboxylate anions and hydronium ion.

The strength of the acid is expressed in terms of the dissociation constant (Ka), also called acidity constant. A stronger acid has higher Ka but lesser pKavalue (pKa == -log Ka).
The electron releasing substituents (+1 effect) decrease the acidic strength of the carboxylic acids by destabilising the carboxylate ion.

The electron withdrawing substituents (-1 effect) such as halogen atoms (X), nitro (NO2) group increase the acidic strength by decreasing the magnitude of the negative charge on the carboxylate anion and thus stabilising it. The release of H+ ion becomes easy.
Acidic strength order

This is because -1 effect decreases in the order : F > C1 > Br > I.
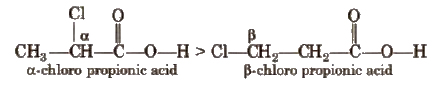
This is because – I effect decreases with distance.
Per acetic acid (CH3COOO-H) is a weaker acid than acetic acid as acetate ion is stabilised by resonance.
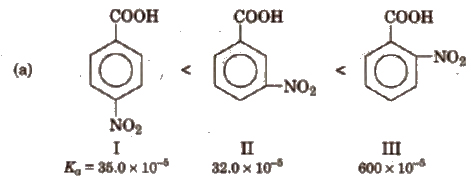
Acidic strength of aromatic acids The parent member of the family benzoic acid which is a weaker acid (Ka = 6.3 x 10-5) than acid (Ka = 17.7 x 10-5) but stronger than acetic acid.
Some order of acidity are
(b) Similarly, Ka values of methyl substituted (toluic acids) at 298 K are as follows:
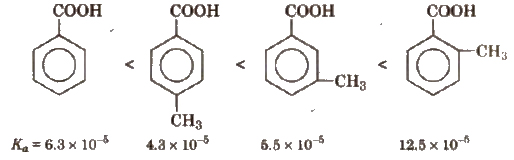
From the Ka values, it is evident that with the exception of o-isomer, both p and m-toluic acids are weaker acids than benzoic acid whereas the three isomeric nitro benzoic acids are stronger acids than benzoic acid.
(ii) Reactions involving cleavage of C-O-H bond
(a) Formation of anhydride
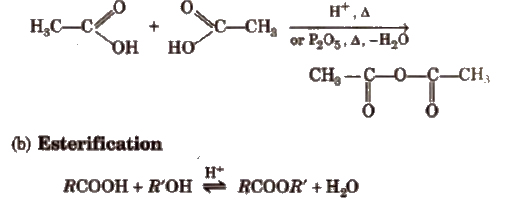
Mechanism


(iii) Chemical reactions involving – COOH group
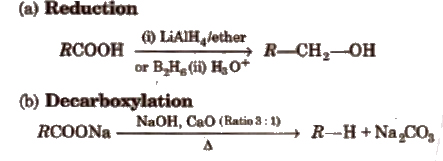
(iv) Substitution reactions in the hydrocarbon part α -hydrogen atoms in carboxylic acids are acidic in nature and can be easily replaced by halogen atoms in HVZ reaction
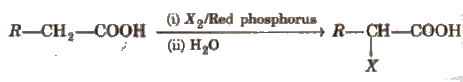
The reaction is known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
(v) Arndt-Eistert reaction It is method of converting lower carboxylic acids to their higher homologues

(vi) Reducing property Among carboxylic acids, formic acid is the only acid that acts as reducing agent. It reduces, acidified KMnO4 to MnSO4, HgCl2 to Hg, Tollen’s reagent to silver mirror and Fehling’s solution to red ppt. and itself gets oxidised to CO2 and H2O.
HCOOH + HgCl2→ Hg + 2HCI + CO2
(vii) Electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic acids -COOH group shows -R effect, therefore, acts as a deactivating and meta-directing group. Carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Craft’s reaction because the carboxylic group IS deactivating and the catalyst AlCl3 (anhy.) gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
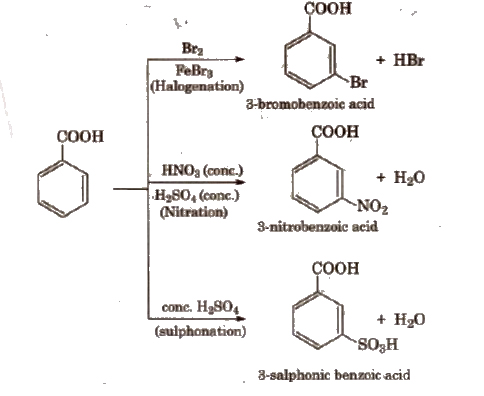
Uses
1. Formic acid is used in leather tanning, textile dyeing and finishing.
2. Acetic acid is used in the manufacture of rayon and in plastics, in in rubber and silk industries, in cooking and in vinegar (a 8-10% solution of acetic acid).
3. Benzoic acid and its salts are used as urinary antiseptics.
4. Formic acid can act as a reducing agent.
Derivatives of Carboxylic acids
These are obtained when -OH group of carboxylic acids is replaced by Cl, NH2, OR’ and OCOR and are called respectively acid chloride, acid amide, ester and acid anhydride.

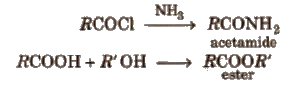
Properties of Acid Derivatives
1. Chemical reactions of acid halides

2. Chemical reactions of acid amides

3. Chemical reactions of ester
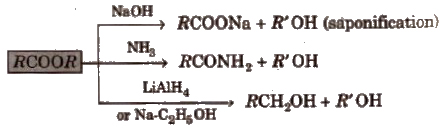
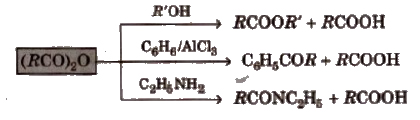
4. Chemical reactions of anhydrides
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

