Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Biomolecules. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that, below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic Biomolecules.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: Biomolecules
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules.
Biomolecules are the organic compounds which form the basis of life, i.e., they build up the living system and responsible for their growth and maintenance.
The sequence that relates biomolecules to living organism is
Biomolecules → Organelles → Cells → Tissues → Organs → Living organism.
Carbohydrates
Optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes (aldcses) or ketones (ketoses) or compounds which on hydrolysis give these units are known as carbohydrates. They are also called saccharides
(Latin Saccharum = sugar) due to sweet taste of simpler members.
Depending upon their behaviour towards hydrolysis, carbohydrates can be of following three types
Monosaccharides
These cannot be hydrolysed to simpler molecules and further subdivided into tetroses, pentoses or hexoses depending upon the number of carbon atoms. These are also called homopolysaccharides.
- Aldotetroses Erythrose, Threose
- Aldopentoses Xylose, Ribose,
- Aldohexoses Glucose, Galactose,
- Ketohexoses Fructose
All naturally occurring monosaccharides belong to D-series.
killiani synthesis is used to convert an aldose into next higher aldose.
Oligosaccharides
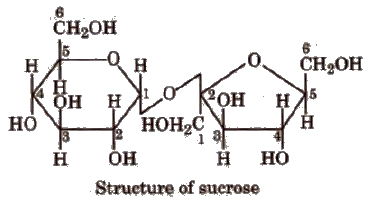
(Greek oligos = few). On hydrolysis, they generally give two to nine monosaccharides (same or different) and are further classified as disaccharides, e.g., sucrose, maltose, lactose, trisaccharides and so on. C12H22O11 is a disaccharide because it gives two monosaccharides.

The bond formed between two monosaccharides is called a glycosidic bond and normally it is (1, 4) bond.
Sucrose is most abundant in plants and known as cane sugar or table sugar or invert sugar as equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose is obtained by hydrolysis of sucrose.
Trisaccharides Raffinose (C18H32O16)

Polysaccharides
These are polymers of monosaccharides. Examples are starch, cellulose, glycogen, etc.
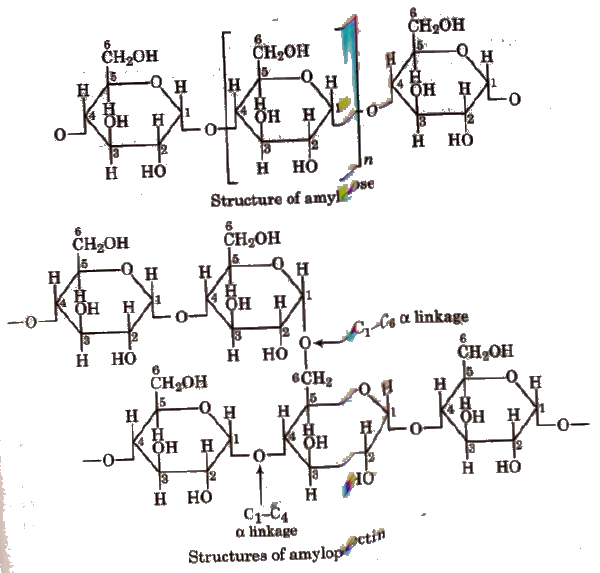
1. Starch, (C6H10O5)N
It is a polymer of a-glucose and a major reserve food in plants. It turns blue with iodine. It is a mixture of two components:
- Amylose (20%), an unbranched water soluble polymer.
- Amylopectin (80%), a branched water insoluble polymer.
Sources of starch are potatoes, wheat, rice, maize, etc.
2. Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n
It is the most abundant and structural, polysaccharide of plants. It is important food source of some animals It is a polymer of D (+) β-glucose.
The chief sources of cellulose are wood (Contains 50% cellulose rest being lignin, resins, etc) and cotton (contains 90% cellulose rest being fats and waxes).

Several materials are obtained from cellulose:
- Mercerised cotton Cellulose treated with cone. sodium hydroxide solution acquire silky lustre. It is called mercerissd cotton.
- Gun cotton It is completely nitrated cellulose (cellulose nitrate), highly explosive in nature and is used in the manufacture of smokeless gun powder, called blasting gelatin.
- Cellulose acetate It is used for making acetate rayon and motion picture films.
- Cellulosexanthate It is obtained by treating cellulose with sodium hydroxide and carbon disulphide and is the basic material for VISCOSE rayon.
Oligosaccharides and heteropolysaccharides are also called heteropolysaccharides.
Reducing and Non-reducing sugars
Based upon reducing and non-reducing properties, carbohydrates are classified as reducing and non-reducing sugars. Carbohydrates reducing Fehling reagent or Tollen’s reagent are termed as reducing carbohydrates. e.g., All monosaccharides and disaccharides (except sucrose). But carbohydrates which do not reduce such reagents are known as non-reducing carbohydrates. e.g., sucrose and polysaccharides.
Sugars and Non-sugars
On the basis of their, taste, carbohydrates are classified as sugars and non-sugars. The monosaccharides and oligosaccharides having sweet taste are collectively known as sugars. Polysaccharides which are insoluble in water and not sweet in taste, are non-sugars.
Glucose
Dextrose, grape sugar, corn sugar, blood sugar (C6H12O6).
Manufacture
By hydrolysis of starch with hot dil mineral acids and by hydrolysis of sucrose.

Extra glucose is stored in liver as glycogen.
α and β glucose
In intermolecular hemiacetal formation (cyclic structure), -CHO is converted into -CHOH which can have two configurations as shown below.

Glucose having (i) configuration about C1 is the α-glucose and having (ii) configuration about C1 is β-glucose.
The carbon C1 is known as anomeric carbon and these compounds are called anomers. Both the forms are optically active. ex-D-glucosehas specific rotation +111.5° and β-D-glucose has specific rotation + 19.5°.
Mutarotation
When either of the two forms of glucose is dissolved in water, there is a spontaneous change in specific rotation till the equilibrium value of +52.5°. This is known as mutarotation.

Properties of glucose
Glucose has one aldehyde group, one primary hydroxyl (-CH2OH) and four secondary hydroxyl (-CHOH) groups and gives the following reactions:
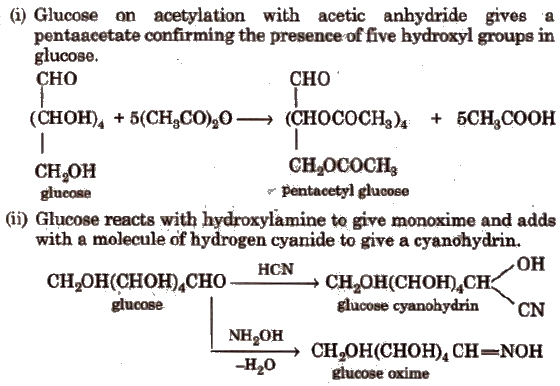
These reactions confirm the presence ofa carbonyl group in glucose.
(iii) Glucose reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollen’s reagent) to metallic silver and also Fehling’S solution or Benedict solution to reddish brown cuprous oxide (Cu2O) and itself gets oxidised to gluconic acid. This confirms the presence of an aldehydic group in glucose.
(iv) With mild oxidising agent like bromine water, glucose is oxidised to gluconic acid. Glucose on oxidation with nitric acid gives saccharic acid.

(vii) Glucose on reaction with methyl alcohol in the presence of dry HCl(g) forms α and β-methyl glycosides. The reaction occurs only at the OH of hemiacetylic carbon.

Cyclic structure of glucose Given by Haworth and Hirst.

Fructose Fruit Sugar (C6H12O6)
Manufacture
By hydrolysis of inulin.
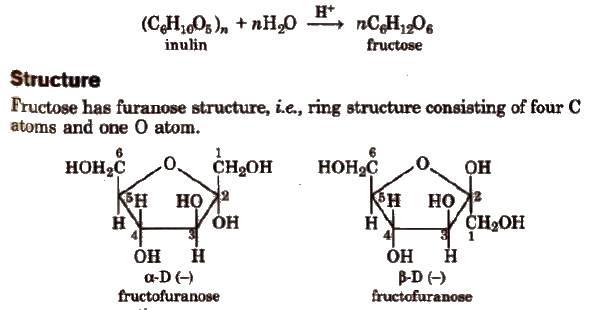
α and β-fructose
The two forms have different configuration about C2.

Fructose does not reduce Br2 water.
Epimers
Monosaccharides differing in configuration at a carbon other than anomeric carbon are called epimers, e.g., glucose and galactose differ in configuration at C4, hence called epimers.
Osazones
Monosaccharides and reducing disaccharides react with excess of phenyl hydrazine to form crystalline substances of the structure
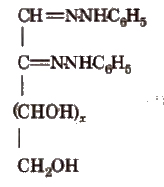
It is known as osazones glucose and fructose give same osazone.
Molisch Test for Carbohydrates
In aqueous solution of compound add solution of α-naphthol in alcohol and then cone. H2SO4 along the walls of the test tube. Purple coloured ring is obtained at the junction.

Amino Acids
The compounds containing amino group (-NH2) and carboxylic group (-COOH) are called amino acids.
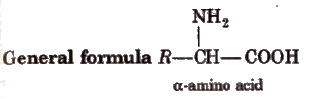
R = H, alkyl or aryl group. Except glycine (H2N.CH2COOH), others are optically active in nature.
Classification of Amino Acids
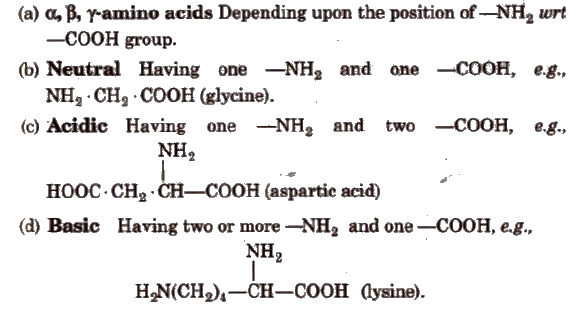
Essential and Non-essential Amino Acids
Human body can synthesise ten amino acids, called non-essential amino acids. The remaining ten amino acids required for protein synthesis are not synthesised by body and are called essential amino acids. They are
- Phenylalanine
- Histidine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
- Methionine
- Threonine
- Arginine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Lysine
Nomenclature
They are known by their common names and abbreviated by first three letters of their common names e.g., glycine as ‘gly’ and alanine a as ‘ala’.
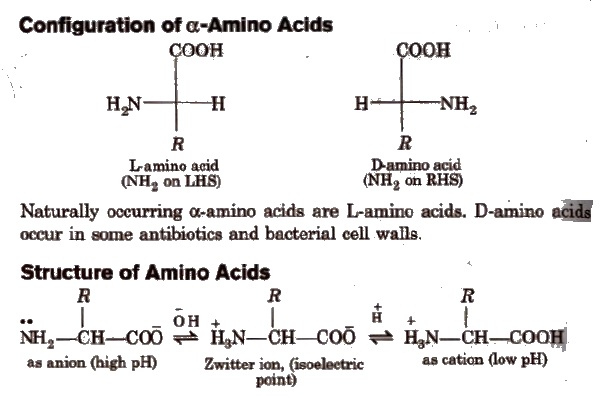
Peptides
Peptides are condensation products of two or more amino acids.

Two molecules of different amino acids can form two dipeptides.Three molecules of different amino acids can give six tripeptides.
Dipeptide has only one peptide bond, tripeptide has two peptide bonds and so on. Thus, a polypeptide made up of n-amino acids has (n – 1) peptide bonds.
Polypeptides
Condensation Products of many amino acids ( ‘In P xiucts of many amino acids (≈ 10000) is known as polypeptide and those polypeptides which have molecular mass above than 10000 are called proteins.
Proteins
They are linear polymers of a-amino acids.
Structure of Proteins
(a) Primary structure
It simply reveals the sequence of amino acids.
(b) Secondary structure α-helix structure maintained by hydrogen bonds or β-pleated sheet structure when R is small group.
(c) Tertiary structure The folding and superimposition of polypeptide chains forms a compact globular shape, termed as tertiary structure. It is stabilised by covalent, ionic, hydrogen and disulphide bonds.
The precise arrangement constitutes the quaternary structure.
Classification on the Basis of Hydrolysis Products
(i) Simple These yield only a-amino acids upon hydrolysis.
e.g., albumin.
(ii) Conjugated proteins These yield α-amino acids and non-protein part, called prosthetic group.
| Protein | Prosthetic group |
| Nucleoproteins | Nucleic acid |
| Phospho proteins | Phosphoric acid |
| Glycoproteins | Carbohydrates |
| Metalioproteins | Metals |
| Lipoproteins | Lipids |
(iii) Derived proteins These are obtained by partial hydrolysis of simple or conjugated proteins.
Proteins → Proteoses → Peptones → Polypeptides
Classification on the Basis Functions
- Structural proteins Fibrous proteins
- Enzymes Serve as biological catalyst e.g., pepsin, trypsin etc.
- Hormones Insulin
- Contractile proteins Found in muscles, e.g., myosin, actin.
- Antibodies Gamma globulins present in blood.
- Blood protein Albumms, haemoglobin and fibrinogen.
Haemoglobin is a globular protein. Its prosthetic group is heme. It Contains 574 amino acid units distributed in four polypeptide chains.
Two chains containing 141 amino acid residues each are called α-chains and the two chains containing 146 amino acid residues are called β-chains.
Sickle cell anaemia is caused by defective haemoglobin obtained by replacing only one amino acid, i.e., glutamic acid by valine.
Denaturation of Proteins
The process that changes the three dimensional structure of native proteins is called denaturation of proteins. It can be caused by Change in pH, addition of electrolyte, heating or addition of solvent like water, alcohol or acetone.
Tests of Proteins
(i) Biuret Test
Protein solution + NaOH + dil. CuSO4 → pink or violet colour.
(ii) Millon’s Test
Protein solution + Millon’s reagent → pink colour
Millon’s reagent is solution of mercuric nitrate and nitrite in nitric acid containing traces of nitrous acid.
(iii) Iodine reaction
Protein solution + iodine in potassium iodide solution → yellow colour.
(iv)Xanthoprotic test
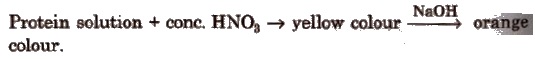
Enzymes
Enzymes constitute a group of complex proteinoid compounds, produced by living organisms which catalyse the chlemical reaction.
Non-proteinous components enhance the activity of certain enzymes and are known as co-enzymes. These include metal ions like Mn2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, Zn2+, Co2+ etc., heterocyclic ring systems (pyrrole, purine, pyridine, etc.), a sugar residue, phosphoric acid residue of vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin etc.
Endoenzyme acts in the same cell in which it is synthesised, while exo-enzyme acts outside the cell in which it is synthesised.
Nomenclature
They are usually named by adding the suffix ‘ase’ to the root name of the substrate e.g., urease, maltase, diastase, invertase, etc.
Oxidative Enzymes
They catalyse oxidation-reduction reaction and are mostly conjugated proteins.
Some Common Enzyme
| Name | Substrate | Products |
| Urease | Urea | CO<sub>2</sub> + NH<sub>3</sub> |
| Maltase | Maltose | Glucose |
| Invertase | Sucrose | Glucose + fructose |
| Amylase | Starch | Maltose |
| Trypsin | Proteins | Amino acids |
| Ascorbic acid oxidase | Ascorbic acid | Dehydroascorbic acid |
Characteristic Features of Enzymes
- Rate of reaction They increase the rate of reaction up to 106 to 107 times.
- Specific nature Urease catalyse the hydrolysis of urea and not methyl urea, so these are specific in nature.
- Optimum temperature It is about 20-30°C.
- pH of medium It is about 7 but for pepsin, it is 1.8·2.2 and for trypsin, it is 7.5-8.3.
- Concentration Dilute solutions are more effective.
- Amount of enzyme Very small amount can accelerate the reaction.
- Enzyme inhibitors These compounds inhibit the enzyme action. With the help of such compounds, the reaction can be controlled.
Mechanism of Enzyme Action
Enzyme + Substrate → [Enzyme substrate] → Product + Enzyme Activated complex
Applications of Enzymes
(i) Treatment of diseases The congenital disease phenyl ketonurie caused by phenylalanine hyroxylase can be cured by diet of low phenylalanine content. Enzyme streptokinase is used for blood clotting to prevent heart disease.
(ii) In industry Tanning of leather, fermentation process etc.
Nucleic Acids
Important Terms of Nucleic Acids
1. Nucleotldes
Nucleotides consist of 5-carbon sugar + nitrogenous base + 1, 3-phosphate groups.
2. Pentose sugar
It is either ribose or deoxy ribose (not having oxygen at C2).
3. Nitrogenous base
Derived from purines having two rings in their structure e.g., Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) and derived from pyrimidines having one ring in their structure e.g.,
Thymine (T), Uracil (U) and Cytosine (C).
Two H-bonds are present between A and T (A = T) while three H-bonds are present between C and G (C ≡ G).
4. Ribonucleotide
Phosphate unit + Ribose + one base unit from A, G, C, or U.
5. Deoxyrlbo nucleotide
Phosphate unit + Deoxyribose + one base from A, G, C or T.
6. Nucleoside
Ribose-/deoxyribose + one base unit from A, G, C, Tor U.
DNA and RNA
Nucleic acid is polynucleotide, present in the living cells or bacterial cells having no nucleus and in viruses having no cells.
(i) DNA Deoxy ribonucleic acid.
DNA + H2O → Phosphoric acid + deoxyribose + A, G, C, T
(ii) RNA Ribonucleic acid
RNA + H2O → Phosphoric acid + Ribose + A, G, C, U
Structure of DNA
It consists of two polynucleotide chains, each chain form a right handed helical spiral with ten bases in one turn of the spiral. The two chains coil to double helix and run in opposite direction. These are held together by hydrogen bonding.
Structure of RNA
It is usually a single strand of ribonucleotides and take up right handed helical conformation. Up to 12000 nucleotides constitute an RNA.
It can base pair with complementary strands of DNA or RNA according to standard base pairing rules-G pairs with C, A pairs with U or T. The paired strands in RNA-RNA or RNA-DNA are anti parallel as in DNA.
In both DNA and RNA, heterocyclic base and phosphate ester linkages are at C1 and C5‘ respectively of the sugar molecule.

Types of RNA
- Messanger RNA (m-RNA) It is produced in the nucleus and carries information for the synthesis of proteins.
- Transfer RNA (Soluble or Adoptive RNA) (s-RNA, t-RNA) It is found in cytoplasm. Its function-is to collect amino acids from cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
Functions of Nucleic Acids
- Direct the synthesis of proteins.
- Transfer the genetic information (hereditary characters).
Replication
It is a process in which a molecule of DNA can duplicate.
Template It means pattern. In the process of replication of DNA, the parent strand serves as template.
Gene The portion of DNA carrying information about a specific protein is Called gene.
Genetic code The relation between the amino acid and the nucleotide triplet is called genetic code.
Codons The nucleotide bases in RNA function in groups of three (triplet) in coding amino acids. These base triplets are called codons.
The world code is used with reference to DNA, codon with reference to m-RNA and anticodon with reference to t-RNA.
Lipids
The constituents of animals and plants soluble in organic solvents (ether, chloroform. carbon tetrachloride), but insoluble in water are called lipids. (Greek lipose = fat)
Types of Lipids
(i) Simple lipids
(a) Fats and oils on hydrolysis give long chain fatty acids + glycerol.
(b) Waxes Long chain fatty acids + long chain alcohols.
Vegetable and animal oils and fats have similar chemical structure and are triesters of glycerol, called glycerol.
Simple glycerides contain one type of fatty acids. Mixed glycerides contain two or three types of fatty acids.
Common saturated fatty acids CH3-(CH2)nCOOH.
When n = 4 caproic acid; n = 6 caprylic acid; n = 8 capric acid, n = 10 lauric acid n = 12 myristic acid; n = 14 palmitic acid, n = 16 stearic acid.
Common unsaturated acids
C17H33COOH oleic acid; C17H33COOH linoleic acid.
Difference between oils and fats Oils are liquids at ordinary temprature (below 20° and contain lower fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acids.
Fats are solids or semisolids above 20°C and contain higher saturated fatty acids. Oils and fats act as “energy reservoirs” for the cells.
(ii) Phospholipids Phosphate + glycerol + fatty acids + a nitrogen containing base.
Function of phospholipids are
1. As emulsifying agents since they carry hydrophilic polar groups and hydrophobic non-polar groups.
2. They absorb fatty acids from the intestine and transport to blood cells.
(iii) Glycolipids They contain one or more simple sugars and are important components of cell membranes and chlorplast membranes.
(iv) Steroids and Terpenes Menthol, camphor are common plant terpenes. Carotenoids and pigments are also terpenes.
(a) Essential oils The volatile, sweet smelling liquids obtained from flowers, leaves, stems, etc. Example of terpenes are esters of lower fatty acid, e.g., clove oil, rose oil, lemon oil.
(b) Drying oils The oils which are converted into tough, transparent mass when exposed to air by oxidation polymerisation process are called drying oils. e.g., Linseed oil, perilla, poppy seed oils.
Cotton seed oil and til oil are semidrying oils.
Acid Value
It is the number of milligrams of KOH required to neutralise the free acid present in 1 g of oil or fat.
Saponification Value
It is the number of milligrams of KOH required to saponify 1g of oil or fat or the number of milligrams of KOH required to neutralise the free acidresulting from the hydrolysis of 1 g of an oil or fat.
Iodine Value
It is the number of grams of iodine absorbed by 100 g of oil or fat.
Relchert-Meissel Value (R/M Value)
It is the number of cc of N/10 KOH required to neutralise the distillate of 5 g of hydrolysed fat.
Blood
An average person has about 6.8 L of blood which is about 6-10% of the body weight. pH of blood is about 7.4.
Haemoglobin is globular protein. It is made up of four polypeptide chains which are arranged in tetrahedral manner. Each chain is associated with a non-protein part, called haem.
Haemoglobin
These axe the chemical substances which are produced by ductless glands in the body. Hormones acts as chemical messengers.
Some examples of ductless ‘(endocrine) glands are thyroid, pitutary, adrenal, pancreas, testes and ovaries.
Hormones are divided into three types:
- steroids
- proteins or polypeptides
- amines.

Insulin is a protein hormone which is secreted by β-cells of the pancreas. Insulin was the first polypeptide in which the amino acid sequence was experimentally determined. Its deficiency leads to diabetes mellitus.
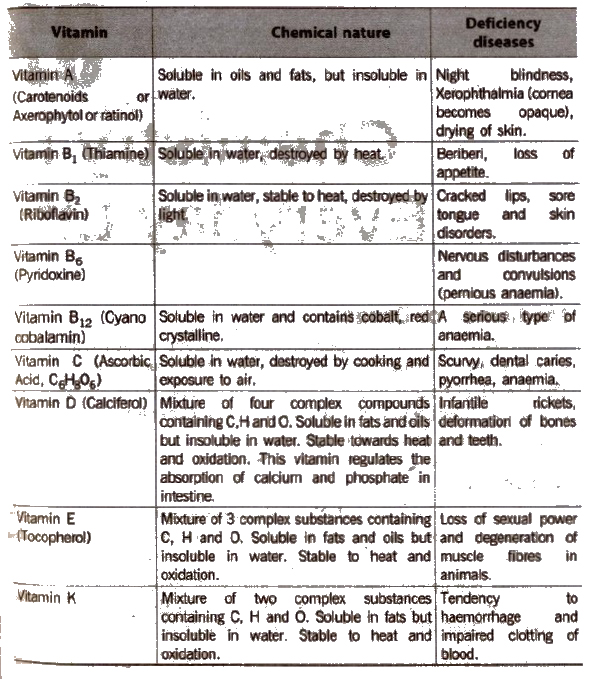
Vitamins
The organic compounds other than carbohydrates, proteins and facts which are required by body to maintain normal health, growth and nutrition are called vitamins.
The vitamins are complex organic molecules. They are represented by letters such as A, B, C, D, E, K.
Vitamins are broadly classified into two types,
- Water soluble vitamins and
- oil soluble vitamins.
Vitamins A, D, E and K are oil soluble whereas vitamins B and C are water soluble. Vitamin H is neither fat soluble nor water soluble.
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

