Class 12 Physics Alternating Currents – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Physics Alternating Currents. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Physics study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 12 Physics for topic Alternating Currents.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Physics
- Topic: Alternating Currents
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Physics Alternating Currents
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Physics Alternating Currents.
Transient Current
An electric current which vary for a small finite time, while growing from zero to maximum or decaying from maximum to zero, is called a transient current.
Growth of Current in an Inductor
Growth of current in an inductor at any instant of time t is given by
I = Io(1 – e -Rt / L)
where, Io = maximum current, L = self inductance of the inductor and R = resistance of the circuit.
Here R / L = τ, is called time constant of a L – R circuit.
Time constant of a L – R circuit is the time in which current in the circuit grows to 63.2% of the maximum value of current.
Decay of current in an inductor at any time t is given by
I = Ioe -Rt / L
Time constant of a L – R circuit is the time in which current decays to 36.8% of the maximum value of current.
Charging and Discharging of a Capacitor
The instantaneous charge on a capacitor on charging at any instant of time t is given by
q = qo(1 – e – t / RC)
where RC = τ, is called time constant of a R – C circuit.
The instantaneous charge on a capacitor in discharging at any instant of time t is given by q = qoe – t / RC
Time constant of a R – C circuit is the time in which charge in the capacitor grows to 63.8% or decay to 36.8% of the maximum charge on capacitor.
Alternating Current
An electric current whose magnitude changes continuously with time and changes its direction periodically, is called an alternating current.
The instantaneous value of alternating current at any instant of time t is given by
I = Io sin ωt
where, 10 = peak value of alternating current.
The variation of alternating current with time is shown in graph given below
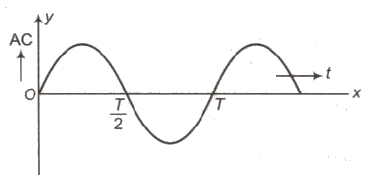
Mean or average value of alternating current for first half cycle
Im = 2Io / π = 0.637 Io
Mean or average value of alternating current for next half cycle
I’m = – 2Io / π = – 0.637 Io
Mean or average value of alternating current for one complete cycle = O.
Root mean square value of alternating current
Iv = Irms = Io / √2 = 0.707 Io
Where, Io = peak value of alternating current.
Root mean square value of alternating voltage
Vrms = Vo / √2 = 0.707 Io = 0.707 Vo
Reactance
The opposition offered by an inductor or by a capacitor in the path of flow of alternating current is called reactance.
Reactance is of two types
(i) Inductive Reactance (XL) Inductive reactance is the resistance offered by an inductor.
Inductive reactance (XL) = Lω = L2πf = L2π / T
Its unit is ohm. XL ∝ f
For direct current, XL = 0 (f = 0)

(ii) Capacitive Reactance (Xc) Capacitive reactance is the resistance offered by an inductor
Capacitive reactance,
Xc = 1 / Cω = 1 / C2πf = T / C 2π
Its unit is ohm Xc ∝ 1 / f
For direct current, Xc = ∞ (f = 0)

Impedance
The opposition offered by an AC circuit containing more than one out of three components L, C and R, is called impedance (Z) of the circuit.
Impedance of an AC circuit, Z = √R2 + (XL – XC)2
Its SI unit is ohm.
Power in an AC Circuit
The power is defined as the rate at which work is being in the circuit.
The average power in an AC circuit,
Pav = Vrms irms cos θ
= V / √2 i / √2 cos θ = Vi / √2 cos θ
where, cos θ = Resistance(R) / Impedance (Z) is called the power factor 0f AC circuit.
Current and Potential Relations
Here, we will discuss current and potential relations for different AC circuits.
(i) Pure Resistive Circuit (R circuit)
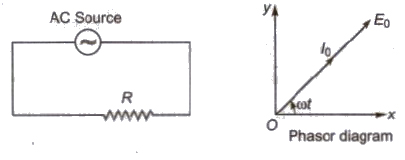
(a) Alternating emf, E = Eo sin ωt
(b) Alternating current, I = Io sin ωt
(c) Alternating emf and alternating current both are in the same phase.
(d) Average power decay, (P) = Ev . Iv
(e) Power factor, cos θ = 1
(ii) Pure Inductive Circuit (L Circuit)
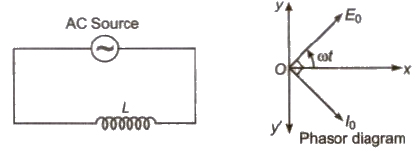
(a) Alternating emf, E = Eo sin ωt
(b) Alternating current, I = Io sin (ωt – π / 2)
(c) Alternating current lags behind alternating emf by π / 2.
(d) Inductive reactance, XL = Lω = L2πf
(e) Average power decay, (P) = 0
(f) Power factor, cos θ = cos 90° = 0
(iii) Pure Capacitive Circuit
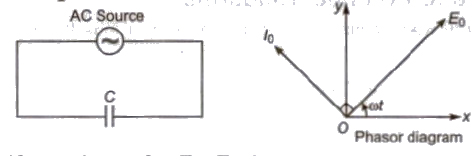
(a) Alternating emf, E = Eo sin ωt
(b) Alternating current, I = Io sin (ωt + π / 2)
(c) Alternating current lags behind alternating emf by π / 2.
(d) Inductive reactance, XL = Cω = C2πf
(e) Average power decay, (P) = 0
(f) Power factor, cos θ = cos 90° = 0
(iv) R – C Circuit

E = Eo sin ωt
I = Eo / 2 sin (ωt – φ)
Z = √R2 + (1 / ωC)2
tan φ = – 1 / ωC / R
Current leading the voltage by φ
V2 = V2R = V2C
(v) L – C Circuit


(vi) L – C – R Circuit
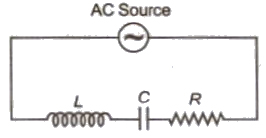
(a) Alternating emf, E = Eo sin Ωt
(b) Alternating current, I = Io sin (Ωt ± θ)
(c) Alternating current lags leads behind alternating emf by ω.
(d) Resultant voltage, V = √V2R + (VL – VC)2
(e) Impedance, Z = √R2 + (XL – XC)2
(f) Power factor, cos θ = R / Z = R / √√R2 + (XL – XC)2
(g) Average power decay, (P)= EVIV cos θ
Resonance in AC Circuit
The condition in which current is maximum or impedance is minimum in an AC circuit, is called resonance.
(i) Series Resonance Circuit
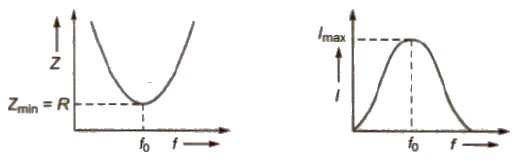
In this circuit components L, C and R are connected in series.
At resonance = XL = XC
Resonance frequency f = 1 / 2π√LC
A series resonance circuit is also known as acception circuit.
(ii) Parallel Resonance Circuit
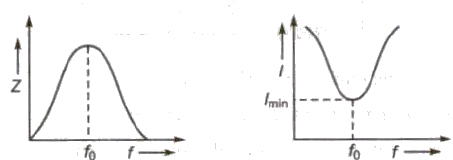
In this circuit L and C are connected in parallel with each other.
At resonance, XL = XC
Impedance (Z) of the circuit is maximum.
Current in the circuit is minimum.
Wattless Current
Average power is given by
Pav = Erms = Irms cos θ
Here the Irms cos φ contributes for power dissipation. Therefore, it is called wattless current.
AC Generator or Dynamo
It is a device which converts mechanical energy into alternating current energy.
Its working is based on electromagnetic induction.
The induced emf produced by the AC generator is given by
e = NBAω sin ωt = eo = sin ωt
There are four main parts of an AC generator

(i) Armature It is rectangular coil of insulated copper wire having a large number of turns.
(ii) Field Magnets These are two pole pieces of a strong electromagnet.
(iii) Slip Rings These are two hollow metallic rings.
(iv) Brushes These are two flexible metals or carbon rods, which remains slightly in contact with slip rings .
Note An DC generator or dynamo contains split rings or commutator inspite of slip rings.
DC Motor
It is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Its working is based on the fact that when a current carrying coil is placed in uniform magnetic field a torque acts on it.

Torque acting on a current carrying coil placed in uniform magnetic field
τ = NBIA sin θ
When armature coil rotates a back emf is produced in the coil.
Efficiency of a motor,
η = Back emf / Applied emf = E / V
Transformer
It is a device which can change a low voltage of high current into a high voltage of low current and vice-versa.
Its working is based on mutual induction.
There are two types of transformers.
(i) Step-up Transformers It converts a low voltage of high current into a high voltage of low current.

In this transformer,
Ns > NP, Es > EP
and IP > IS
(ii) Step-down Transformer It converts a high voltage of low current into a low voltage of high current.
In this transformer,
NP > NS, EP > ES and IP < IS
Transformation Ratio
Transformation ratio,
K = NS / NP = ES / EP = IP / IS
For step-up transformer, K > 1
For step-down transformer, K < 1
Energy Losses in a Transformer
The main energy losses in a transformer are given below
- Iron loss
- Copper loss
- Flux loss
- Hysteresis loss
- Humming loss
Important Points
- Transformer does not operate on direct current. It operates only on alternating voltages at input as well as at output.
- Transformer does not amplify power as vacuum tube.
- Transformer, a device based on mutual induction converts magnetic energy into electrical energy.
- Efficiency, η = Output power / Input power
Generally efficiency ranges from 70% to 90%.
- A choke coil is a pure inductor. Average power consumed per cycle is zero in a choke coil.
- A DC motor connects DC energy from a battery into mechanical energy of rotation.
- An AC dynamo/generator produces are energy from mechanical energy of rotation of a coil.
- An induction coil generates high voltages of the order of 1OS V from a battery.
It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction.
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.




