CBSE Class 11 Chemistry General Organic Chemistry – Get here the Notes for Class 11 General Organic Chemistry. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 11 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 11 Chemistry study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of CBSE Class 11 Chemistry for topic General Organic Chemistry.
- Class: 11th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: General Organic Chemistry
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry General Organic Chemistry
Candidates who are pursuing in CBSE Class 11 Chemistry are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for CBSE Class 11 Chemistry General Organic Chemistry from this article.
The hydrides of carbon (hydrocarbons) and their derivatives are called organic compounds. The branch of chemistry which deals with these compounds is called organic chemistry.
Berzelius (1808) defined organic chemistry as the chemistry of substances found in living matter and gave the vital force theory. Synthesis of urea. the first organic compound synthesised in laboratory, by Wohler. gave death blow to the vital force theory.
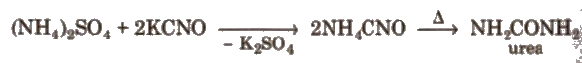
Acetic acid is the first organic compound synthesised from its elements.
Reasons for Large Number of Organic Compounds
(a) Catenation It is the tendency of self combination and is maximum in carbon. A carbon atom can combine with other carbon atoms by single, double or triple bonds. Thus, it forms more compounds than the others.
(b) Tetravalency and small size Carbon being tetravalent, is capable of bonding with four other C atoms or some other monovalent atoms. Carbon can form compound with oxygen. hydrogen. chlorine, sulphur, nitrogen and phosphorus. These compounds have specific properties depending upon the nature of the element or group attached with the carbon.
Furthermore, these compounds are exceptionally stable because of the small size of carbon.
General Characteristics of Organic Compounds
1. These are the compounds of carbon with H, 0, N, S, P, F, CI, Br and 1.
2. These are generally found in living organisms. e.g., carbohydrates, proteins etc.
3. These may be gases, liquids or solids.
4. Being covalent in nature, these have low boiling point and melting point and soluble in organic solvents.
5. These are generally volatile and inflammable.
6. They do not conduct electricity because of the absence of free ions.
7. They possess distinct colour and odour.
Classification of Organic Compounds

Classification of Carbon Atoms
1. On the Basis of Number of C Attached
(i) Primary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with one other carbon atom only, it is called primary or 1° carbon atom.
(ii) Secondary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with two other carbon atoms, it is called secondary or 2°carbon atom.
(iii) Tertiary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with three other carbon atoms, it is called tertiary or 3° carbon atom.
(iv) Quaternary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with four other carbon atoms, it is called quaternary or 40 carbon atom.
Reactivity order of carbon atoms is as follows 3° > 2° > 1°.

On the Basis of Position of Functional Group
(i) α – carbon Carbon which is directly attached to the functional group.
(ii) β- carbon Carbon which is directly attached to the n-carbon.
Classification of Hydrogen Atoms
- 1°-hydrogen (primary) attached to 10-carbon,
- 2°-hydrogen (secondary) attached to 2°-carbon.
- 3°-hydrogen (tertiary) attached to 3°·carbon.
- α- hydrogen(s) Hydrogens which are attached to n-carbon atom.
- β – hydrogen(s) Hydrogens which are attached to ~-carbon atom.

Functional Group
The atom e.g., -CI, -Br etc., or group of atoms e.g., -COOH, – CHO, which is responsible for the chemical properties of the molecule, is
called functional group.
Double and triple bonds are also functional groups.
R – F ← functional group.
R is called alkyl group, it contains only single bond; alkenyl group if contains double bond and alkynyl group if contains triple bond.
Homologous Series
The series in which the molecular formula of adjacent members differ by a – CH2 unit, is called homologous series and the individual members are called homologous. e.g., The homologous series of alkene group is

The general characteristics of this series are :
1. All the homologues contain same functional group. That’s why their chemical properties are almost similar.
2. All the members of a series have same general formula, e.g.,

3. All the members can be prepared by almost similar methods.
4. With increase in the molecular weight of a series, the physical properties varies gradually.
Representation of Different Formulae
An organic compounds can be represented by the following ways :
1. Complete formula
In it, all the bonds present between any two atoms are shown clearly.

2. Condensed Formula
In it, all the bonds are not shown clearly.

3. Bond Line Formula
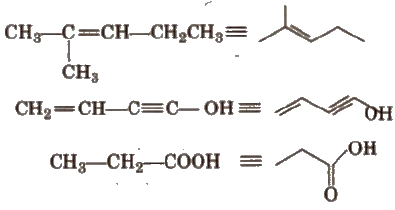
In it, every fold and free terminal represents a carbon and lines represent the bonds. e.g.,

In such formulae, it is assumed that required number of H-atoms are present, where ever, they are necessary (to satisfy tetravalency of carbon) e.g.,
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Trivial System
It is the oldest system in which names are derived from source or some property. These are mainly derived from Latin or Greek names e.g.,
acetic acid (acetum = vinegar), oxalic acid (oxalic), malic acid (pyrus malus), citric acid (citric), formic acid (obtained from red ant
(formicidae)],
IUPAC System
The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system, given in 1957, is superior and widely used. IUPAC amends these rules from time to time. Here. we are following the 1993 recommendations of IUPAC nomenclature.
Following rules are used to write the IUPAC name of an organic compound.
Rule I
Longest chain rule The chain containing the principal functional group, secondary functional group and multiple bonds as many as possible is the longest possible chain.
In the absence of functional group, secondary group and multiple bonds, the chain containing the maximum number of C-atoms will be the longest possible chain e.g
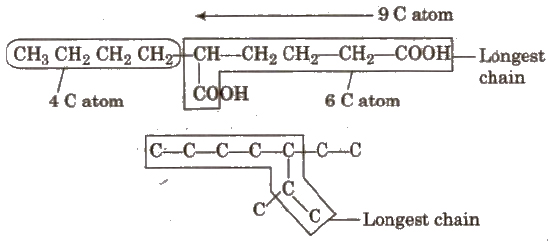
Choose the word root from the table given below for the longest possible chain.
Word Root for Carbon Chain

Rule 2
Lowest number rule Numbering is done in such a way so that
1. branching if present gets the lowest number.
2. the sum of numbers of side chain is lowest.
3. principal functional group gets the lowest number.
Select the principal functional group from the preference series :

Functional group other than the principal functional group are called substituents.
Rule 3.
Naming the prefixes and suffixes Prefix represents the substituent and suffix is used for principal functional group.
Primary prefixes are cycle, bicycle, di, tri, tetra, tries. tetrakis etc.
Secondary prefixes are tabulated below :

Primary suffix are ene, ane, or yne used for double, single and triple bonds respectively.
Secondary suffixes are tabulated below :

Hence. according to the rules. given above, the IUPAC name of a compound can be written as
or Prefixes + Root word + Suffixes Primary prefix + secondary prefix + Root word + primary suffix + secondary suffix

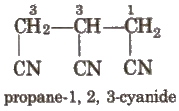
If more than two similar functional groups are present, all the groups are considered as substituent, e.g.,
Naming Alicyclic Compounds
For alicyclic compounds, prefix cyclo is used e.g.,
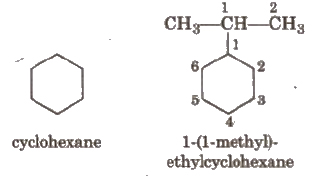
If the alkyl chain contains a greater number of C-atoms than the ring, the ring is designated as substituent, e.g.,

If side chain contains a multiple bond or a functional group, the ring is treated as a substituent e.g

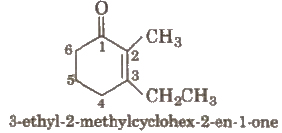
Other examples are
Naming Spiro Compounds
Prefix ‘spiro’ is used for the compounds in which one carbon is c nunOli between two rings ;
Here, smaller ring is numbered first, e.g.,

Naming Bicyclo Compounds
Prefix ‘bicycle’ is used for such compounds e.g.,
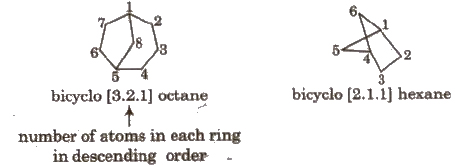
In bicycle compounds, numbering is done first in larger ring, then in smaller ring.
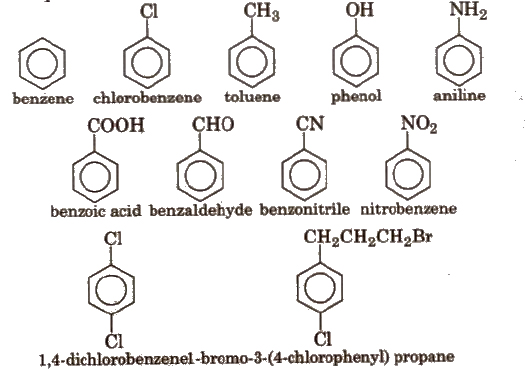
Naming Aromatic Compounds
IUPAC accepted their common trivial names e.g.,
Fission of a Covalent Bond
1.Homolytic Fission
In this, one of the electrons of the shared pair in a covalent bond goes with each of the bonded atoms. The neutral chemical species thus formed, is called free radical. Generally, homolytic fission takes place in non-polar, covalent molecules in the presence of sunlight or high temperature.
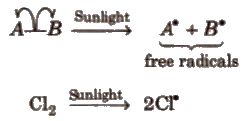
Free radicals are highly reactive. neutral and electron deficient species
2. Heterolytic Fission
In this, the bond breaks in such a fashion that the shared pair of electrons goes with one of the fragments.
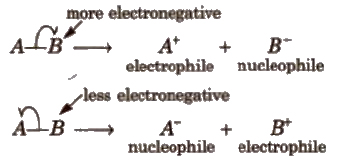
Carbon bearing a positive charge is called carbocation and carbon bearing negative charge is called carbanion.
Heterolytic fission generally takes place in polar covalent molecules but in non-polar molecules, it takes place in the presence of catalyst like AiCI3) (anhy.), FeCl3)(anhy.)etc.
Attacking Reagent
These are of two types :
1. Electrophiles or Electrophilic Reagents
These are electron deficient species i.e., behave as Lewis acids. The following species behave as electrophiles :
(i) All non-metal cations and metal cations which have vacant d- orbitals.
e.g., CI+, NO+2, CH3CO+ etc.
(ii) Lewis acids (incomplete octet) e.g., BF3, ZnC12 (anhydrous), FeCl3 (anhydrous), AlCl3(anhydrous), :CH2 etc.
(iii) Non-metal (acidic) oxides e.g., CO2, SO2 etc.
2. Nucleophiles or Nucleophilic Reagents
These are electron rich species i.e., behave as Lewis bases.
These attack at electron deficient area.
The following species behave as nucleophiles :
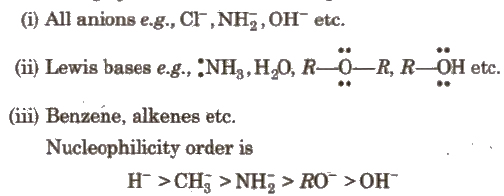
In case of same nucleophilic site, nucleophilicity parallels basicity i.e.. as the basicity increases, nucleophilicity also increases.
(if nucleophilic sites (or attacking atoms) are different nucleophilicity varies inversely with electronegativity)
3. Amphiphiles
These species behave like both electrophiles as well as nucleophiles. Organic compounds containing a multiple bond between carbon and a more electronegative atom can act as amphiphiles, e.g.,

Reaction Intermediates
These are formed as a intermediate during the course of a reaction.
These are short lived and highly reactive.
Free radicals, carbocations, carbanions, carbenes and nitrenes are important reactions intermediates.
1. Free Radicals
These are the product of homolysis and contain an odd electron. These are highly reactive planar species with Sp2 hybridisation.
Their order of stability is

2. Carbocations
These are the product of heterolysis and contain a carbon bearing positive charge. These are electron deficient species. Carbocations contain six electrons in the valence shell.
These are also planar chemical species i.e., sp2 hybridised with an empty p-orbital

The stability order of carbocations is
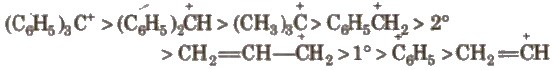
3. Carbanions
These are also the product of heterolysis and contain a carbon bearing negative charge and 8 electrons in its valence shell
These have pyramidal shape with Sp3 hybridised carbon (having one lone pair)
The order of stability of carbanions is

4. Carbenes
These are divalent carbon species having two non-bonding electrons along WIth two bond pairs.
These are obtained by photolysis or pyrolysis. e.g.,
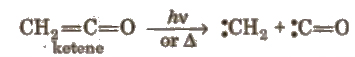
These being electron deficient behave as Lewis acids. These are of two types:
(i) Singlet carbene In it, the C-atom is Sp2 hybridised. Then Hybridised orbitals contain no electrons and a hybridised orbital contains two electrons :

Singlet carbene has bent structure and is less stable than triplet carbene.
The order of stability of singlet carbenes is

(ii) Triplet carbene In it, the central C-atom is sp-hybridised. The sp – hybridised orbitals contain 1 electron each .

Triplet carbene has linear geometry.
5. Nitrene
These are neutral monovalent nitrogen species in which N atom has two unshared pair of electrons with a monovalent atom or group attached.

These are obtained by thermolysis of azides and as reactive as carbenes.
6. Arynes
It contains a formal carbon-carbon triple bond in aromatic molecule.

The additional bond is formed between two neighbouring C-atoms by sideways overlapping of two Sp2 orbitals. The new bond lies along with side of the ring and has little interaction with the 1t electron cloud lying above and below the ring.
The sideways overlapping is weak and thus, makes the benzene more reactive.
Inductive Effect
It is just like shifting of shared pair of electrons in polar covalent molecules. If shared pair is more shifted towards the more electronegative atom, the less electronegative atom acquires slight positive charge and more electronegative atom acquires partial negative charge, e.g.,

It is a permanent effect and propagates through carbon chain.
Atoms or groups having greater electron affinity than hydrogen. are said to have electron attracting or negative inductive effect (- I) while that having, smaller electron affinity than hydrogen are said to have electron releasing or positive inductive effect (+ I) e.g.,
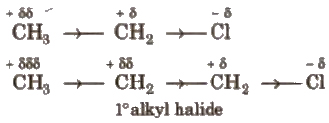
Here, Cl has – I effect and alkyl group has + I effect.
Order of groups producing – I effect is

Order of groups producing + I effect is
Applications of Inductive Effect
1. Presence of groups showing + I effect increases the stability of carbocation while presence of groups showing – I effect decreases their stability.
2. Strength of acid increases with the attachment of group showing – 1 effect and decreases with the attachment of group showing + I effect.
3. Presence of + I showing groups increases the basic strength of amines.
4. Reactivity of carbonyl compound is increased by – I showing groups.
5. Reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN 1 is increased by + 1 showing groups.
Electromeric Effect
It is defined as the polarity produced in a multiple bonded compound as a reagent approaches it. In the presence of attacking reagent, the two π electrons are completely transferred to any of the one atom. This effect is temporary.
This may be of + E type (when displacement of electron pair is away from the atom or group) or of – E type (when the displacement is towards the atom or group). e.g.,
Hyperconjugation
It involves delocalisation of σ electron of a C – H bond of an alkyl group attached directly to an atom of unsaturated system or to an atom with an unshared p-orbital.

This effect is also called no bond formation or Baker Nathan effect.
Applications of Hyperconjugation
(i) Stability of alkenes More the number of a-hydrogen atoms, more stable is the alkene.

(ii) Stability of carbocation Greater the number of alkyl groups attached to a positively charged carbon atom, the greater is the stability.

Resonance Effect
When all the properties of a molecule cannot be shown by a single structure and two or more structures are required to show all the properties of that molecule, then the structures are called resonating structures or canonical forms and the molecule is referred as resonance hybrid. This phenomenon is called resonance.
In resonance,
1. The arrangement of atoms must be identical in all the formulae.
2. The energy content of all the canonical forms must be nearly same.
3. Each canonical form must have the same number of unpaired electrons.
It involves delocalisation of 1t electrons. This effect may be of + R type or – R type.
Positive Resonance Effect (+R)
Electron donating groups with respect to conjugate system show +R effect. Central atom of functional groups should be more electronegative than the surrounding atoms or groups to show +R effect. e.g., halogens, -OH. -OR, -OCOR, -NH2,-NHCOR etc

Electron donating groups producing. + R effect are ortho and para directing. ‘They activate the benzene ring towards the electrophilic SUbstitution reactions except halogens. Halogens slightly deactivate the benzene ring towards the electrophilic substitution reaction. More the E.D.G. more is the basic nature.
Negative Resonance Effect (-R)
Electron withdrawing groups with respect to conjugate system show – R effect. Central atom of functional groups should be less electronegative than surrounding atoms or groups to show – R effect. e.g., halogens, – COOH,- COOR,- CHO,- CN,-NO2 etc.

Electron withdrawing group (E.W.G.) producing – R effect are meta directing. They deactivate the benzene ring towards the electrophilic substitution reaction. More the E.W.G, more is the acidic nature.
Resonance Energy
Number of π bonds ∝ contributing structures ∝ resonance energy ∝ stability.
In benzene, resonance energy is 36 kcal/mol.
Stability of Canonical Forms
It can be judged by the following rules :
1. Non-polar structure is more stable than the polar structure.
2. Among polar structures, structure with maximum number of covalent bonds is most stable.
3. The structure with maximum charge separation is more stable.
4. Structure with positive charge on more electropositive element and negative charge on more electronegative element is more stable.
Resonance and Bond order

Isomerism
The compound having same molecular formula but differ in properties are known as isomers and the phenomenon is known as isomerism.
There are two main types of isomerism i.e.,
1. Structural Isomerism
In this type of isomerism, compounds have same molecular formula but different structures.
It can further be of following types:
(i) Chain Isomerism
It arises when two or more compounds have similar molecular formula but different carbon skeletons, e.g.,

(ii) Position Isomerism
When two or more compounds have same molecular formula but different position of functional groups or substituents, they are called positional isomers and the phenomenon is called position isomerism
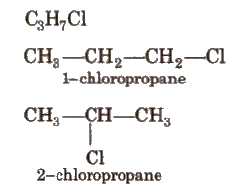
(iii) Functional Isomerism
It arises when two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional group. e.g., C3H6O represents an aldehyde and a ketone as

(iv) Metamerism
It arises due to different alkyl groups on either side of the same functional group in a molecule, e.g.,

(v) Tautomerism
It is a special type of functional isomerism which arises in carbonyl compounds containing α – H atom e.g.,
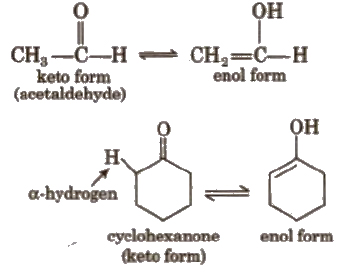
2. Stereoisomerism
The compounds having same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms or groups are called stereoisomers and the phenomenon is called stereoisomerism.
Stereoisomerism is of three types : optical isomerism, geometrical isomerism and conformations.
(i) Optical Isomerism
Compounds having similar physical and chemical properties but. differ only in behaviour towards plane polarised light are called enantiomer & or optical isomers and the phenomenon is known as optical isomerism. e.g.,

The isomer which rotate +he plane of polarised light towards right (clockwise) is known as dextrorotatory or d-form while that which rotates towards left (anticlockwise) is known as laevorotatory or l-form.
Generally asymmetric or chiral compounds show optical isomerism Chiral compounds are those which contain chiral centre i.e., chiral carbon, the carbon all the four valencies of which are satisfied by four different groups. Allenes, spiranes and biphenyl compounds, although have absence of chiral centre, but are asymmetric. That’s why they are also optically active.
Number of optical active isomers = 2n (where, n = chiral carbon). If two end are similar number of optical active isomers = 2n – 1 (if n = even) and meso form = 2n – 2 / 2. If n = odd, number of optical active isomers = 2n – 1 – 2(n – 1) / 2.
Terms Related to Optical Isomerism
(a) Enantiomers The non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers e.g.,

(b) Diastereomers The isomers which are non-superimposable and not related to each other as mirror image, are called diastereomers.

They have different physical and chemical properties.
(c) Meso form The compound in which half part of a molecule is the mirror image of other half, is called meso form. Generally, a meso compound have two or more chiral centres and a plane of symmetry. It is optically inactive due to internal compensation, thus, it is not
possible to convert it into d and I form e.g.,

(d) Racemic mixture It is a mixture of enantiomers in 1 : 1. It is optically inactive due to external compensation.
Separation of a racemic mixture into d and I form IS called resolution. It can be done by mechanical method, biochemical method and chemical method.
(e) Atropisomers These are the isomers that can be interconvertible by rotation about single bond but for which the rotation barrier is large enough that they can be separated and do not convert readily at room temperature.
(f) Specific rotation It is given by the expression.

Nomenclature of Enantiomers
(i) D-L configuration The optical isomer in which H is present towards left hand side and the other group towards right hand side, IS D-form while in which, H is present towards right and the other group occupy the left position, is L-form. This system is applicable mainly for compounds containing one chiral atom.
(ii) Threo-erythro system When the same groups are present at the same side of the carbon chain, the form is called erythro form. When the same groups are present on the opposite side of the carbon chain, the form is called threo form. e.g.,

(iii) R-S system This system was proposed by Cabo, Ingold and Prelog. In this system, configuration R is given to the isomer in which sequence of groups is clockwise and S is given to the isomer in which sequence of groups is anticlockwise.
Priority sequence is decided by following rules :
1. Priority is given to the atom having high atomic number e.g., in CI, Br and F, the priority order is Br > CI > F.
2. In case of group of atoms, priority is decided by the atomic number of first atom. e.g., in -COOR, -OH and -NH2 priority order is
-OH > -NH22 > -COOH
3. If the first atom of the group of atoms is same, the priority is decided by second atom of the group e.g., among -COOH, -CH2OH and-CHO. priority order is
-COOH > – CHO > -CH2OH
4. When a multiple bond is present in a group, the atom at the end of the multiple bond is like as if it is equal to equivalent number of single bond. e.g
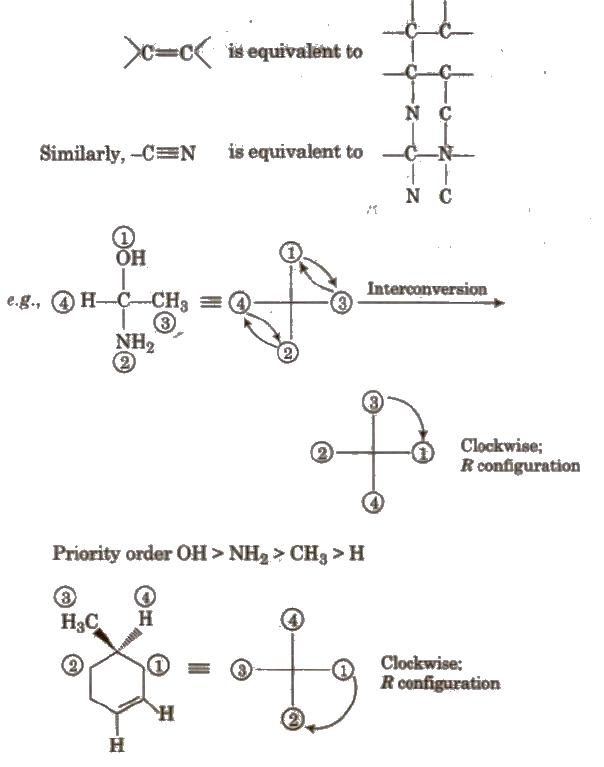
(ii) Geometrical Isomerism
The isomers having same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms about the double bond are known as geometrical isomers and this phenomenon is called geometrical isomerism, e.g.,
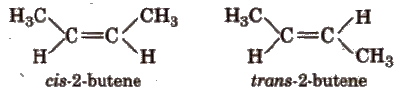
For exhibiting geometrical isomerism, the essential conditions are :
1. The compound must contain at least one double bond.
2. The groups present at the double bonded carbon atoms, must be different. However, one similar group should be present at the adjacent double bonded carbon atoms.
Number of geometrical isomers (if two ends are not similar = 2n where, n = number of double bonds).
Types of Geometrical Isomers
(a) Cis-trans isomers In cis-isomer, similar groups are present on the same side of the double bond and in trans- isomer, similar groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond. e.g.,

(b) Syn-anti isomers compounds containing C=N bond (as in aldoxime), N=N bond (as in H2N2O) exhibit this type of isomerism

(c) E-Z isomers In E-isomer, bulkier (heavier) groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond and in Z-isomer, heavier groups are present on the same side of the double bond. E is entgegen means opposite and Z is Zusammen means together, e.g.,

(iii) Conformational Isomerism
In conformational isomerism because of the free rotation of carbon-carbon single bond, different arrangement of atoms in space are obtained. These arrangements are called conformers
Different Conformers
(a) Staggered conformation In it, the atoms or groups bonded to carbons at each end of a C-C bond are as far apart as possible.
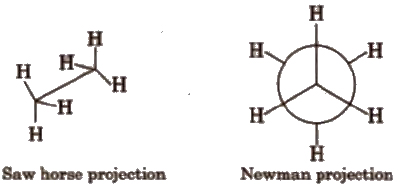
In staggered conformation. the dihedral angle between the bonds at each of the C-C bonds is 180°.
(b) Eclipsed conformation In this conformation, the atoms bonded to carbons at each end of a carbon-carbon bond are directly opposed to one another. i.e., they are as close as possible

In this conformation, the dihedral angle is 0°.
(c) Skew or Gauche conformation All other conformations in between eclipsed and staggered conformations are called skew or Gauche conformations.
Torsional Strain
The increase in electron-electron repulsion upon rotation from staggered to an eclipsed conformation is referred to as torsional strain.
Confirmation of Alkanes
(a) Conformers of ethane

Order of stability: I > II > III.
(b) Conformers of n-butane

Order of stability : IV > II > > I.
(c) Conformers of 3 – fluoro butan – 2 – ol

Stability order : II > I > III
(d) Conformers of cyclohexane The cyclohexane ring can assume many shapes due to rotation around C-C bonds. The chair form and the boat forms are extreme cases.

Each carbon atom of cyclohexane is bonded to two types hydrogens. Hydrogen lying in the plane of ring, are called equatorial hydrogen (He) while that are parallel to the axis are called axial hydrogens. (Ha)
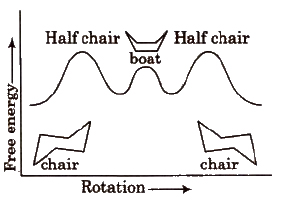
The conformations in which bulkier group occupy the equatorial position is more stable.
Types of Reactions
Reactions are of following types :
1. Addition Reactions
These reactions are given by unsaturated compounds or compounds containing multiple bonds. .
In these reactions, the reagent adds to the substrate molecule.
These are of two types (depending upon the nature of attacking species) :
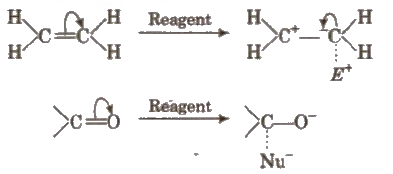
(i) Electrophilic addition reactions In these reactions, H+ (or electrophile) is added to the substrate in the rate determining step. These reactions are given by alkenes and alkynes. e.g.,
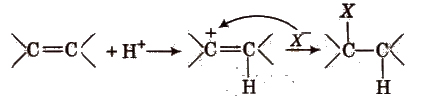
(ii) Nucleophilic addition reactions In these reactions, nucleophile is added to the substrate in the rate determining step. These reactions are given by carbonyl compounds e.g.,

2. Substitution Reactions
In these reactions, one atom or group of atoms, called the leaving group, is substituted by a nucleophile or an electrophile. On this basis these reactions are of two types :
(i) Electrophilic substitution reactions When leaving group is replaced by an electrophile, the reaction is called electrophilic substitution reaction

(ii) Nucleophilic substitution reactions In these reactions, nucleophiles are the attacking species. These are of two types :
(a) SN1(Nucleophilic substitution unimolecular) reaction is a two step process, e.g.,

(b) SN2 (Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular) reaction is a single step process e.g.,

3. Elimination Reactions
In these reactions, two groups from the same or adjacent atoms are lost and electron deficient or unsaturated compound is formed.
These can be of two types :
(i) α – elimination In it, both the groups are eliminated from the same carbon atom. Such reactions are rare. e.g.,

(ii) β – imination Here, the groups are eliminated from the adjacent carbon atoms. These can further be E1 or E2 reactions e.g.,

Class 11 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 11 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 11 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 11 can also check Class 11 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 11th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 11 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 11 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 11 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 11 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 11 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 11 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 11. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 11.
CBSE Notes for Class 11 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

