Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 9, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids
NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 is for Mechanical Properties of Fluids. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 9. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
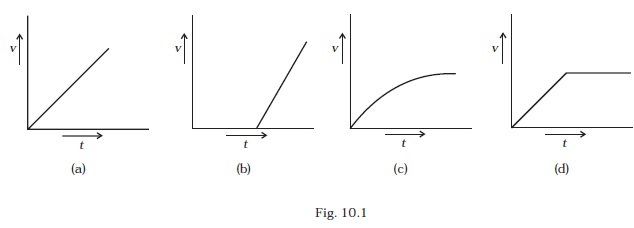
- A tall cylinder is filled with viscous oil. A round pebble is dropped from the top with zero initial velocity. From the plot shown in Fig. 10.1, indicate the one that represents the velocity (v) of the pebble as a function of time (t ).
- Which of the following diagrams (Fig. 10.2) does not represent a streamline flow?
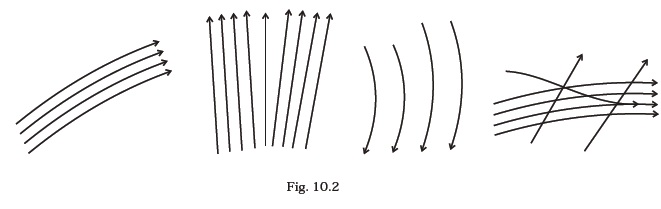
- Along a streamline
(a) the velocity of a fluid particle remains constant.
(b) the velocity of all fluid particles crossing a given position is constant.
(c) the velocity of all fluid particles at a given instant is constant.
(d) the speed of a fluid particle remains constant. - An ideal fluid flows through a pipe of circular cross-section made of two sections with diameters 2.5 cm and 3.75 cm. The ratio of the velocities in the two pipes is
(a) 9:4
(b) 3:2
(c) √3 : √2
(d) √2 : √3 - The angle of contact at the interface of water-glass is 0°, Ethyl Alcohol-glass is 0°, Mercury-glass is 140° and Methyl Iodide Glass is 30°. A glass capillary is put in a trough containing one of these four liquids. It is observed that the meniscus is convex. The liquid in the trough is
(a) water
(b) ethyl alcohol
(c) mercury
(d) methyl iodide.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- For a surface molecule
(a) the net force on it is zero.
(b) there is a net downward force.
(c) the potential energy is less than that of a molecule inside.
(d) the potential energy is more than that of a molecule inside. - Pressure is a scalar quantity because
(a) it is the ratio of force to area and both force and area are vectors.
(b) it is the ratio of the magnitude of the force to area.
(c) it is the ratio of the component of the force normal to the area.
(d) it does not depend on the size of the area chosen. - A wooden block with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as shown in Fig.10.3.
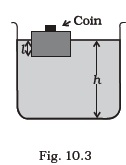
- The distance l and h are shown in the figure. After some time the coin falls into the water. Then
(a) l decreases.
(b) h decreases.
(c) l increases.
(d) h increase. - With increase in temperature, the viscosity of
(a) gases decreases.
(b) liquids increases.
(c) gases increases.
(d) liquids decreases. - Streamline flow is more likely for liquids with
(a) high density.
(b) high viscosity.
(c) low density.
(d) low viscosity.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Is viscosity a vector?
- Is surface tension a vector?
- Iceberg floats in water with part of it submerged. What is the fraction of the volume of iceberg submerged if the density of ice is ρi = 0.917 g cm–3?
- A vessel filled with water is kept on a weighing pan and the scale adjusted to zero. A block of mass M and density ρ is suspended by a massless spring of spring constant k. This block is submerged inside into the water in the vessel. What is the reading of the scale?
- A cubical block of density ρ is floating on the surface of water. Out of its height L, fraction x is submerged in water. The vessel is in an elevator accelerating upward with acceleration a . What is the fraction immersed?
Short Answer Type Questions
- The sap in trees, which consists mainly of water in summer, rises in a system of capillaries of radius r = 2.5×10–5 m. The surface tension of sap is T = 7.28 * 10–2 Nm–1 and the angle of contact is 0°. Does surface tension alone account for the supply of water to the top of all trees?
- The free surface of oil in a tanker, at rest, is horizontal. If the tanker starts accelerating the free surface will be titled by an angle θ. If the acceleration is a m s–2, what will be the slope of the free surface?.
- Two mercury droplets of radii 0.1 cm. and 0.2 cm. collapse into one single drop. What amount of energy is released? The surface tension of mercury T= 435.5 × 10–3 N m–1.
- If a drop of liquid breaks into smaller droplets, it results in lowering of temperature of the droplets. Let a drop of radius R, break into N
small droplets each of radius r. Estimate the drop in temperature. - The surface tension and vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and 2.33×103 Pa, respectively. What is the radius of the smallest spherical water droplet which can form without evaporating at 20°C?
Long Answer Type Questions
- (a) Pressure decreases as one ascends the atmosphere. If the density of air is ρ, what is the change in pressure dp over a differential height dh?
(b) Considering the pressure p to be proportional to the density, find the pressure p at a height h if the pressure on the surface of the earth is po.
(c) If po = 1.03 × 105 N m-2, ρo = 1.29 kg m-3 and g = 9.8 m s-2, at what height will the pressure drop to (1/10) the value at the surface of the earth?
(d) This model of the atmosphere works for relatively small distances. Identify the underlying assumption that limits the model. - Surface tension is exhibited by liquids due to force of attraction between molecules of the liquid. The surface tension decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at boiling point. Given that the latent heat of vaporization for water Lv = 540 k cal kg–1, the mechanical equivalent of heat J = 4.2 J cal–1, density of water ρw = 103 kg l–1, Avagadro’s No NA = 6.0 × 1026 k mole -1 and the molecular weight of water MA = 18 kg for 1 k mole.
(a) estimate the energy required for one molecule of water to evaporate.
(b) show that the inter–molecular distance for water is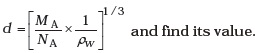
(c) 1 g of water in the vapor state at 1 atm occupies 1601 cm3. Estimate the intermolecular distance at boiling
point, in the vapour state.
(d) During vaporisation a molecule overcomes a force F, assumed constant, to go from an inter-molecular distance d to d ′ . Estimate the value of F.
(e) Calculate F/d, which is a measure of the surface tension. - A hot air balloon is a sphere of radius 8 m. The air inside is at a temperature of 60°C. How large a mass can the balloon lift when the outside temperature is 20°C? (Assume air is an ideal gas, R = 8.314 J mole–1K–1, 1 atm. = 1.013 * 105 Pa; the membrane tension is 5 N m–1.)
Click here to download the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids.
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions











Physics Chemistry Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

