Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 11, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 Thermodynamics
NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 is for Thermodynamics. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 11. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
- An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig. 12.1). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
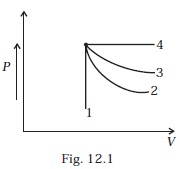
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1 - If an average person jogs, hse produces 14.5 × 103 cal/min. This is removed by the evaporation of sweat. The amount of sweat evaporated per minute (assuming 1 kg requires 580 × 103 cal for evaporation) is
(a) 0.25 kg
(b) 2.25 kg
(c) 0.05 kg
(d) 0.20 kg - Consider P-V diagram for an ideal gas shown in Fig 12.2.

- Out of the following diagrams (Fig. 12.3), which represents the T-P diagram?
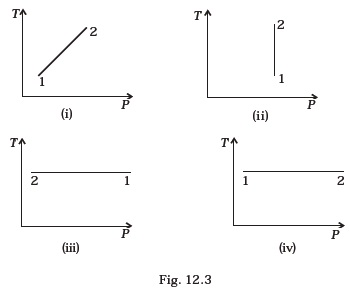
(a) (iv)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (i) - An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram (Fig. 12.4).
The amount of work done by the gas is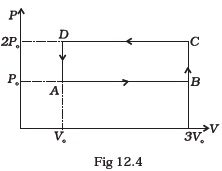
- Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is
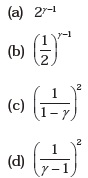
- Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3 ). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temperature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
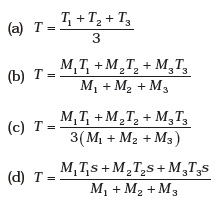
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- Which of the processes described below are irreversible?
(a) The increase in temperature of an iron rod by hammering it.
(b) A gas in a small container at a temperature T1 is brought in contact with a big reservoir at a higher temperature T2 which increases the temperature of the gas.
(c) A quasi-static isothermal expansion of an ideal gas in cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston.
(d) An ideal gas is enclosed in a piston cylinder arrangement with adiabatic walls. A weight W is added to the piston, resulting in compression of gas. - An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
(a) dU = 0
(b) dQ= 0
(c) dQ = dU
(d) dQ = dW - Figure 12.5 shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.
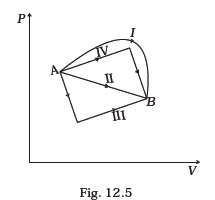
(a) Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
(b) Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
(c) Work done is maximum in case I
(d) Work done is minimum in case II. - Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Fig. 12.6)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic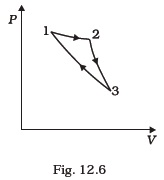
Such a process does not exist because
(a) heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
(b) mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process,which is not possible.
(c) curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
(d) curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect. - Consider a heat engine as shown in Fig. 12.7. Q1 and Q2 are heat added to heat bath T1 and heat taken from T2 in one cycle of engine. W is the mechanical work done on the engine.
If W > 0, then possibilities are: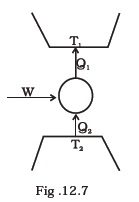
(a) Q1 > Q2 > 0
(b) Q2 > Q1 > 0
(c) Q2 < Q1 < 0
(d) Q1 < 0, Q2 > 0
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
- A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in Fig. 12.8. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?

- If a refrigerator’s door is kept open, will the room become cool or hot? Explain.
- Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
- Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
Short Answer Type Questions
- Consider a Carnot’s cycle operating between T1 = 500K and T2 = 300K producing 1 k J of mechanical work per cycle. Find the heat transferred to the engine by the reservoirs.
- A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
- Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ΔV≤V)
of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2? - In a refrigerator one removes heat from a lower temperature and deposits to the surroundings at a higher temperature. In this process, mechanical work has to be done, which is provided by an electric motor. If the motor is of 1kW power, and heat is transferred from –3°C to 27°C, find the heat taken out of the refrigerator per second assuming its efficiency is 50% of a perfect engine.
- If the co-efficient of performance of a refrigerator is 5 and operates at the room temperature (27 °C), find the temperature inside the refrigerator.
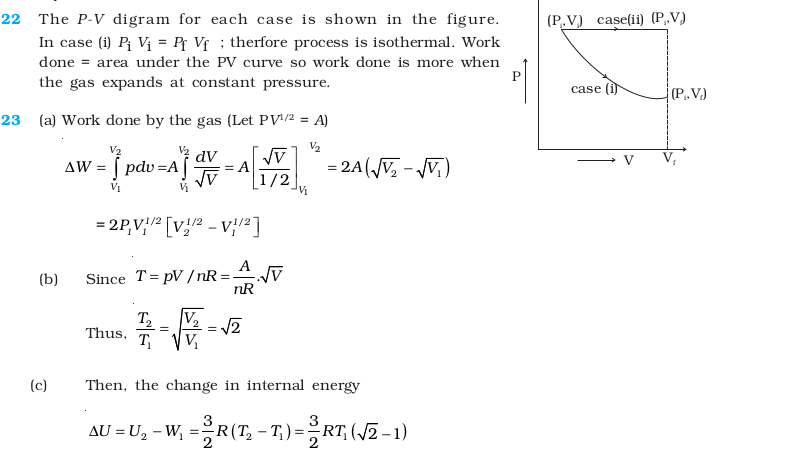
- The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf . Consider the following two cases:
(a) the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
(b) the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
Long Answer Type Questions
- Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in Fig. 12.9.
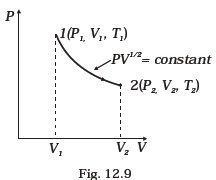
(a) Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
(b) What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
(c) Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the \
gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1. - A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Fig. 12.10.
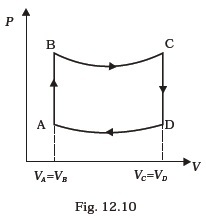
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB(a) In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
(b) In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
(c) What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
(d) What is the efficiency of the engine?
[ 5 γ = 5 / 3 for the gas], (CV = 3 / 2 R for one mole) - A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Fig. 12.11. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2) R)
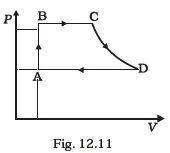
AB : constant volume
BC : constant pressure
CD : adiabatic
DA : constant pressure - Consider that an ideal gas (n moles) is expanding in a process given by P = f ( V ), which passes through a point (Vo, Po). Show that the gas is absorbing heat at (Po, Vo) if the slope of the curve P = f (V ) is larger than the slope of the adiabat passing through (Po, Vo).
- Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (Fig. 12.12). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from Vo to V1.
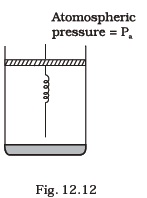
(a) What is the initial pressure of the system?
(b) What is the final pressure of the system?
(c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
Click here to download the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 Thermodynamics.
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions












Physics Chemistry Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.
