Class 11 Physics Measurement – Get here the Notes for Class 11 Physics Measurement. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 11 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 11 Physics study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 11 Physics for topic Measurement.
- Class: 11th
- Subject: Physics
- Topic: Measurement
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Measurement
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 11 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 11 Physics Measurement from this article.
The comparison of any physical quantity with its standard unit is called measurement.
Physical Quantities
All the quantities in terms of which laws of physics are described, and whose measurement is necessary are called physical quantities.
Units
- A definite amount of a physical quantity is taken as its standard unit.
- The standard unit should be easily reproducible, internationally accepted.
Fundamental Units
Those physical quantities which are independent to each other are called fundamental quantities and their units are called fundamental units.
| S.No. | Fundamental Quantities | Fundamental Units | Symbol |
| 1. | Length | metre | m |
| 2. | Mass | kilogram | kg |
| 3. | Time | second | S |
| 4. | Temperature | kelvin | kg |
| 5 | Electric current | ampere | A |
| 6 | Luminous intensity | candela | cd |
| 7 | Amount of substance | mole | mol |
Supplementary Fundamental Units
Radian and steradian are two supplementary fundamental units. It measures plane angle and solid angle respectively.
| S.No. | Supplementary Fundamental Quantities | Supplementary Unit | Symbol |
| 1 | Plane angle | radian | rad |
| 2 | Solid angle | steradian | Sr |
Derived Units
Those physical quantities which are derived from fundamental quantities are called derived quantities and their units are called derived units.
e.g., velocity, acceleration, force, work etc.
Definitions of Fundamental Units
The seven fundamental units of SI have been defined as under.
- 1 kilogram A cylindrical prototype mass made of platinum and iridium alloys of height 39 mm and diameter 39 mm. It is mass of 5.0188 x 1025 atoms of carbon-12.
- 1 metre 1 metre is the distance that contains 1650763.73 wavelength of orange-red light of Kr-86.
- 1 second 1 second is the time in which cesium atom vibrates 9192631770 times in an atomic clock.
- 1 kelvin 1 kelvin is the (1/273.16) part of the thermodynamics temperature of the triple point of water.
- 1 candela 1 candela is (1/60) luminous intensity of an ideal source by an area of cm’ when source is at melting point of platinum (1760°C).
- 1 ampere 1 ampere is the electric current which it maintained in two straight parallel conductor of infinite length and of negligible cross-section area placed one metre apart in vacuum will produce between them a force 2 x 10-7 N per metre length.
- 1 mole 1 mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains a many elementary entities (may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons or group of particles, as this and atoms in 0.012 kg of carbon isotope 6C12.
Systems of Units
A system of units is the complete set of units, both fundamental and derived, for all kinds of physical quantities. The common system of units which is used in mechanics are given below:
- CGS System In this system, the unit of length is centimetre, the unit of mass is gram and the unit of time is second.
- FPS System In this system, the unit of length is foot, the unit of mass is pound and the unit of time is second.
- MKS System In this system, the unit of length is metre, the unit of mass is kilogram and the unit of time is second.
- SI System This system contain seven fundamental units and two supplementary fundamental units.
Relationship between Some Mechanical SI Unit and Commonly Used Units
| S.No. | Physical Quantity | Unit | |
| 1 | Length | (a) | 1 micrometre = 10-6 m |
| (b) | 1 angstrom =10-10 m | ||
| 2 | Mass | (a) | 1 metric ton = 103 kg |
| (b) | 1 pound = 0.4537 kg | ||
| (c) | 1 amu = 1.66 x10-23 kg | ||
| 3 | Volume | 1 litre = 10-32 m3 | |
| 4. | Force | (a) | 1 dyne = 10-5 N |
| (b) | 1 kgf = 9.81 N | ||
| 5. | Pressure | (a) | 1 kgfm2 = 9.81Nm-2 |
| (b) | 1 mm of Hg = 133 Nm-2 | ||
| (c) | 1 pascal = 1 Nm-2 | ||
| (d) | 1 atmosphere pressure = 76 cm of Hg = 1.01 x 105 pascal | ||
| 6. | Work and energy | (a) | 1 erg =10-7 J |
| (b) | 1 kgf-m = 9.81 J | ||
| (c) | 1 kWh = 3.6 x 106 J | ||
| (d) | 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J | ||
| 7. | Power | (d) | 1 kgf- ms-1 = 9.81W |
| 1 horse power = 746 W |
Some Practical Units
- 1 fermi =10-15 m
- 1 X-ray unit = 10-13 m
- 1 astronomical unit = 1.49 x 1011 m (average distance between sun and earth)
- 1 light year = 9.46 x 1015 m
- 1 parsec = 3.08 x 1016 m = 3.26 light year
Some Approximate Masses
| Object | Kilogram |
| Our galaxy | 2 x 1041 |
| Sun | 2 x 1030 |
| Moon | 7 x 1022 |
| Asteroid Eros | 5 x 1015 |
Dimensions
Dimensions of any physical quantity are those powers which are raised on fundamental units to express its unit. The expression which shows how and which of the base quantities represent the dimensions of a physical quantity, is called the dimensional formula.
Dimensional Formula of Some Physical Quantities
| S.No. | Physical Quantity | Dimensional Formula | MKS Unit |
| 1 | Area | [L2] | metre2 |
| 2 | Volume | [L3] | metre3 |
| 3 | Velocity | [LT-1] | ms-1 |
| 4 | Acceleration | [LT-2] | ms-2 |
| 5 | Force | [MLT-2] | newton (N) |
| 6 | Work or energy | [ML2T-2] | joule (J) |
| 7 | Power | [ML2T-3] | J s-1 or watt |
| 8 | Pressure or stress | [ML-1T-2] | Nm-2 |
| 9 | Linear momentum or Impulse | [MLT-1] | kg ms-1 |
| 10 | Density | [ML-3] | kg m-3 |
| 11 | Strain | Dimensionless | Unitless |
| 12 | Modulus of elasticity | [ML-1T-2] | Nm-2 |
| 13 | Surface tension | [MT-2] | Nm-1 |
| 14 | Velocity gradient | T-1 | second-1 |
| 15 | Coefficient of velocity | [ML-1T-1] | kg m-1s-1 |
| 16 | Gravitational constant | [M-1L3T-2] | Nm2/kg2 |
| 17 | Moment of inertia | [ML2] | kg m2 |
| 18 | Angular velocity | [T-1] | rad/s |
| 19 | Angular acceleration | [T-2] | rad/S2 |
| 20 | Angular momentum | [ML2T-1] | kg m2S-1 |
| 21 | Specific heat | L2T-2θ-1 | kcal kg-1K-1 |
| 22 | Latent heat | [L2T-2] | kcal/kg |
| 23 | Planck’s constant | ML2T-1 | J-s |
| 24 | Universal gas constant | [ML2T-2θ-1] | J/mol-K |
Homogeneity Principle
If the dimensions of left hand side of an equation are equal to the dimensions of right hand side of the equation, then the equation is dimensionally correct. This is known as homogeneity principle.
Mathematically [LHS] = [RHS]
Applications of Dimensions
- To check the accuracy of physical equations.
- To change a physical quantity from one system of units to another system of units.
- To obtain a relation between different physical quantities.
Significant Figures
In the measured value of a physical quantity, the number of digits about the correctness of which we are sure plus the next doubtful digit, are called the significant figures.
Rules for Finding Significant Figures
- All non-zeros digits are significant figures, e.g., 4362 m has 4 significant figures.
- All zeros occuring between non-zero digits are significant figures, e.g., 1005 has 4 significant figures.
- All zeros to the right of the last non-zero digit are not significant, e.g., 6250 has only 3 significant figures.
- In a digit less than one, all zeros to the right of the decimal point and to the left of a non-zero digit are not significant, e.g., 0.00325 has only 3 significant figures.
- All zeros to the right of a non-zero digit in the decimal part are significant, e.g., 1.4750 has 5 significant figures.
Significant Figures in Algebric Operations
(i) In Addition or Subtraction In addition or subtraction of the numerical values the final result should retain the least decimal place as in the various numerical values. e.g.,
If l1= 4.326 m and l2 = 1.50 m
Then, l1 + l2 = (4.326 + 1.50) m = 5.826 m
As l2 has measured upto two decimal places, therefore
l1 + l2 = 5.83 m
(ii) In Multiplication or Division In multiplication or division of the numerical values, the final result should retain the least significant figures as the various numerical values. e.g., If length 1= 12.5 m and breadth b = 4.125 m.
Then, area A = l x b = 12.5 x 4.125 = 51.5625 m2
As l has only 3 significant figures, therefore
A= 51.6 m2
Rules of Rounding Off Significant Figures
- If the digit to be dropped is less than 5, then the preceding digit is left unchanged. e.g., 1.54 is rounded off to 1.5.
- If the digit to be dropped is greater than 5, then the preceding digit is raised by one. e.g., 2.49 is rounded off to 2.5.
- If the digit to be dropped is 5 followed by digit other than zero, then the preceding digit is raised by one. e.g., 3.55 is rounded off to 3.6.
- If the digit to be dropped is 5 or 5 followed by zeros, then the preceding digit is raised by one, if it is odd and left unchanged if it is even. e.g., 3.750 is rounded off to 3.8 and 4.650 is rounded off to 4.6.
Error
The lack in accuracy in the measurement due to the limit of accuracy of the instrument or due to any other cause is called an error.
1. Absolute Error
The difference between the true value and the measured value of a quantity is called absolute error.
If a1 , a2, a3 ,…, an are the measured values of any quantity a in an experiment performed n times, then the arithmetic mean of these values is called the true value (am) of the quantity.
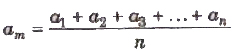
The absolute error in measured values is given by
Δa1 = am – a1
Δa2 = am – a1
………….
Δam = Δam – Δan
2. Mean Absolute Error
The arithmetic mean of the magnitude of absolute errors in all the measurement is called mean absolute error.
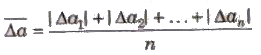
3. Relative Error The ratio of mean absolute error to the true value is called relative

4. Percentage Error The relative error expressed in percentage is called percentage error.

Propagation of Error
(i) Error in Addition or Subtraction Let x = a + b or x = a – b
If the measured values of two quantities a and b are (a ± Δa and (b ± Δb), then maximum absolute error in their addition or subtraction.
Δx = ±(Δa + Δb)
(ii) Error in Multiplication or Division Let x = a x b or x = (a/b).
If the measured values of a and b are (a ± Δa) and (b ± Δb), then maximum relative error

Class 11 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 11 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 11 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 11 can also check Class 11 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 11th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 11 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 11 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 11 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 11 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 11 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 11 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 11. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 11.
CBSE Notes for Class 11 Physics Notes Biology Notes Maths Notes Chemistry Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

