Class 12 Business Studies Directing – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Business Studies Directing. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Business Studies study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 12 Business Studies for topic Directing.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Business Studies
- Topic: Directing
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Business Studies Directing
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Business Studies Directing.
Points to Remember
1. Directing Directing function of management is concerned with instructing, guiding, inspiring and motivating the employees in the organisation so that their efforts result in achievement of organisational goal.
According to Ernest Dale, “Directing is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the best of their ability.”
2. Characteristics of Directing
- It initiates action.
- Continuing function.
- It takes place at every level.
- It flow from top to bottom.
- It is performance oriented.
- It is human element.
3. Importance of Directing
- To initiate action
- To integrate employees efforts
- Means of motivation
- Balance in the organisation
- To facilitate change
4. Principles of Directing
- Maximum individual contribution
- Harmony of objectives
- Unity of command
- Appropriate technique
- Managerial communication
- Strategic use of informal organisation(vii) Effective leadership
- Follow through
5. Elements of Staffing There are four main elements of directing
- Supervision
- Motivation
- Leadership
- Communication

6. Supervision The supervision means instructing, guiding, monitoring and observing the employees while they are performing jobs in the organisation.
(i) Role of Supervisor
(a) Role of mediator or linking pin
(b) Role of a guide
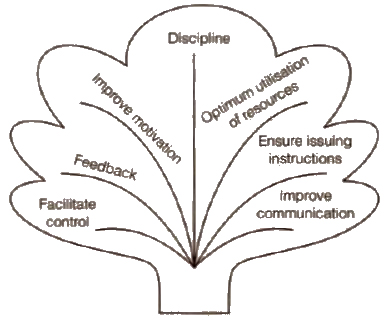
7. Importance of a Supervision
8. Motivation Motivation can be defined as stimulating, inspiring and inducing the employees to perform to their best capacity. Motivation is a psychological term which means it can not be forced on employees.
9. Interrelated Teams of Motivation
- Motive
- Motivation
- Motivator
10. Characteristics of Motivation
- Motivation is a psychological phenomenon.
- Motivation produces goal directed behaviour.
- Motivators can be positive as well as negative.
- Motivation is a complex process.
- Motivation is a dynamic and continuous process.
11. Process of Motivation
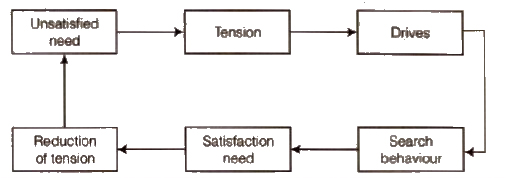
- Unsatisfied need
- Tension
- Drive
- Search behaviour
- Satisfaction need
- Reduction of tension
12. Importance of Motivation
- Motivation helps change negative attitude to positive attitude.
- Motivation improve performance level of employees.
- Helps in achieving the organisational goal.
- Motivation creates supportive work environment.
- Motivation help the managers to introduce changes.
- Reduction in employees turnover.
13. Need Hierarchy
Theory or Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory Need or the desire is a very important elements in motivation because the employees get motivated only for their needs.
Maslow has given a sequence or hierarchy of needs in the follows way
(i) Physiological needs
(ii) Safety and security needs
(iii) Social or belonging needs
(iv) Esteem needs
(v) Self-actualisation needs
14. Assumptions of Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
(i) Behaviour of people depends upon their need. Human behaviour can be changed or motivated by fulfilling their needs.
(ii) Generally the needs follow the hierarchy i.e ., starting from physiological need.15. Financial and Non-Financial Incentives Incentive means all measures which are used to motivate people to improve performance. These incentives may be broadly classified
(i) Financial Incentives The reward or incentive which can be calculated in terms of money is known as monetary incentive.
The common monetary incentives are
(a) Pay and allowances
(b) Profit sharing
(c) Co-Partnership/stock option
(d) Bonus
(e) Commission
(f) Suggestion system
(g) Productivity linked with wage incentives
(b) Retirement benefits
(i) Perks/Fringe benefits/perquisites
(ii) Non-Financial Incentives The incentives which can not be calculated in terms of money are known as non-financial incentives.
The common non-financial incentives are
(a) Status
(b) Organisational climate
(c) Career advancement
(d) Job enrichment
(e) Employees recognition
(f) Job security
(g) Employee’s participation
(h) Autonomy/Employee empowerment
16. Leadership It is a process of influencing the behaviour of people at work towards the achievement of specified goal.
(i) Features of Leadership
(a) It indicates the ability of an individual to influence others.
(b) It tries to bring change in behaviour.
(c) It shows interpersonal relationship between leader and followers.
(d) It is to achieve common goal.
(e) It is a continuous process.17. Different Styles of Leadership
(i) Autocratic or Authoritative Leadership
17. Different Styles of Leadership
(i) Autocratic or Authoritative Leadership
(ii) Democratic or Participative Leadership

(iii) Free-rein or Laissez-Faire Leadership

18. Importance of Leadership
(i) Helps in inspiring and guiding the employees.
(ii) Secures co-operation of the members of organisation.
(iii) Creates confidence.
(iv) Improves productivity.
(v) Improves job satisfaction.
(vi) Improves team-spiritor group cohesion.
19. Qualities of a Good Leader
(i) Physical qualities
(ii) Knowledge, intelligence and scholarship
(iii) Integrity and honesty
(iv) Self confidence and sense of responsibility
(v) Initiative
(vi) Communication skill
(vii) Decisiveness
(viii) Social skill
20. Communication It can be defined as transmission or exchange of ideas, views message information or instruction between two or more persons by different means.
21. Communication Process

22. Importance of Communication
- Act as basis of co-ordination and co-operation
- Act as basis for decision making
- Increase managerial efficiency
- Establish effective leadership
- Helps in process of motivation and morale development
- Helps in smooth working of an enterprise
- Promoter co-operation and peace
23. Form of Organisational Communication
(i) Formal Communication It refers to official communication taking place in the organisation. According to direction of flow, formal communication can be divided into four types
(a) Downward communication
(b) Upward communication
(c) Horizontal communication
(d) Diagonal communication
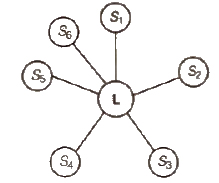
Common Networks of formal communication are
(a) Wheel pattern
(b) Chain pattern
(c) Circle pattern
(d) Channel or free flow pattern
(e) Inverted’V’
(ii) Informal Communication Informal communication between different members of organisation who are not officially attached to each other is known as Informal communication.
Common networks of informal communication are
(a) Gossip
(b) Clusters
(c) Single strand
(d) probability
24. Methods of Communication
- Oral communication
- Written communication
25. Barriers to Effective Communication
(i) Semantic Barrier
(a) Badly expressed message
(b) Symbols with different meanings
(c) Faulty translation
(d) Unclarified assumption
(e) Technical jargon
(f) Body language
(ii) Psychological Barrier
(a) Premature evaluation
(b) Lack of attention
(c) Loss by poor retention
(d) Distrust
(iii) Organisational Barrier
(a) Organisational policy
(b) Rules and regulations
(c) Status difference
(d) Complex organisation
(iv) Personal Barriers
(a) Lack of confidence
(b) Lack of incentives
(c) Fear of authority
26. Improving Effective Communication
- Clarify the idea
- Consult others
- Use of proper language
- Proper feedback
- Communication for present as well as for future
- Follow up
- Good listener
- Open mind
- Completeness of message
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Business Studies Notes Maths Notes Economics Notes Sociology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


