Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Chemical Kinetics. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic Chemical Kinetics.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: Chemical Kinetics
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics.
The branch of chemistry, which deals with the rate of chemical reactions. the factors affecting the rate of reactions and the mechanism of the reaction. is called chemical kinetics.
Chemical Reactions on the Basis of Rate of Reaction
- Fast/instantaneous reactions Chemical reaction which completes in less than Ips (10-12 s) time, IS known as fast reaction. It IS practically impossible to measure the speed of such reactions, e.g., ionic reactions. organic substitution reactions.
- Slow reactions Chemical reactions which completes in a long time from some minutes to some years are called slow reactions. e.g., rusting of iron. transformation of diamond etc.
- Moderately slow reactions Chemical reactions which are intermediate between slow and fast reactions are called moderately slow reactions.
Rate of Reaction
Rate of a chemical reaction IS the change in the concentration of any one of the reactants or products per unit time. It is expressed in mol L-1 s-1 or Ms-1 or atm time-1 units.
Rate of reaction
= (decrease/increase in the concentration of reactant/product/time taken)
This rate of reaction is known as average rate of reaction (rav).(rav can be calculated by dividing the concentration difference by the time interval).
For a chemical reaction,

Instantaneous Rate of Reaction
Rate of a chemical reaction at a particular moment of time, is known as the instantaneous rate of reaction.
For reaction,

Methods for measuring reaction rate (i) pH measurement, (ii) change in optical activity, (iii) change in pressure, (iv) change in conductance.
Slowest step of a reaction was called rate determining step by van’t Hoff.
Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction
- Nature and concentration of reactant
- Temperature
- Surface area of reactant
- Radiations and catalyst
- Pressure of gas
Rate Law Expressions
According to the law of mass action,
For a chemical reaction,
aA + bB → Products
Rate α [A]a [B]b = k[A]a [B]b
But experimentally, it is observed that the rate of reaction is found to depend upon ‘α’ concentration terms of A and ‘β’ concentration terms of B Then,
Rate α [A]α [B]β = k[A]α [B]β
where, [A] and [B] molar concentrations of A and B respectively and k is the velocity constant or rate constant. The above expression is known as rate law.
Rate Constant
In the above expression, k is called rate constant or velocity constant.
Rate constant may be defined as the specific rate of reaction when the molar concentrations of the reactants is taken to be unity, i.e.,
Rate = k, if [A] = [B] = 1
Units of rate constant or specific reaction rate for a nth order reaction is given as
K = (1/Time) x (1/[Conc.]n – 1)
Characteristics of rate constant
- Greater the value of rate constant, faster is the reaction.
- Each reaction has a particular value of rate constant at a particular temperature.
- The value of rate constant for the same reaction changes with temperature.
- The value of rate constant for a reaction does’t depend upon the concentration of the reactants.

Integrated Rate Equation for Zero Order Reactions

Integrated Rate Equation for First Order Reactions

Half-life period (t1/2) : It is concentration independent term.
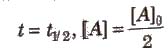

For first order chemical reactions,

(Vo, Vt, and ∞ are the volumes of NaOH solution used for the titration of same volume of the reaction mixture after times 0, t and ∞ respectively.)
Pseudo First Order Reaction
Chemical reactions which appear to be of higher order but actually are of the lower order are called pseudo order reactions. In case of pseudo first order reaction, chemical reaction between two sr” stances takes place and one of the reactant is present in execess. e.g., hydrolysis of ester.
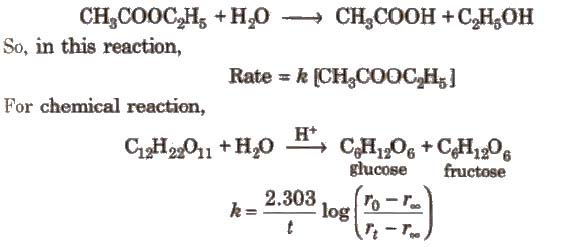
[rO rt, and r∞.. are the polarimetric readings at t = 0, t and ∞, respectively.]
Methods to Determine Order of Reaction
(i) Graphical method

(ii) Initial rate method In this method, the order of a reaction is determined by varying the concentration of one of the
reactants while others are kept constant.
(iii) Integrated rate law method In this method out different integrated rate equation which gives the most constant value for the rate constant corresponds to a specific order of reaction.
(iv) Half-life period (t1/2) method In general half-life period (t1/2) of a reaction of nth order is related to initial concentration of the reactant as

This method is employed only when the rate law involved only one concentration term.
(v) Ostwald’s isolation method This method is employed in determining the order of complicated reactions by isolating one
of the reactants so far as its influence on the reaction rate is concerned.
Temperature Dependence of Rate of a Reaction
For every 10°C rise in temperature, the rate of reaction becomes double, but only 16% collisions increases. It can be explained by Arrhenius equation.
Temperature coefficient is the ratio of rate constant of a reaction at two temperature differing by 10. Temperature selected are usually 298 K and 308 K
Temperature coefficient = ℜt + 10/ℜt ≈ 2 to 3
Arrhenius Equation
Arrhenius equation is a mathematical expression to give a quantitative relationship between rate constant and temperature, and the expression is
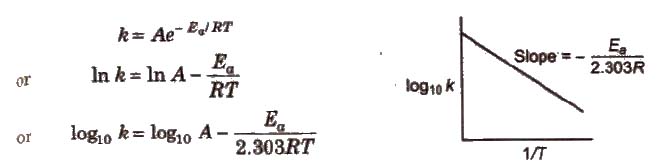
where, A = frequency or Arrhenius factor. It is also called pre-exponential factor
R = gas constant
Ea = activation energy
Activated complex (or transition state)
Activated complex is the highest energy unstable intermediate between the reactants and products and gets decomposed immediately (having very short life), to give the products. In this state, bonds of reactant are not completely broken while the bonds of products are not completely formed.

Threshold energy (ET) The minimum amount of energy which the reactant must possess in order to convert into products is known as threshold energy.
Activation energy (Ea) The additional amount of energy, required by the reactant so that their energy becomes equal to the threshold value is known as activation energy.
⇒ Ea = ET – ER
Lower the activation energy, faster is the reaction.
Different reactions have different rates because their activation energies are different.
Larger the value of Eo, smaller the value of rate constant and greater is the effect of a given temperature rise on K
Important points about Arrhenius equation
(i) If ℜ2 and ℜ1 are rate constant at temperature T2 and T1; then
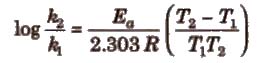
.
ii) Fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy is called Boltzmann factor and is given by
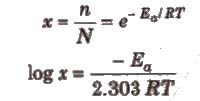
(iii) Ea is constant for a particular reaction.
(iv) Ea does’t depend on temperature, volume, pressure, etc., but gets affected by catalyst.
In the Arrhenius equation, when T → ∞ then ℜ = Ae° = A when Ea = 0,k = A and the rate of reaction becomes independent temperature.
Role of Catalyst in a Chemical Reaction
A catalyst is a chemical substance which alters the rate of a reaction WIthout itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
In the chemical reactions, catalyst provides an alternate pathway or reaction mechanism by reducing the activation energy between reactants and products and hence. lowering the potential energy barrier as shown.

In the presence of catalyst, activation energy decreases and hence.

where, P denotes presence of catalyst and a denotes absence of catalyst.
Theory of Reaction Rates
Collision Theory
According to this theory, the reactant molecules are assumed to be hard spheres and the reaction is postulated to occur, when molecules collide with each other.
The number of collisions between the reacting molecules taking place per second per unit volume is known as collision frequency (ZAB)·
But only those collisions in which the colliding species are associated with certain minimum amount of energy and collide in proper orientation result in the product formation, such collisions are called fruitful collisions or effective collision.
Here, rate = – (dv/dt) = collision frequency x fraction of effective collision
= ZAB x f = ZAB x e-Ea/RT
where, ZAB represents the collision frequency of reactants, A and B e-Ea/RT represents the fraction of molecules with energies equal to or greater than Ea.
So, to account for effective collisions, another factor, P called the probability or steric factor is introduced.
So, rate = PZABe-Ea/RT
The Activated Complex Theory or Transition State Theory
Reactants ⇔ Activated complex → Products
This theory is based on the fact that bond cleavage and bond formation, involved in a chemical reaction, must occur simultaneously. Hence, the reactants are not converted directly into the products. There is an energy barrier or activated complex [intermediate product with partially formed bond] between the reactants and products. The reactants must cross this energy barrier before converting into products. The height of the barrier determines the threshold energy.
Photochemical Reactions
Chemical reactions, that occur on exposure to visible radiation are called photochemical reactions.
- The rate of a photochemical reactions is affected by the the intensity of light.
- Temperature has little effect on photochemical reactions.
Quantum yield or quantum efficiency of a photochemical reaction,
φ = (number of reactant molecules reacting in a given time / number of photons (quanta) of light absorbed ill the same time)
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


