Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Unit 6 Thermodynamics
NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 is for Thermodynamics. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
- Thermodynamics is not concerned about______.
(i) energy changes involved in a chemical reaction.
(ii) the extent to which a chemical reaction proceeds.
(iii) the rate at which a reaction proceeds.
(iv) the feasibility of a chemical reaction. - Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) The presence of reacting species in a covered beaker is an example of open system.
(ii) There is an exchange of energy as well as matter between the system and the surroundings in a closed
system.
(iii) The presence of reactants in a closed vessel made up of copper is an example of a closed system.
(iv) The presence of reactants in a thermos flask or any other closed insulated vessel is an example of a closed system. - The state of a gas can be described by quoting the relationship between___.
(i) pressure, volume, temperature
(ii) temperature, amount, pressure
(iii) amount, volume, temperature
(iv) pressure, volume, temperature, amount - The volume of gas is reduced to half from its original volume. The specific heat will be ______.
(i) reduce to half
(ii) be doubled
(iii) remain constant
(iv) increase four times - During complete combustion of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of heat is released.
The thermochemical reaction for above change is
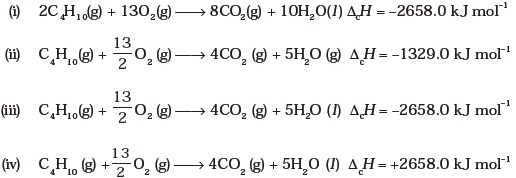
- ΔfU⊖ of formation of CH4(g) at certain temperature is –393 kJ mol–1. The value of ΔfH⊖ is
(i) zero
(ii) < ΔfU⊖
(iii) > ΔfU⊖
(iv) equal to Δf U⊖ - In an adiabatic process, no transfer of heat takes place between system and surroundings. Choose the correct option for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition from the following.
(i) q = 0, ΔT ≠ 0, w = 0
(ii) q ≠ 0, ΔT = 0, w = 0
(iii) q = 0, ΔT = 0, w = 0
(iv) q = 0, ΔT < 0, w ≠ 0 
(i) w (reversible) = w (irreversible)
(ii) w (reversible) < w (irreversible)
(iii) w (reversible) > w (irreversible)
(iv) w (reversible) = w (irreversible) + pex.ΔV- The entropy change can be calculated by using the expression ΔS = (qrev/T).
When water freezes in a glass beaker, choose the correct statement amongst the following :
(i) ΔS (system) decreases but ΔS (surroundings) remains the same.
(ii) ΔS (system) increases but ΔS (surroundings) decreases.
(iii) ΔS (system) decreases but ΔS (surroundings) increases.
(iv) ΔS (system) decreases and ΔS (surroundings) also decreases. - On the basis of thermochemical equations (a), (b) and (c), find out which of the algebric relationships given in options (i) to (iv) is correct.
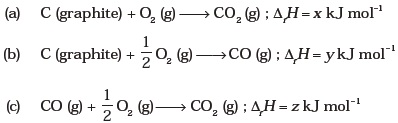
(i) z = x + y
(ii) x = y – z
(iii) x = y + z
(iv) y = 2z – x - Consider the reactions given below. On the basis of these reactions find out which of the algebric relations given in options (i) to (iv) is correct?
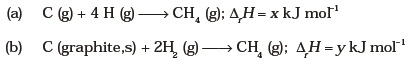
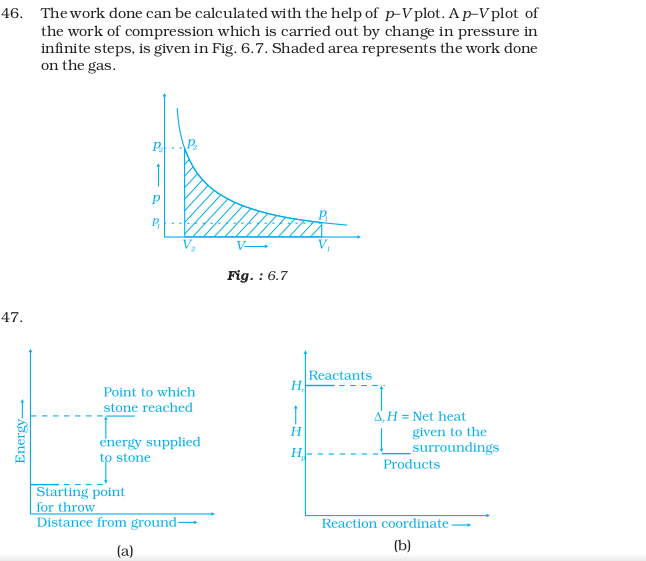
(i) x = y
(ii) x = 2y
(iii) x > y
(iv) x < y - The enthalpies of elements in their standard states are taken as zero. The enthalpy of formation of a compound
(i) is always negative
(ii) is always positive
(iii) may be positive or negative
(iv) is never negative - Enthalpy of sublimation of a substance is equal to
(i) enthalpy of fusion + enthalpy of vapourisation
(ii) enthalpy of fusion
(iii) enthalpy of vapourisation
(iv) twice the enthalpy of vapourisation - Which of the following is not correct?
(i) ΔG is zero for a reversible reaction
(ii) ΔG is positive for a spontaneous reaction
(iii) ΔG is negative for a spontaneous reaction
(iv) ΔG is positive for a non-spontaneous reaction
Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
- Thermodynamics mainly deals with
(i) interrelation of various forms of energy and their transformation from one form to another.
(ii) energy changes in the processes which depend only on initial and final states of the microscopic systems
containing a few molecules.
(iii) how and at what rate these energy transformations are carried out.
(iv) the system in equilibrium state or moving from one equilibrium state to another equilibrium state. - In an exothermic reaction, heat is evolved, and system loses heat to the surrounding. For such system
(i) qp will be negative
(ii) Δr H will be negative
(iii) qp will be positive
(iv) Δr H will be positive - The spontaneity means, having the potential to proceed without the assistance of external agency. The processes which occur spontaneously are
(i) flow of heat from colder to warmer body.
(ii) gas in a container contracting into one corner.
(iii) gas expanding to fill the available volume.
(iv) burning carbon in oxygen to give carbon dioxide. - For an ideal gas, the work of reversible expansion under isothermal condition can be calculated by using the expression w = – nRT ln(Vf/Vi)
A sample containing 1.0 mol of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly to ten times of its original volume, in two separate experiments.
The expansion is carried out at 300 K and at 600 K respectively. Choose the correct option.
(i) Work done at 600 K is 20 times the work done at 300 K.
(ii) Work done at 300 K is twice the work done at 600 K.
(iii) Work done at 600 K is twice the work done at 300 K.
(iv) ΔU = 0 in both cases. - Consider the following reaction between zinc and oxygen and choose the correct options out of the options given below :
2 Zn(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ 2 ZnO(s); ΔH = – 693.8 kJ mol–1
(i) The enthalpy of two moles of ZnO is less than the total enthalpy of two moles of Zn and one mole of oxygen by 693.8 kJ.
(ii) The enthalpy of two moles of ZnO is more than the total enthalpy of two moles of Zn and one mole of oxygen by 693.8 kJ.
(iii) 693.8 kJ mol–1 energy is evolved in the reaction.
(iv) 693.8 kJ mol–1 energy is absorbed in the reaction.
Short Answer Type Questions
- 18.0 g of water completely vapourises at 100°C and 1 bar pressure and the enthalpy change in the process is 40.79 kJ mol-1. What will be the enthalpy change for vapourising two moles of water under the same conditions? What is the standard enthalphy of vapourisation for water?
- One mole of acetone requires less heat to vapourise than 1 mol of water. Which of the two liquids has higher enthalpy of vapourisation?
- 22. Standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔfH⊖ is just a special case of enthalpy of reaction, ΔrH⊖. Is the ΔrH⊖ for the following reaction same as ΔfH⊖? Give reason for your answer.
CaO(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s); ΔfH⊖ = –178.3 kJ mol–1 - The value of ΔfH⊖ for NH3 is – 91.8 kJ mol–1. Calculate enthalpy change for the following reaction :
2NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3H2(g) - Enthalpy is an extensive property. In general, if enthalpy of an overall reaction A→B along one route is ΔrH and ΔrH1, ΔrH2, ΔrH3….. represent enthalpies of intermediate reactions leading to product B. What will be the relation between ΔrH for overall reaction and ΔrH1, ΔrH2….. etc. for intermediate reactions.
- The enthalpy of atomisation for the reaction CH4(g)→ C(g) + 4H (g) is 1665 kJ mol–1. What is the bond energy of C–H bond?
- 26. Use the following data to calculate Δlattice H⊖for NaBr.
Δsub H⊖for sodium metal = 108.4 kJ mol–1
Ionization enthalpy of sodium = 496 kJ mol-1
Electron gain enthalpy of bromine = – 325 kJ mol-1
Bond dissociation enthalpy of bromine = 192 kJ mol-1
Δf H⊖ for NaBr (s) = – 360.1 kJ mol-1 - Given that ΔH = 0 for mixing of two gases. Explain whether the diffusion of these gases into each other in a closed container is a spontaneous process or not?
- Heat has randomising influence on a system and temperature is the measure of average chaotic motion of particles in the system. Write the mathematical relation which relates these three parameters.
- Increase in enthalpy of the surroundings is equal to decrease in enthalpy of the system. Will the temperature of system and surroundings be the same when they are in thermal equilibrium?
- At 298 K. Kp for the reaction N2O4(g) ⇔ 2NO 2 (g) is 0.98. Predict whether the reaction is spontaneous or not.
- A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process of expansion and compression as shown in Fig. 6.1. What will be the value of ΔH for the cycle as a whole?
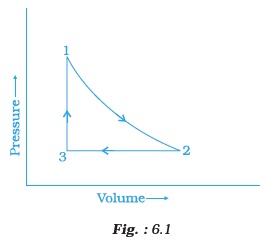
- The standard molar entropy of HO(l) is 70 JK-1 mol-1. Will the standard molar entropy of H2O(s) be more, or less than 70 J K-1 mol-1?
- Identify the state functions and path functions out of the following :
enthalpy, entropy, heat, temperature, work, free energy. - The molar enthalpy of vapourisation of acetone is less than that of water. Why?
- Which quantity out of ΔrG and ΔrG⊖ will be zero at equilibrium?
- Predict the change in internal energy for an isolated system at constant volume.
- Although heat is a path function but heat absorbed by the system under certain specific conditions is independent of path. What are those conditions? Explain.
- Expansion of a gas in vacuum is called free expansion. Calculate the work done and the change in internal energy when 1 litre of ideal gas expands isothermally into vacuum until its total volume is 5 litre?
- Heat capacity (Cp) is an extensive property but specific heat (c) is an intensive property. What will be the relation between Cp and c for 1 mol of water?
- The difference between CP and CV can be derived using the empirical relation H = U + pV. Calculate the difference between CP and CV for 10 moles of an ideal gas.
- If the combustion of 1g of graphite produces 20.7 kJ of heat, what will be molar enthalpy change? Give the significance of sign also.
- The net enthalpy change of a reaction is the amount of energy required to break all the bonds in reactant molecules minus amount of energy required to form all the bonds in the product molecules. What will be the enthalpy change for the following reaction.
H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g)
Given that Bond energy of H2, Br2 and HBr is 435 kJ mol-1 , 192 kJ mol-1 and 368 kJ mol–1 respectively. - The enthalpy of vapourisation of CCl4 is 30.5 kJ mol–1 . Calculate the heat required for the vapourisation of 284 g of CCl4 at constant pressure. (Molar mass of CCl4 = 154 g mol–1).
- The enthalpy of reaction for the reaction :
2H2 (g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) is ΔRH⊖ = – 572 kJ mol–1. What will be standard enthalpy of formation of H2O(l) ? - What will be the work done on an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder, when it is compressed by a constant external pressure, pext in a single step as shown in Fig. 6.2. Explain graphically.

- How will you calculate work done on an ideal gas in a compression, when change in pressure is carried out in infinite steps?
- Represent the potential energy/enthalpy change in the following processes graphically.
(a) Throwing a stone from the ground to roof.
(b) (1/2)H2(g) + (1/2)Cl2(g) ⇔ HCL(g) ΔrH⊖ = –92.32 kJ mol–1 - Enthalpy diagram for a particular reaction is given in Fig. 6.3. Is it possible to decide spontaneity of a reaction from given diagram. Explain.

- 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state (1) to state (2) as shown in Fig. 6.4. Calculate the work done for the expansion of gas from state (1) to state (2) at 298 K.
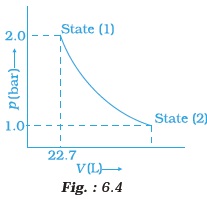
- An ideal gas is allowed to expand against a constant pressure of 2 bar from 10 L to 50 L in one step.
Calculate the amount of work done by the gas. If the same expansion were carried out reversibly, will the work done be higher or lower than the earlier case?
(Given that 1 L bar = 100 J)
Matching Type Questions
In the following questions more than one correlation is possible between options of both columns.
- Match the following :

- Match the following processes with entropy change:

- Match the following parameters with description for spontaneity :

- Match the following :

Assertion and Reason Type Questions
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
- Assertion (A): Combustion of all organic compounds is an exothermic reaction.
Reason (R) : The enthalpies of all elements in their standard state are zero.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A is false but R is true. - Assertion (A) : Spontaneous process is an irreversible process and may be reversed by some external agency.
Reason (R) : Decrease in enthalpy is a contributory factor for spontaneity.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A is false but R is true. - Assertion (A) : A liquid crystallises into a solid and is accompanied by decrease in entropy.
Reason (R) : In crystals, molecules organise in an ordered manner.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A is false but R is true.
Long Answer Type Questions
- Derive the relationship between ΔH and ΔU for an ideal gas. Explain each term involved in the equation.
- Extensive properties depend on the quantity of matter but intensive properties do not. Explain whether the following properties are extensive or intensive.
Mass, internal energy, pressure, heat capacity, molar heat capacity, density, mole fraction, specific heat, temperature and molarity. - The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mole of an ionic compound present in its gaseous state, dissociates into its ions. It is impossible to determine it directly by experiment. Suggest and explain an indirect method to measure lattice enthalpy of NaCl(s).
- ΔG is net energy available to do useful work and is thus a measure of “free energy”. Show mathematically that ΔG is a measure of free energy. Find the unit of ΔG. If a reaction has positive enthalpy change and positive entropy change, under what condition will the reaction be spontaneous?
- Graphically show the total work done in an expansion when the state of an ideal gas is changed reversibly and isothermally from (pi, Vi) to (pF ,VF). With the help of a pV plot compare the work done in the above case with that carried out against a constant external pressure pF.
Click here to download the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Unit 6 Thermodynamics.
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions

Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)


















Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Short Answer Type
Matching Type
Assertion and Reason Type
Long Answer Type
Chemistry Physics Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.