Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 2, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 is for Motion in a Straight Line. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 2. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
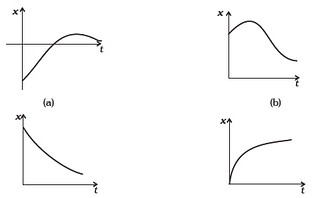
- Among the four graphs (Fig. 3.1), there is only one graph for which average velocity over the time intervel (0, T ) can vanish for a suitably chosen T. Which one is it?
- A lift is coming from 8th floor and is just about to reach 4th floor. Taking ground floor as origin and positive direction upwards for all quantities, which one of the following is correct?
(a) x < 0, v < 0, a > 0
(b) x > 0, v < 0, a < 0
(c) x > 0, v < 0, a > 0
(d) x > 0, v > 0, a < 0 - In one dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v satisfies 0 ≤ v < v0 .
(a) The displacement in time T must always take non-negative values.
(b) The displacement x in time T satisfies – v0T < x < v0T.
(c) The acceleration is always a non-negative number.
(d) The motion has no turning points. - A vehicle travels half the distance L with speed V1and the other half with speed V2, then its average speed is
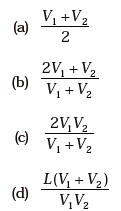
- The displacement of a particle is given by x = (t – 2)2 where x is in metres and t in seconds. The distance covered by the particle in first 4 seconds is
(a) 4 m
(b) 8 m
(c) 12 m
(d) 16 m - At a metro station, a girl walks up a stationary escalator in time t1. If she remains stationary on the escalator, then the escalator take her up in time t2. The time taken by her to walk up on the moving escalator will be
(a) (t1 + t2)/2
(b) t1 t2 /(t2 – t1)
(c) t1t2 /(t2 + t1)
(d) t1 –t2
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- The variation of quantity A with quantity B, plotted in Fig. 3.2 describes the motion of a particle in a straight line.
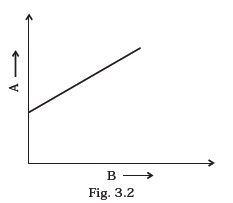
(a) Quantity B may represent time.
(b) Quantity A is velocity if motion is uniform.
(c) Quantity A is displacement if motion is uniform.
(d) Quantity A is velocity if motion is uniformly accelerated. - A graph of x versus t is shown in Fig. 3.3. Choose correct alternatives from below.
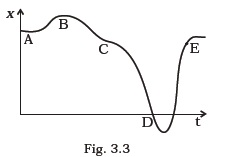
(a) The particle was released from rest at t = 0.
(b) At B, the acceleration a > 0.
(c) At C, the velocity and the acceleration vanish.
(d) Average velocity for the motion between A and D is positive.
(e) The speed at D exceeds that at E. - For the one-dimensional motion, described by x = t–sint
(a) x (t) > 0 for all t > 0.
(b) v (t) > 0 for all t > 0.
(c) a (t) > 0 for all t > 0.
(d) v (t) lies between 0 and 2. - A spring with one end attached to a mass and the other to a rigid support is stretched and released.
(a) Magnitude of acceleration, when just released is maximum.
(b) Magnitude of acceleration, when at equilibrium position, is maximum.
(c) Speed is maximum when mass is at equilibrium position.
(d) Magnitude of displacement is always maximum whenever speed is minimum. - A ball is bouncing elastically with a speed 1 m/s between walls of a railway compartment of size 10 m in a direction perpendicular to walls. The train is moving at a constant velocity of 10 m/s parallel to the direction of motion of the ball. As seen from the ground,
(a) the direction of motion of the ball changes every 10 seconds.
(b) speed of ball changes every 10 seconds.
(c) average speed of ball over any 20 second interval is fixed.
(d) the acceleration of ball is the same as from the train.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Refer to the graphs in Fig 3.1. Match the following.

- A uniformly moving cricket ball is turned back by hitting it with a bat for a very short time interval. Show the variation of its acceleration with time. (Take acceleration in the backward direction as positive).
- Give examples of a one-dimensional motion where
(a) the particle moving along positive x-direction comes to rest periodically and moves forward.
(b) the particle moving along positive x-direction comes to rest periodically and moves backward. - Give example of a motion where x > 0, v < 0, a > 0 at a particular instant.
- An object falling through a fluid is observed to have acceleration given by a = g – bv where g = gravitational acceleration and b is constant. After a long time of release, it is observed to fall with constant speed. What must be the value of constant speed?
Short Answer Type Questions
- A ball is dropped and its displacement vs time graph is as shown Fig. 3.4 (displacement x is from ground and all quantities are +ve upwards).
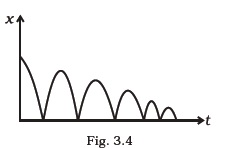
(a) Plot qualitatively velocity vs time graph.
(b) Plot qualitatively acceleration vs time graph. - A particle executes the motion described by x(t) = x0 (1 − e−γt) ; t ≥ 0 , x0 > 0.
(a) Where does the particle start and with what velocity?
(b) Find maximum and minimum values of x (t), v (t), a (t). Show that x (t) and a (t) increase with time and v (t) decreases with time. - A bird is tossing (flying to and fro) between two cars moving towards each other on a straight road. One car has a speed of 18 m/h while the other has the speed of 27km/h. The bird starts moving from first car towards the other and is moving with the speed of 36km/h and when the two cars were separted by 36 km. What is the total distance covered by the bird? What is the total displacement of the bird?
- A man runs across the roof-top of a tall building and jumps horizontally with the hope of landing on the roof of the next building which is of a lower height than the first. If his speed is 9 m/s, the (horizontal) distance between the two buildings is 10 m and the height difference is 9 m, will he be able to land on the next building ? (take g = 10 m/s2 )
- A ball is dropped from a building of height 45 m. Simultaneously another ball is thrown up with a speed 40 m/s. Calculate the relative speed of the balls as a function of time.
- The velocity-displacement graph of a particle is shown in Fig. 3.5.
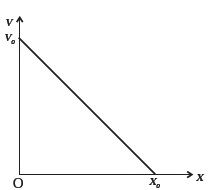
(a) Write the relation between v and x.
(b) Obtain the relation between acceleration and displacement and plot it.
Long Answer Type Questions
- It is a common observation that rain clouds can be at about a kilometre altitude above the ground.
(a) If a rain drop falls from such a height freely under gravity, what will be its speed? Also calculate in km/h. (g = 10m/s2)
(b) A typical rain drop is about 4mm diameter. Momentum is mass x speed in magnitude. Estimate its momentum when it hits ground.
(c) Estimate the time required to flatten the drop.
(d) Rate of change of momentum is force. Estimate how much force such a drop would exert on you.
(e) Estimate the order of magnitude force on umbrella. Typical lateral separation between two rain drops is 5 cm.(Assume that umbrella is circular and has a diameter of 1m and cloth is not pierced through !!) - A motor car moving at a speed of 72km/h can not come to a stop in less than 3.0 s while for a truck this time interval is 5.0 s. On a higway the car is behind the truck both moving at 72km/h. The truck gives a signal that it is going to stop at emergency. At what distance the car should be from the truck so that it does not bump onto (collide with) the truck. Human response time is 0.5s.
(Comment : This is to illustrate why vehicles carry the message on the rear side. “Keep safe Distance”) - A monkey climbs up a slippery pole for 3 seconds and subsequently slips for 3 seconds. Its velocity at time t is given by v(t) = 2t (3-t); 0< t < 3 and v (t)=–(t–3)(6–t) for 3 < t < 6 s in m/s. It repeats this cycle till it reaches the height of 20 m.
(a) At what time is its velocity maximum?
(b) At what time is its average velocity maximum?
(c) At what time is its acceleration maximum in magnitude?
(d) How many cycles (counting fractions) are required to reach the top? - A man is standing on top of a building 100 m high. He throws two balls vertically, one at t = 0 and other after a time interval (less than 2 seconds). The later ball is thrown at a velocity of half the first. The vertical gap between first and second ball is +15 m at t = 2 s. The gap is found to remain constant. Calculate the velocity with which the balls were thrown and the exact time interval between their throw.
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions







Physics Chemistry Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.
