Class 10 Science Light (Reflection and Refraction) – Get here the Notes for Class 10 Science Light (Reflection and Refraction). Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 10 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 10 Science study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will help you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 10 Science for topic Light (Reflection and Refraction).
- Class: 10th
- Subject: Science
- Topic: Light (Reflection and Refraction)
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 10 Science Light (Reflection and Refraction)
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 10 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for CBSE Class 10 Science Light (Reflection and Refraction) from this article.
1. Ray of Light : A line drawn in the direction of propagation of light is called a ray of light.
2. Beam of Light : A group of rays of light emitted by a source of light is called a beam of light. A light beam is of three types.
(i) Parallel beam : A group of light rays parallel to each other is known as parallel beam of light. 7.
(ii) Divergent beam : A group of light rays spreading out from a source of light is called divergent beam of light.
(iii) Convergent beam : A group of light rays meeting at a point is called convergent beam 8. of light.
3. Reflection of Light : There are some surfaces which have ability to send the light back in the same medium when light strikes it. This 9. phenomena of sending the light back in the same medium by a surface is called reflection of light.
(i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in a same plane.
(ii) The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, ∠i = ∠r.
4. Image : When light rays meet or appear to meet after reflection from a mirror,then it is called an image.
1. Real Image : It is a kind of image which is formed by actual intersection of light rays after reflection.
2. Virtual Image : It is a kind of image which is formed by producing the reflected rays backward after reflection.
5. Plane Mirror : Plane mirror is a piece of glass whose one side is polished by using silver paint, which is covered by a coating of red paint to protect the silver layer.
6. Spherical Mirrors : It is part of hollow glass sphere whose one surface is polished.
There are two types of spherical mirror.
(i) Concave Mirror : It is a spherical mirror whose outer surface is polished and inner or concave side is reflecting surface.
(ii) Convex Mirror : It is a spherical mirror whose inner is polished and outer side or convex side is the reflecting surface.
Principal Focus :
A point on the principal axis of a spherical mirror where the rays of light parallel to the principal axis meet or appear to meet after reflection from the mirror.
Focal Length :
The distance between the pole (P) and principal focus(F) of a spherical mirror is called the focal length of the mirror. It is denoted by f.
Uses of Concave Mirror :
(i) It is used as a shaving mirror because when it is placed close to the face, it forms a large image.
(ii) It is used in solar heating devices like solar cooker, because it converges Sun’s rays over a small area to produce high temperature.
(iii) It is used for security checking purposes.
10. Uses of Convex Mirror :
(i) It is used as rear view mirror in automobiles because it gives erect image as well as diminished due to which Pt has wider field of view.
(ii) It is also used in street lights.
11. Mirror Formula :
It is a relation between distance of object, distance ofimage from the pole ofthe mirror and it’s focal length, i.e., relation between ‘u’, ‘v and It is given by
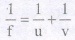
12. Magnification : It is defined as the ratio of height of image to the height of the object. It is denoted by letter m.

13. Refraction of Light : The bending of ray of light when it passes from one medium to another is called refraction of light.
Laws of Refraction :
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
(ii) When a ray of light undergoes refraction then the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is constant.
14. The Refractive Index : The refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium is given by the ratio of the speed of light in medium 1 and the speed of light in medium 2. This is usually represented by the symbol n21. This can be expressed in an equation form as

15. Refraction by spherical lenses : Lens is a transparent medium which is formed by joining two pieces of spherical glass. There are two types of lenses.
(i) Convex Lens : It is a lens which is thicker at the centre and thinner at the edges.
(ii) Concave Lens : It is a lens which is thinner at the centre and thicker at the edges.
16. Terms related to a lens
Optical Centre of Lens : It is the centre of the lens through which light can pass without any deviation.
Principal Axis : It is the line passing through optical centre and is perpendicular to the line joining its edges.
Principal Focus : It is a point on the principal axis where all light rays which are parallel to principal axis either converge or appear to diverge from, after refraction.
17. Lens formula :
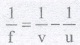
18. Magnification : Magnification, m = h2/h1
Ratio of height of image to the height of object.
It is also given by v/u i.e., Ratio of distance of image to the distance of object.
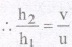
19. Power of a lens : A beam of light parallel to principal axis either gets converged or diverged after refraction by a lens. Some lenses converge the beam of light to a small extent and some lenses converge it to a large extent. This ability of lens to converge or diverge a beam of light is known as the power of lens.
Si unit of power of lens is dioptre : One dioptre is the power of a lens whose focal length is 1 m.
Power of a combination of two or more lenses :
If two or more lenses are placed together to form a combined lens then the power of this combined lens is equal to the sum of the powers of individual lenses.
P = P1 + P2 + P3 + ……
Class 10 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 10 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
| Class 10 Maths | कक्षा 10 गणित |
| Class 10 Science | कक्षा 10 विज्ञान |
| Class 10 Social Science | कक्षा 10 सामाजिक विज्ञान |
| Class 10 English |
Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 10 can also check Class 10 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 10th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 10 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 10 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 10 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 10 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 10 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 10 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 10. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 10.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Maths Notes Social Science Notes English Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

