Class 9 Maths Statistics – Get here the Notes for Class 9 Statistics. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 9 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 9 Maths study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 9 Maths for topic Statistics.
- Class: 9th
- Subject: Maths
- Topic: Statistics
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 9 Maths Statistics
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 9 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 9 Maths Statistics from this article.
BASIC TERMS
Primary data : Data which collected for the first time by the statistical investigator or with the help of his workers is called primary data.
Secondary data : These are the data already collected by a person or a society and these may be in published or unpublished form. These data should be carefully used.
PRESENTATION OF DATA
Raw data : When the data is compiled in the same form and order in which it is collected, it is known as Raw data.
The difference of the highest and the lowest values in the data is called the range of the data.
Frequency : It is a number, which tells that how many times does a particular data appear in a given set of data.
Frequency Distribution :
A tabular arrangement of data showing their corresponding frequencies is called a frequency distribution. The table showing data with their corresponding frequencies is called a frequency table.
Grouped Frequency Distribution :
Consider an example : 100 plants each were planted in 100 schools during Van Mahotsava. After one month, the number of plants that survived were recorded as :
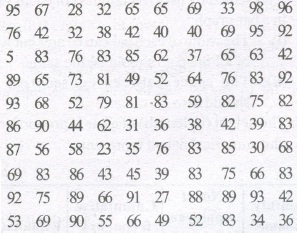
To present such a large *amount of data so that a reader can make sense of it easily, we condense it into groups like 20-29, 30-39, . . 90-99
The data above can be condensed in tabular form as follows:
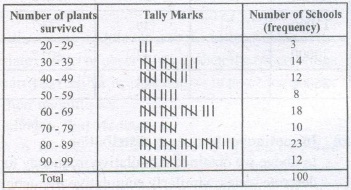
This is called a grouped frequency distribution table.
In each of these classes, the least number is called the lower class limit and the greatest number is called the upper class limit, e.g., in 20-29, 20 is the `lower class limit’ and 29 is the `upper class limit’.
Classes (Class -intervals) : We have groups like 20 – 29, 30 – 39, 90 – 99 in above given example.
Class Mark : The mid-point of a class is called the class mark of the class.
Thus,

Descrete frequency distribution :
When number of terms is large and variate are descrete, variate can accept some particular values only under finite limits and is repeated then it is called descrete frequency distribution.
(iii) Continuous frequency distribution :
When number of terms is large and variate is continuous, i.e., variate can accept all values under finite limits and they are repeated then it is called continuous frequency distribution.
CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY
(a) In descrete frequency distribution :
We add all previous frequencies and get cumulative frequency. It will be more clear from the following table :
| Monthlyincomevariate (x) | No. ofemployeefrequency(t) | Cumulativefrequency(c.f) | Explanation |
| 5000 | 10 | 10 | 10±10 |
| 6000 | 7 | 18 | 10+8 |
| 8000 | 5 | 23 | 18+5 |
| 11000 | 7 | 30 | 23+7 |
| 20000 | 2 | 32 | 30+2 |
| 26000 | 1 | 33 | 32+1 |
(b) In continuous frequency distribution :
In above we obtained cumulative frequency for descrete series. Similarly cumulative frequency table can be made from continuous frequency distribution also. For example, for table
| Class | Frequency | Cumulativefrequency (c.f) |
| 0-5 | 82 | 82 |
| 5-10 | 92 | 82+92=174 |
| 10-15 | 53 | 174+53=227 |
| 15-20 | 27 | 227+27=254 |
Here we see that number of students whose age is less than 5 is 82, number of students whose age is less than 10 is 174, number of students whose age is less than 15 is 227 and number of students whose age is less than 20 is 254. Above table can also be written as follows :
| Class | Cumulative frequency (c.f) |
| Less than 5 | 82 |
| Less than 10 | 174 |
| Less than 15 | 227 |
| Less than 20 | 254 |
From this table the number of students of age less than the upper limit of a class, i.e. number of student whose age is less than 5, 10, 15, 20 years – can determined by merely seeing the table but if we need the number students whose age is more than zero, more than 5, more than 10 or more than 15, then table should be constructed as follows :
| Frequency Distribution, | Cumulatiw FrequencyDistrib ution | ||
| Class | Frequency | Age | Cumulativefrequency(c.f) |
| 0-5 | 82 | 0 and more | 254 |
| 5-10 | 92 | 5 and more | 254 — 82=172 |
| 10-15 | 53 | 10 and more | 172 — 92=80 |
| 15-20 | 27 | 15 and more | 80 — 53=27 |
Note : The cumulative frequency of the last class is the total number of frequencies or the total number of observations in the data in the raw form.
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA
The representation of data through diagrams helps us to visualize the Whole meaning of a numerical distribution at a single glance. There are various methods of representing the data by means of graphs.
(A) Bar graphs
(B) Histograms of uniform width, and of varying widths
(C) Frequency polygons
(1) Bar graph : It is the simplest and most widely used graph in which the numerical data is represented by bars (rectangles) of equal width. . In a bar graph :
(i) The width of each bar can be any, but widths of all the bars should be the same.
(ii) The space between consecutive bars should also be same.
The height (or length) of a bar is proportional to the numerical data it represents.
(2) Histogram : A histogram is a graphical representation of a frequency distribution in the form of rectangles one after the other.
The bases of these rectangles represent the magnitudes of the variables of the class boundaries. So these are taken along the x-axis.
The heights of these represent the frequencies of the corresponding magnitudes of the variable of the class-boundaries.
(3) Frequency polygon : After drawing the histogram of a frequency distribution, when the mid-points of the respective tops of the rectangles are joined by the line segment, the figure so obtained is known as frequency polygon.
The mid-point of the top of the first rectangle is joined to the mid-point of the earlier interval (imagined) on the x-axis. Similarly the mid-point of the top of the last rectangle is joined to the mid-point of the next interval (imagined) on the x-axis.
Note : If both histogram and frequency polygon are to be drawn, then it is advisable first to draw histogram and then join the mid-points of the tops of the rectangles of the histogram to get frequency polygon.
But if only frequency polygon is to be drawn then first represent the class marks along x-axis and frequencies along y-axis and then plot the point corresponding to the frequency at each class mark.
Note : Frequency polygons can also be drawn independently without drawing histograms. For this, we require the mid-points of the class-intervals used in the data.
These mid-points of the class-intervals are called class-marks.
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY (AVERAGES)
There are three main averages :
(1) Mean
(2) Median
(3) Mode
Mean: The mean (or average) of a number of observations is the sum of the values of all the observations divided by the total number of observations.
It is denoted by the symbol x as a’x bar’.

In general, for n observal as
For an grouped frequency distribution,
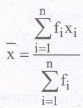
where fi is the frequency corresponding to the observation xi.
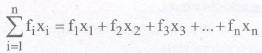
Note :.
MEDIAN:
The median is that value of the given number of observations, which divides it into exactly two parts.
Median is the middle most or the central value of the variate in a set of observations,when the observations are arranged either in ascending or in descending order
of their magnitudes.
Methods to find Median:
When the data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order the median of ungrouped data is calculated as follows:
When the number of observation (n) is odd, the median is the value of the ((n + 1)/2)th observation.
(ii) When the number of observations (n) is even, the median is the mean of the (n/2)th and the n/2 + 1th observations.
MODE:
The mode is that value ofthe observation which occurs most frequently, i.e., an observation with the maximum frequency is called the mode.
Note: It is not effected by presence of extremely large or small items.
Class 9 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 9 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
| Class 9 Maths | कक्षा 9 गणित |
| Class 9 Science | कक्षा 9 सामाजिक विज्ञान |
| Class 9 English | |
| Class 9 Social Science |
Class 9 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 9 can also check Class 9 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 9th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 9 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 9 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 9 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 9 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 9 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 9 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 9. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 9.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Notes Science Notes Social Science Notes English Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


