AP Intermediate 1st Year History Syllabus 2024 contains all the topics you study in History subject in 11th standard. BIEAP (Andhra Pradesh Board of Intermediate Education) issues the AP Inter 1st Year syllabus for History. You can now download the Andhra Pradesh Board class 11 History syllabus PDF from this page on aglasem to know what to study from AP SCERT textbooks.
AP Intermediate 1st Year History Syllabus 2024
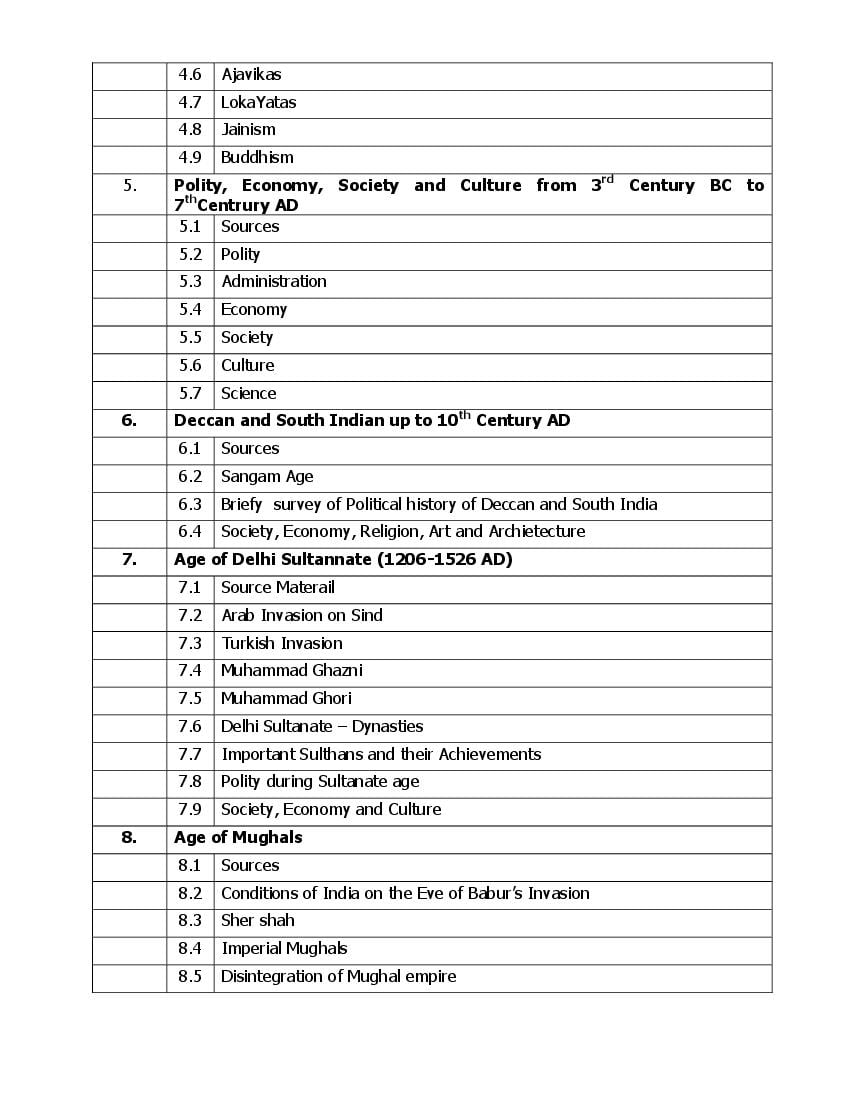
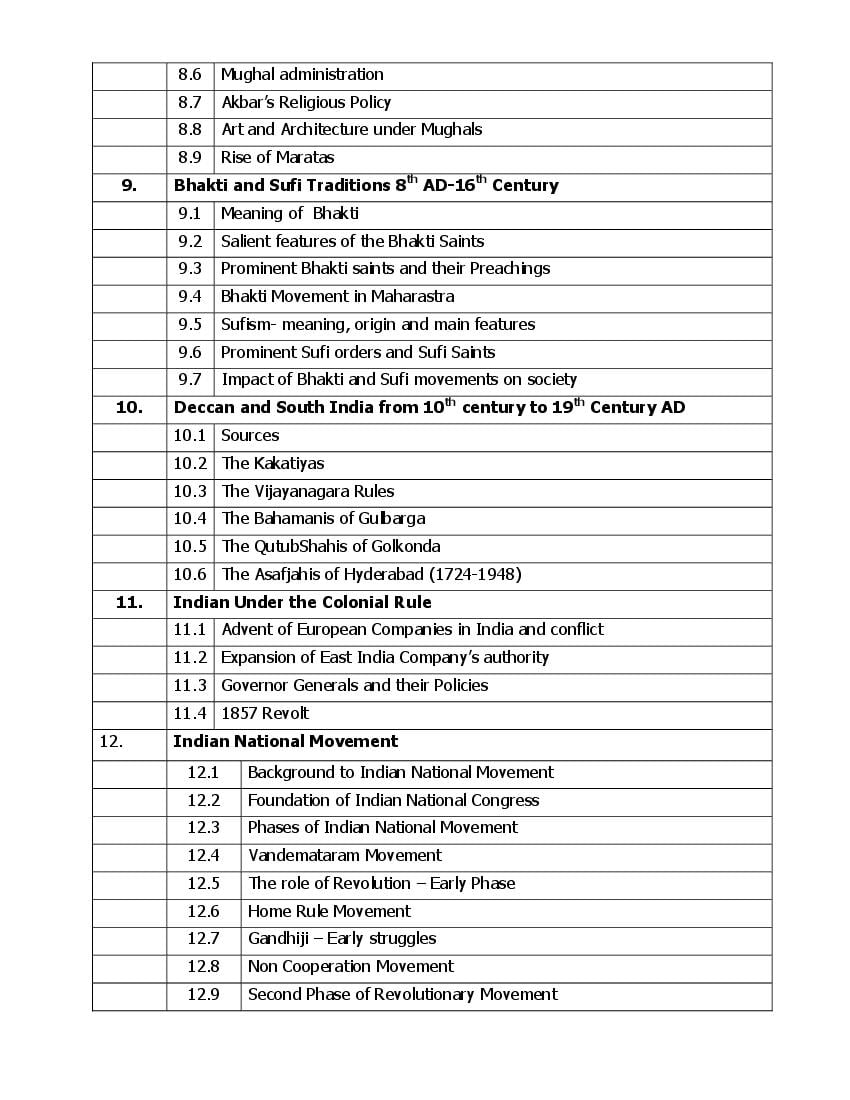
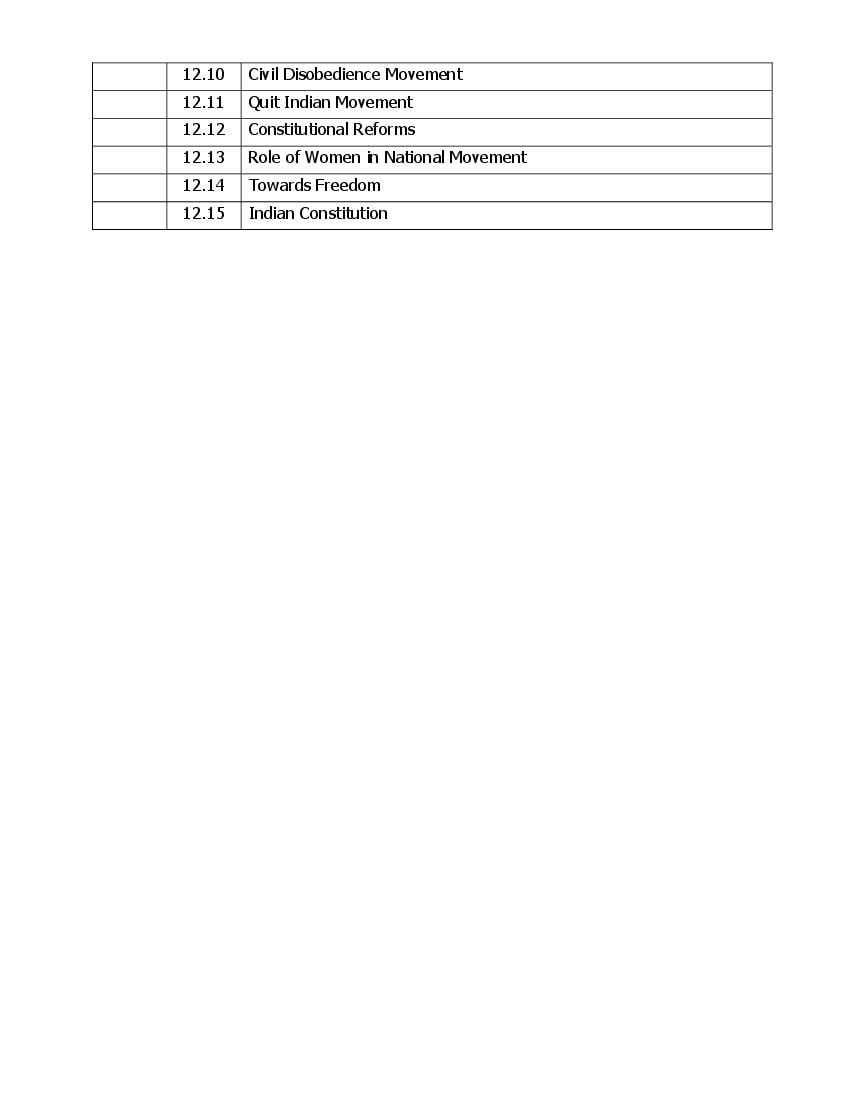
The Andhra Pradesh board syllabus for Inter 1st Year History is as follows.
AP Board Intermediate 1st Year History Syllabus 2024 Download Link – Click Here to Download Syllabus PDF
AP Intermediate 1st Year History Syllabus 2024 PDF
The entire curriculum is as follows.
AP Inter 1st Year Syllabus 2023 History View DownloadAndhra Pradesh Board Inter 1st Year Syllabus 2024
If you want to know the curriculum for any subject besides History, then you can check all subject-wise syllabus for AP Board Class 11 as follows.
- Accountancy
- Botany
- Chemistry
- Civics
- Commerce
- Economics
- English
- Geography
- Hindi
- History
- Maths IA
- Maths IB
- Physics
- Sanskrit
- Telugu
- Urdu
- Zoology
AP Board Syllabus
And besides Intermediate 1st Year History, you can see all class wise syllabus for Andhra Pradesh board here.
Class 11 Exams
Here are some more resources and details for your Intermediate 1st Year exams.
- AP Inter 1st Year Time Table
- AP Inter 1st Year Results
- AP Inter 1st Year Question Papers
- AP Class 11th Model Paper
Andhra Pradesh Board Inter 1st Year History Syllabus 2024 – An Overview
The key information pertaining to this list of topics is as follows.
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| State | Andhra Pradesh |
| Class | Class 11 / Intermediate 1st Year / Inter 1st Year |
| Subject | History |
| Study Material Here | AP Board Syllabus for Class 11 History |
| More Syllabus of This Class | AP Board Syllabus for Class 11 |
| More Syllabus of This Board | AP Board Syllabus |
| Further Information on This Board | Andhra Pradesh Board |
If you have any queries on AP Intermediate 1st Year History Syllabus 2024, then please ask in comments below.
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.