Class 12 Chemistry Solutions – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Solutions. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic Solutions
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: Solutions
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Solutions
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Solutions.
Solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in same or different physical phases. The substances forming the solution are called components of the solution. On the basis of number of components a solution of two components is called binary solution.
Solute and Solvent
In a binary solution, solvent is the component which is present in large quantity while the other component is known as solute.
Classification of Solutions
(A) Following types of solutions are seen on the basis of physical state of solute and solvent.
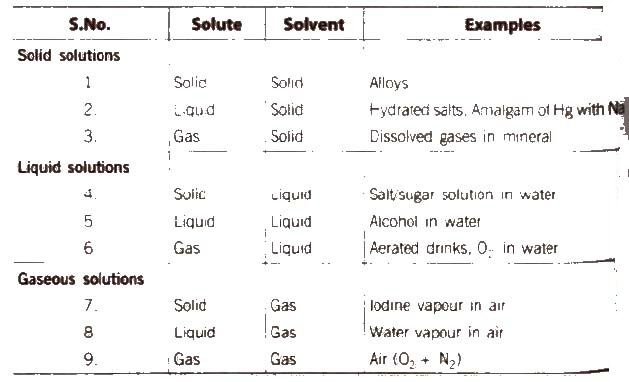
[if water is used as a solvent, the solution is called aqueous solution and if not, the solution is called non-aqueous solution.]
(B) Depending upon the amount of solute dissolved in a solvent we have the following types of solutions:
(i) Unsaturated solution A solution in which more solute can be dissolved without raising temperature is called an unsaturated solution.
(ii) Saturated solution A solution in which no solute can be dissolved further at a given temperature is called a saturated solution.
(iii) Supersaturated solution A solution which contains more solute than that would be necessary to saturate it at a given temperature is called a supersaturated solution.
Solubility
The maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent (generally 100 g) at a given temperature is termed as its solubility at that temperature.
The solubility of a solute in a liquid depends upon the following factors:
(i) Nature of the solute
(ii) Nature of the solvent
(iii) Temperature of the solution
(iv) Pressure (in case of gases)
Henry’s Law
The most commonly used form of Henry’s law states “the partial pressure (P) of the gas in vapour phase is proportional to the mole fraction (x) of the gas in the solution” and is expressed as
p = KH . x
Greater the value of KH, higher the solubility of the gas. The value of KH decreases with increase in the temperature. Thus, aquatic species are more comfortable in cold water [more dissolved O2] rather than Warm water.
Applications
1. In manufacture of soft drinks and soda water, CO2 is passed at high pressure to increase its solubility.
2. To minimise the painful effects (bends) accompanying the decompression of deep sea divers. O2 diluted with less soluble. He gas is used as breathing gas.
3. At high altitudes, the partial pressure of O2 is less then that at the ground level. This leads to low concentrations of O2 in the blood of climbers which causes ‘anoxia’.
Concentration of Solutions
The concentration of a solution is defined as the relative amount of solute present in a solution. On the basis of concentration of solution there are two types of solutions.
(i) Dilute solution
(ii) Concentrated solution
Methods of Expressing Concentration of Solutions
Various expression for the concentrations of solutions can be summarised as
(i) Percentage by weight (w / w %) It is defined as the amount of solute present in 100 g of solution.
w / w % = weight of solute / weight of solution * 100
(ii) Percentage by volume (w / V%) It is defined as the weight 01 solute present in 100 mL of solution.
w / V % = weight of solute / weight of solution * 100
or the volume of solute present in 100 mL of solution.
u / V % = volume of solute / volume of solution * 100
(iii) Mole fraction (x) It is defined as the ratio of the number of moles of a component to the total number of moles of all the components. For a binary solution, if the number of moles of A and B are nA and nB respectively, the mole fraction of A will be

(iv) Parts per million (ppm) It is defined as the parts of a component per million parts (106) of the solution. It is widely used when a solute is present in trace quantities.
ppm = number of parts of the component / total number of parts of all the components * 106
(v) Molarity (M) It is the number of moles of solute present in 1L(dm3) of the solution.
M = number of moles of solute / volume of solution (L)
M = mass of solute (in gram) * 1000 / mol. wt. of solute x volume of solution (in mL)
Molarity varies with temperature due to change in volume of solution.
[When molarity of a solution is 1 M, it is called a molar solution. 0.1 M solution is called a decimolar solution while 0.5 M solution is known as semi molar solution]
Molarity = Percent by mass * density * 10 / molecular weight
Dilution law, M1 V1 = M2 V2 (for dilution from volume V1 to V2)
For reaction between two reactants, M1 V1 / n1 = M2 V2 / n2
where, n1 and n2 arc stoichiometric coefficient in balanced equation.
(vi) Molality (m) It is the number of moles of solute per kilogram of the solvent.
Molality = mass of solute in gram * 1000 / mol. wt. of solute * mass of solvent (in g)
Molality is independent of temperature.
[Whcn solvent used is water, a molar (1 M) solution is more concentrated than a molal (1 M) solution.]
(vii) Normality (N) The number of gram equivalents of solute present in 1 L of solution.
Normality = number of grams – equivalent of solute / volume of solution in L
Number of gram-equivalents of solute = mass of solute in gram / equivalent weight
[Relationship between normality and molarity N x Eq. weight = M x mol. weight ]
If two solutions of the same solute having volumes and molarities V1, M1 and V2, M2 are mixed, the molarity of the resulting solution is

To dilute V1 mL of a solution having molarity M1 to molarity M2 up to the final volume V2 mL, the volume of water added is

(viii) Formality (F) It is the number of formula weights of solute present per litre of the solution.
Formality = moles of substance added to solution / volume of solution (in L))
(ix) Mass fraction Mass fraction of any component in the solution is the mass of that component divided by the total mass of the solution.
Molality, mole fraction and mass fraction are preferred over molarity, normality, etc., because former involve weights which do not change with temperature.
(x) Demal (D) It represents one mole of solute present in 1L of solution at O°C.
Raoult’s Law
The Raoult’s law states “For a solution of two volatile liquids, the vapour pressure of each liquid in the solution is less than the respective vapour pressure of the pure liquids and the equilibrium partial vapour pressure of the liquid is directly proportional to its mole fraction.
For a solution containing two liquids A and B, the partial vapour pressure of liquid A is
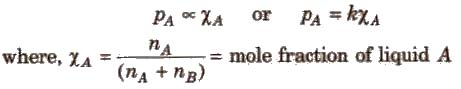
The proportionality constant is obtained by considering the pure liquid when χA = 1 then k = P°A, the vapour pressure of pure liquid, hence

Konowaloff Rule
At any fixed temperature, the vapour phase is always richer in the more volatile component as compared to the solution phase. In other words, mole fraction of the more volatile component is always greater in the vapour phase than in the solution phase.
The composition of vapour phase in equilibrium with the solution is determined by the partial pressure of components. If Y1 and Y2 are the
component 1 and 2 respectively in the vapour phase then. using Dalton’s law of partial pressure,
p1 = y1 * Ptotal
p2 = y2 * Ptotal
Ideal Solutions
Those solutions in which solute-solute (B-B) and solvent-solvent (A-A) interactions are almost similar to solvent solute (A-B) interactions are called ideal solutions. These solutions satisfy the following conditions :

(i) Solution must obey Raoult’s law, i.e.,
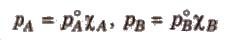
(ii) ΔHmix = 0 (No energy evolved or absorbed)
(iii) ΔVmix = 0 (No expansion or contraction on mixing)
Some solutions behave like nearly ideal solutions, e.g., benzene + toluene. n-hexane + n-heptane, ethyl iodide + ethyl bromide, chlorobenzene + bromobenzene.
Non-ideal Solutions
Those solutions which shows deviation from Raoult’s law is called non-ideal solution.
For such solutions,
ΔHmix ≠ 0
ΔVmix ≠ 0
(a) Non-ideal solutions showing positive deviation In such a case, the A – B interactions are weaker than A – A or B – B interactions and the observed vapour pressure of each component and the total vapour pressure are greater than that predicted by Raoult’s law.

For such solutions

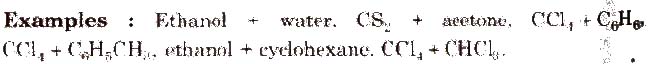
(b) Non-ideal solution showing negative deviation In such a case, the A – B interactions are stronger than A – A or B – B interactions and the observed vapour pressure of each component and the total vapour pressure are lesser than that predicted by Raoult’s law.


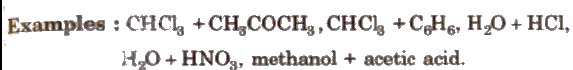
Azeotropic Mixture
A mixture of two liquids which boils at a particular temperature like a pure liquid and distils over in the same composition is known as constant boiling mixtures. These are formed by non-ideal solutions.
(i) Minimum boiling azeotropes are formed by those liquid pairs which show positive deviation from ideal behaviour. Such azeotropes have boiling points lower than either of the components, e.g., C2H5OH (95.57%) + H2O (4.43%)(by mass).
(ii) Maximum boiling azeotropes are formed by those liquid pain; which show negative deviation from ideal behaviour. Such azeotropes have boiling points higher than either of the components. e.g., H2O(20.22O%)+ HCl (79.78%] by mass.
Colligative Properties
[Colligatil1e : from Latin. = Co mean ‘together’; ligare means ‘to bind’.]
Colligative properties are those properties which depends only upon the number of solute particles in a solution irrespective of their nature.
Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure
It is the ratio of lowering in vapour pressure to vapour pressure of pure solvent. The relative lowering in vapour pressure of solution containing a nonvolatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of solute in the solution.
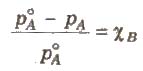

Above expression is used to find the molecular weight of an unknown solute dissolved in a given solvent. Where, WB and WA = mass of Solute and solvent respectively. MB and MA = molecular weight of solute and solvent respectively.
Ostwald and Walker method is used to determine the relative lowering of vapour pressure.
Elevation in Boiling Point (ΔTb)
Boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapour pressure becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. As the vapour pressure of a solution containing a nonvolatile solute is lower than that of the pure solvent, it boiling point will be higher than that of the pure solvent as shown in figure. The increase in boiling point is known as elevation in boiling point, ΔTb
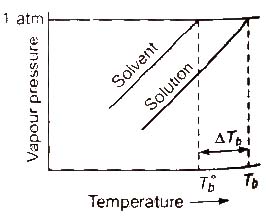
ΔTb = Tb – T°b
ΔTb = Kb m (where; m = molality)
Kb is molal elevation constant or ebullioscopic constant. Molecular mass of solute can be calculated as


where, WB and WA = mass of solute and solvent respectively.
Kb has units of K / m or K kg mol-1, for water, Kb = 0.52 K kg mol-1
The boiling point elevation of a solution is determined by
(i) Landsberger’s method
(ii) Cottrell’s method
Depression in Freezing Point (ΔTf)
Freezing point of a liquid is the temperature at which vapour pressure of the solvent in its liquid and solid phase become equal. As we know that vapour pressure of solution containing non-volatile solute is lower than that of pure solvent, solid form gets separated out at a lower temperature as shown in the figure.
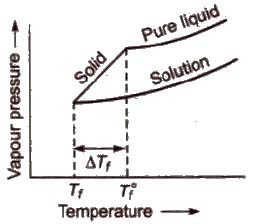
This decrease in freezing point of a liquid is known as depression in freezing point.
Depression in freezing point (ΔTf) = T°f – Tf
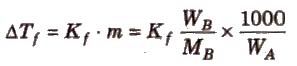
To find molecular mass of solute,

where, Kf is molal depression constant or cryoscopic constant.
Kf has units of K / m or K kg mol-1.
Ethylene glycol is usually added to water in the radiator to lower its freezing point. It is called antifreeze solution.
[Common salt (NaCI) and anhydrous CaC12 are used to clear snow on the roads because they depress the freezing point of water. The freezing point depression is determined by Beckmann method or Rast method.]
Calculations of molal elevation constant (Kb) and molal depression constant (Kf)

Osmotic Pressure (π)
Osmosis is the phenomenon of spontaneous flow of the solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from pure solvent to solution or from a dilute solution to concentrated solution. It was first observed by Abbe Nollet.
Some natural semipermeable membranes are animal bladder, cell membrane etc.
CU2[Fe(CN)6]is an artificial semipermeable membrane which does not work in non-aqueous solutions as it dissolves in them.
Osmosis may be
(i) Exosmosis It is outward flow of water or solvent from a cell through semipermeable membrane.
(ii) Endosmosis It is inward flow of water or solvent from a cell through a semipermeable membrane.
The hydrostatic pressure developed on the solution which just prevents the osmosis of pure solvent into the solution through a semipermeable membrane is called osmotic pressure.
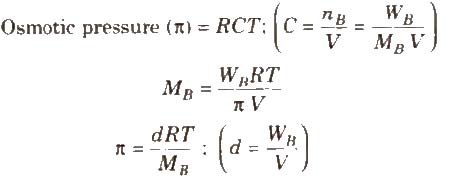
where, d = density, R = solution constant,
T = temperature, MB = molar mass of solute
Osmotic pressure can be determined by anyone of the method listed below
(i) Pfeffer’s method
(ii) Berkeley and Hartley’s method (very good method)
(iii) Morse and Frazer’s method
On the basis of osmotic pressure, -the solution can be
(i) Hypertonic solution A solution is called hypertonic if its osmotic pressure is higher than that of the solution from which it is separated by a semipermeable membrane.
When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the fluid from the plant cell comes out and cell shrinks, this phenomenon is called plasmolysis.
(ii) Hypotonic solution A solution is called hypotonic if its osmotic pressure is lower than that of the solution from which it is separated by a semipermeable membrane.
(iii) Isotonic solution Two solutions are called isotonic if they exert the same osmotic pressure. These solutions have same molar concentration. 0.91% solution of pure NaCl is isotonic with human RBC’s.
Two solutions are isotonic if they have the same molar concentration, e.g., if x % solution of X is isotonic with y % solution of Y, this means molar concentration of X = Molar concentration of Y

Osmotic pressure method is the best method for determining the molecular masses of polymers since observed value of any other colligative property is too small to be measured with reasonable accuracy.
Reverse osmosis When the external pressure applied on the solution is more than osmotic pressure, the solvent flows from the solution to the pure solvent, I which is called reverse osmosis. Desalination of sea water is done by reverse Osmosis.
Abnormal Molecular Masses
In some cases, observed colligative properties deviate from their normal calculated values due to association or dissociation of molecules. As we know,
Colligative property ∝ 1 / MB
lienee, higher and lower values of molar mass is observed in case of association and dissociation respectively, e.g., in benzene, acetic acid gets associated, so, its observed molecular mass is 120. Similarly KCI undergoes dissociation in aqueous solution, so its observed molecular mass is 37.25.
These observed values are corrected by multiplying with van’t Hoff factor (i).
van’t Hoff Factor (i)
It is the ratio of observed value of colligative property to the calculated value of colligative property.
i = observed value of colligative property / calculated value of colligative property
or i = normal molecular mass / observed molecular mass
or i = number of particles after association or dissociation / number of particles initially
So to correct the observed value of molar mass, van’t Hoff factor (i) must be included in different expressions for colligative properties.
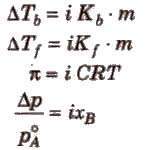
Degree of Dissociation (α) and van’t Hoff Factor (i)
(i) If one molecule of a substance gets dissociated into n particles or molecules and α is the degree of dissociation then
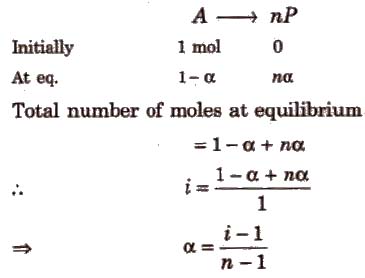
Degree of Association (α) and van’t Hoff Factor (i)
If n molecules of a substance A associate to form An and α is the degree of association then

van’t Hoff factor (i) > 1 for solutes undergoing dissociation and it is < 1 for solutes undergoing association.
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


