Class 12 Chemistry The d- and f- Block Elements – Get here the Notes for Class 12 The d- and f- Block Elements. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic The d- and f- Block Elements.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: The d- and f- Block Elements
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry The d- and f – Block Elements
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry The d- and f- Block Elements.
The d-block of the Periodic Table contains the elements of the groups 3-12 in which the d·orbitals are progressively filled. There are mainly three series of the elements, 3d-series (Sc to Zn) 4d-series (Y to Cd) and 5d-series (La to Hg omitting Ce to Lu). The fourth 6d-series which begins with Ac is still incomplete.
Transition Elements
Elements having partially filled d-orbitals in ground state or in excited state, are known as transition elements. They have been placed in the centre of the Periodic Table between s-block and p-block elements.
Iron is the most abundant and widely used transition metal.
General Electronic Configuration of Transition Elements
Transition elements have the electronic configuration (n – 1)d1 – 10 nso – 2, Zn, Cd, Hg, the end members of first three series have general electronic configuration (n – 1)d10ns2. These elements do not show properties of transition elements to any extent and are called non-typical transition elements.
Electronic Configuration of Transition Elements

General Physical Properties of Transition Elements
(i) Atomic and ionic size Ions of the same charge in a given series exhibit regular decrease in radius with increasing atomic number, because the new electron enters in a d – orbital and nuclear charge increases by unity.
In last of the series, a small increase in size is observed due to electron-electron repulsion.
(Atomic and ionic radii increase from 3d-series to 4d-series but the radii of the third (Sd) series elements are virtually the same as those of the corresponding member of the second series. It can be explained on the basis of lanthanoid contraction [poor shielding of 4f ].
Due to lanthanide contraction Zr and Hf Have almost similar radii.
(ii) Ionisation enthalpies In a series as we move from left to right, ionization enthalpy increases due to increase in nuclear charge but not in regular trend.
The irregular trend in the first ionisation enthalpy of the 3d metals, though of little chemical significance, can be accounted by considering that the removal of one electron alters the relative energies of 4s and 3d-orbitals.
(iii) Oxidation states Transition metals show variable oxidation state due to two incomplete outermost shells. Only stable oxidation states of the first row transition metals are
Sc(+3) , Ti(+4). V(+5), Cr(+3, +6), Mn(+2, +7), Fe(+2. +3). Co(+2, +3). Ni(+2), Cu(+2), Zn(+2).
The transition elements in their lower oxidation states (+2 and +3) usually forms ionic compounds. In higher oxidation state compounds are normally covalent.
Only Os and Ru show +8 oxidation states in fluorides and oxides. Ni and Fe in Ni(CO)4 and Fe(CO)5 show zero oxidation state.
(iv) Enthalpy of atomisation Transition elements exhibit higher enthalpies of atomization. Because of the presence of a large number of unpaired electrons in their atoms, they have stronger interatomic interactions and hence, stronger bond.
(v) Trends in the M2+ / M standard electrode potentials
EoM2+ / M is governed by three factors. Enthalpy of sublimation, enthalpy of ionisation and enthalpy of hydration.
The irregular trend in 3d series is due to irregular variation in ionisation enthalpy and heat of sublimation.
Except copper 3d – elements are good reducing agents.
[If sum of the first and second ionisation enthalpies is greater than hydration enthalpy standard potential (EoM2+ / M) will be positive and reactivity will be lower and vice-versa.]
(vi) Melting and boiling point Due to strong metallic bond, they have high m.p. and b.p. The m.p. of these elements becomes maximum and then decreases with the increase in atomic number.
Manganese and technetium show abnormal values in the trend. Tungsten has the highest m.p. (3410oC).
Mercury is liquid at room temperature (m.p. – 38.9°C) due to absence of unpaired electrons, and weak metallic bonding.
(vii) Density d-block elements have high density because of their small atomic size and strong metallic bonding.
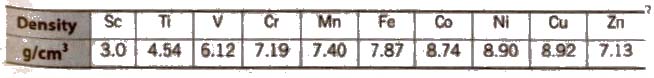
Osmium has slightly lower density (22.52 g cm-3) as compared to iridium (22.61 g cm-2). Thus, iridium has the highest density among transition metals.
(viii) Atomic volume Atomic volume decreases along the period due to decrease in atomic size.
(ix) Reactivity d-block elements are less reactive due to high ionisation energies. Some are almost inert and known as noble metals, e.g., Au; Pt, Os, Ir, etc
(xii) Complex formation They are well known to form a large number of complex compounds mainly due to
(a) small atomic size and high nuclear charge
(b) presence of partly filled or vacant d-orbitals, e.g.,K4[Fe(CN)6]
(xiii) Coloured ions Colour exhibited by transition metal ions is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in d-orbitals and is due to the d-d transitions of electrons, when invisible light is incident on the ion.
Colour of a complex depends on the metal, its oxidation state and its ligands, e.g., [Cu(H2O)4]2+ is pale blue while [Cu(NH3)4]2+ is dark blue. CuSO4· 5H2O is blue in colour and anhydrous CuSO4 is colourless.
Charge transfer also give intense colour e.g., MnO–4 ion does not contain any unpaired d-electron. Its purple colour is due to charge transfer from O to MD, thus O-2 change to O– and Mn(VII) to Mn(Vl). Charge transfer is possible only when the energy levels on the two different atoms involved are fairly close.
(xiv) Magnetic properties
(a) Paramagnetic nature is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in d-orbitals. Paramagnetic character increases with increase in the number of unpaired electrons and highest for Mn(II) [among 3d-series].
(b) Diamagnetic substances are repelled by applied magnetic field and have no unpaired electron.
(c) In ferromagnetism, permanent magnetic character is acquired by substance e.g., Fe.
Magnetic moment is given by
μ = √n (n + 2) BM,
Where, n = number of unpaired electrons and BM = Bohr magneton (unit of magnetic moment).
(xv) Catalytic properties The transition metals anti their compounds behave like catalyst due to
(a) the presence of partly filled d-orbitals resulting in variable oxidation states.
(b) formation of intermediate complex with reactants by lowering the energy of activation.
(c) their rough surface area which provides active sites for adsorption of reactant molecules.
Iron in the preparation of NH3 (Haber’s process), finely divided nickel for hydrogenation, Pt in the preparation of nitric acid (Ostwald’s process)
Some important catalysts having transition metals are
1. Ziegler Natta catalyst : TiCI4 + (C2H5)3 AI
2. Lindlar’s catalyst : Pd / BaSO4
3. Wilkinson’s catalyst : [Ph3P3RhCI
4. Adam’s catalyst : Pt / PtO
5. Brown’s catalyst or P-2 catalyst: Nickel boride
(xiv) Formation of alloys d-block elements have a strong tendency to form alloys, because their atomic :;ires are Vel’)’ similar and in the crystal lattice one metal can be readily replaced by another. Alloys so formed have high m.p.. The metals Mo, W, Cr, Ni, and V are used for the production of stainless steel.
Amalgam is an alloy formed by mercury with other metals, Iron and platinum do not form any alloy with mercury.
List of Alloys

(xv) Interstitial compounds The vacant space present in a crystal lattice is known as interstitial site or void. The non-metal atoms (e.g., H, N, C, etc.) due to their small size when occupy such place, the resulting compound is known as interstitial compound. Such compounds are hard and rigid, e.g., cast iron and steel.
(xvi) Non-stoichiometric compounds The compounds not navm the elements in the exact ratio as in the ideal crystal are known non-stoichiometric compounds e.g., in Fe0.94O1 the Fe : O is approx 0.94 : 1 and not exactly 1 : 1. It is due to the variability of Oxidation state in the transition metal. These elements form such compound by trapping H, B, C and N etc.
(xvii) Spinel These are the mixed oxides in which oxygen atoms constitute a fcc lattice e.g., ZnFe2O4 It is a normal spinel in which the trivalent ions occupy the octahedral holes and divalent ions occupy the tetrahedral holes.
In inverse spinel, the trivalent ion occupy the tetrahedral holes and divalent ion occupy the octahedral holes. e.g., FeFe2O4 or Fe3O4.
Some important reagents having transition metals
1. Baeyer’s reagent Dilute alkaline KMnO4 used to test the presence of unsaturation.
2. Tollen’s reagent Ammoniacal solution of AgNO3, i.e., [Ag(NH3)2]OH. used to test the aldehyde group.
3. Nessler’s reagent Alkaline solution of K2HgI43 (g) and NH: .
4. Benedict’s solution CuSO4 solution + sodium citrate + Na2CO3, used to test the aldehyde group.
5.Lucas reagent HCl (cone.) + anhydrous ZnCl2, used to distinguish between 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols.
Applications of transition elements
1. A mixture of TiO2 and BaSO4 is called titanox and a mixture of ZnS + BaSO4 is called lithopone.
2. TiCI2 and TiO2 are used in smoke screens. TiO2 is also used as white pigment of paints.
3. Tantalum is used in surgical venables and analytical weights.
4. Chromium is used in stainless steel and chrome plating.
5. Mo is used in X-rays tubes. Pt is used in resistance thermometers.
6. Cd is used for making joints in jewellery.
7. Ce is used as a scavenger of oxygen and sulphur in many metals-
8. Alkaline solution of K2HgI4 is called Nessler’s reagent and is used to test the presence of ammonium ion (NH+4).
1. Potassium Dichromate (K2 Cr2 O7)
Ore Ferrochrome or chromite (FeO· Cr2O3) or (FeCr2O4)
Preparation

Sodium dichromate is more soluble than potassium dichromate.
Chromates and dichromates are interconvertible in aqueous solution depending upon pH of the solutions.

Properties Sodium and potassium dichromates are strong oxidising agents, thus, acidified K2Cr27 will oxidise iodides to iodine, sulphides to sulphur, tin (ll) to tin (IV) and iron (ll) salts to iron (III).

Uses
1. K2Cr27 is used as oxidising agent in volumetric analysis.
2. It is used in mordant dyes, leather industry, photography (for hardening of film).
3. It is used in chromyl chloride test.
4. It is used in cleaning glassware.
2. Potassium Permanganate (KMnO 4)
Ore Pyrolusite (MnO2)
Preparation

Commercial preparation
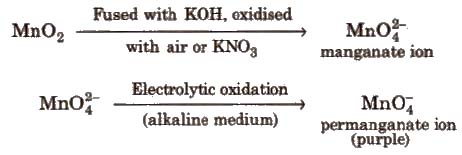
Properties KMnO4 acts as strong oxidising agent.
1. In the presence of dilute H2SO4, KMnO4 is reduced to manganous salt.
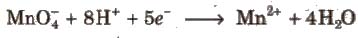
Acidic KMnO4 solution oxidises oxalates to CO2, iron(II) to iron (lll), nitrites to nitrates and iodides to iodine. The half-reactions of reductants are
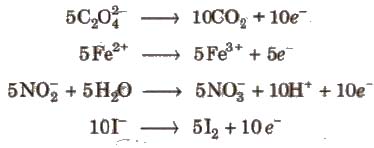
To acidify KMnO4, only H2SO4 is used and not HCI or HNO3 because HCI reacts with KMnO4 and produce Cl2 while HNO3, itself acts as oxidising agent.
2. In alkaline medium, KMnO4 is reduced to insoluble MnO2.
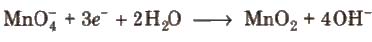
Alkaline or neutral KMnO4 solution oxidises I– to IO–3, S2O2-3 to SO2-4, Mn2+ to MnO2, etc.
Aqueous KMnO4, reacts with NH$ to liberate N2 gas.
2KMnO4 + 2NH3 → 2KOH + 2MnO2 + N2 + 2H2O
Uses
KMnO4 is used
(i) in laboratory preparation of CI2.
(ii) as an oxidising agent and disinfectant.
(iii) in making Baeyer’s reagent.
Structures
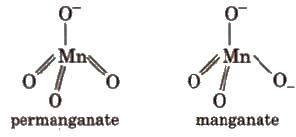
3. Copper Sulphate (CUSO4 ·5H2O)
It is also known as blue vitriol.
Method of preparation It is obtained by the action of dil H2SO4 on copper scrap in the presence of air.
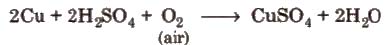
Properties
1. On heating it turns white due to loss of water of crystallisation.
At 1000 K, CuSO4 decomposes into CuO and So3

2. It gives blue solution with NH4OH and white ppt of Cu2I2 with KI.
Uses It 1S used in electroplating, as mordant in dyeing, in making bordeaux mixture [(Ca(OH) 2 + CuSO4)], etc.
4. Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
It is also called Lunar caustic.
Method of preparation It is prepared by heating silver with dilute nitric acid
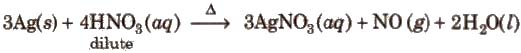
Properties
1. It is colourless, crystalline compound which blackens when comes in contact of organic substances (skin, cloth, etc.)
2. With potassium dichromate, it gives red ppt of Ag2CrO4.
3. On strong heating, it decomposes to metallic silver.

4. Ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate is known as Tollen’s reagent.
Uses It is used as laboratory reagent, in silvering of mirror, in the preparation of inks and hair dyes, etc.
Inner-Transition Elements
The elements in which the filling of atomic orbitals by electrons take place in {-subshells, two levels inside the outer subshell, are known as inner-transition elements. They are also known as f-block elements
Classification of f-block Elements
They have been classified into two series.
(a) 4f-series (first inner-transition series) The last electron enters in 4f-orbital. The elements belonging to this series are also known as lanthanoids.
(b) 5f-series (second inner-transition series) The last electron enters in 5f-orbital. The elements belonging to this series are also known as actinides.
Lanthanides
The fifteen elements from lanthanum (at. no. 57) to lutetium (at. no. 71) are known as lanthanides or rare earths. Their properties are as follows :
1. Electronic configuration
The general electronic configuration of these elements is [Xe]4f0 – 14 5d0-1 6s2. The lanthanum, electronic configuration [Xe]4f0 5d1 6s2 and lutetium, electronic configuration [Xe]4f14 5d1 6s2, have no partially filled 4f-orbital in their ground state, are considered as lanthanides due to their properties close to these elements.
2. Oxidation state
The most common and most stable oxidation state of lanthanides is +3 but some elements also exhibit +2 and +4 oxidation states in which they leave behind stable ions, e.g.,
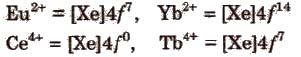
An aqueous solution of Ce4+ is a good oxidising agent. The Eu2+ and Yb2+ can exist in aqueous solution and are good reducing agents. But there are exceptions also e.g.,
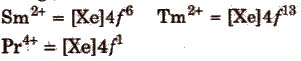
3. Magnetic properties
Magnetic properties have spin and orbit contributions. Hence, magnetic moments are given by the formula
μ = √4S(S + 1)+ L (L + 1)
Where, L = orbital quantum number, S = spin quantum number
All lanthanide ions with the exception of La3+, Lu3+ and Ce4+, are paramagnetic in nature.
4. Lanthanoid contraction
Steady decrease in the atomic and ionic (Ln3+) radii as the atomic Dumber of the lanthanide elements increases is called lanthanide contraction. This is because the additional electron goes to 4f-subshell and 4f-orbitals being large and diffuse, have poor shielding effect. The effective nuclear charge increases which causes the contraction in the size of electron charge cloud. This contraction in size is quite regular and is known as lanthanoid contraction.
The f- f transitions are possible due to absorption of light from the visible region.
Consequences of lanthanoid contraction
(i) Covalent character of cations increase.
(ii) The electronegativity of trivalent ions increases slightly.
(iii) There is decrease in basic strength of oxides and hydroxides from La to Lu.
(iv) There is small increase in standard electrode potential values.
(v) Sizes of Zr and Hf; Nb and Ta are similar, so they are called chemical twins.
5. Colour
The species containing unpaired electrons are coloured and so on in the case of lanthanide ions.
6. Melting and boiling pOints
Lanthanides have high melting and boiling points but there is no regular trend.
7. Density
Lanthanides have densities varying . from 6.67 to 9.7 g cm-3, but there IS no regular trend for these values.
8. Electronegativity
For lanthanides the electronegativity values are almost same as that of $-block elements. Lanthanides form ionic compounds.
9. Ionisation energies
The ionisation energy values of lanthanoids are not very high due to their large size and comparable with those of alkaline earth metals.
10. Complex compound
Due to their large ionic SIze, they have little tendency to form complexes.
11. Reactivity
Due to their low values of ionisation energies, the lanthanides are very reactive.
12. Alloys
They form alloy especially with iron e.g., misch metal rare earths 94 _ 95%, iron ~ 5% and S, C, Ca and AI in traces. Mg mixed with 3% misch metal is used for making jet engine parts.
Actinides
The fifteen elements from actinium (at. no. 89) to lawrencium (at. no. 103) are known as actinides and constitute the 5f series. From neptunium to onwards the elements are man-made (artificially prepared) and also known as transuranic elements.
1. Electronic configuration
The last electron in such elements enters in the 5f atomic orbital.
Their general electronic configuration is
[Rn]5 f0 – 14 6d0 – 1 7s2
There is not much difference between the energies of 5f and 6d, so it is difficult to predict whether the electron has entered in 5f or 6d.
2. Oxidation state
The common oxidation state is +3 but other oxidation states are also exhibited by actinides upto the maximum being +7.
3. Magnetic properties
The magnetic moments of actinide ions are smaller than theoretical values. It is hard to interpret due to large spin orbit coupling.
4. Actinide contraction
It is similar to lanthanide contraction due to poor shielding or 5f – electrons
5. Melting and boiling points
They have high values for melting and boiling points but there is no regular trend.
6. Density
The value of density vary from 7.0 gcm-3 to 20 gcm-3. Again there is no regular trend in density.
7. Reducing character
They are strong reducing agents as they have high E° values approximately 2.0 V.
8. Reactivity
Actinide are very reactive in nature and combine with oxygen and halogens like lanthanoids.
9. Coloured ions
Actinide ions are coloured due to the presence of unpaired electrons and f-f transitions.
10. Complex formation
They have higher tendency to form complex compounds.
Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.


