Class 12 Chemistry Principal and Processes of Isolation of Elements – Get here the Notes for Class 12 Principal and Processes of Isolation of Elements. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 12 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes, study material, and a smart preparation plan. CBSE 2019 Class 12th Exam is approaching and candidates will have to make the best use of the time available towards the last stage of your CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Preparation. To help you with that below we have provided the Notes of 12 Chemistry for topic Principal and Processes of Isolation of Elements.
- Class: 12th
- Subject: Chemistry
- Topic: Principal and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Principal and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 12 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Principal and Processes of Isolation of Elements.
Earth crust is the source of many elements. Out of these elements, 70% are metals. Aluminium is the most abundant metal of earth crust and iron comes second. The percentage of different elements in earth crust are
O-49%, Si-26%, Al-7.5%, Fe-4.2%, Ca-3.2%, Na-2.4%, K-2.3%, Mg-2.3%, H-l%
Metals occur in two forms in nature (i) in native state (ii) in combined state, depending upon their chemical reactivities.
Native State
Elements which have low chemical reactivity or noble metals having least electropositive character are not attacked by oxygen. moisture and CO2 of the air. These elements, therefore, occur in the free state or in the native state, e.g., Au, Ag, Pt, S, O, N, noble gases, etc.
Combined State
Highly reactive elements such as F, CI, Na, K, etc., occur in nature combined form as their compounds such as oxides, carbonates sulphides. halides, etc.
Hydrogen is the only non-metal which exists in oxidised form only.
Minerals and Ores
The naturally occurring substances in the form of which the metals occur in the earth crust are called minerals.
Every mineral is not suitable for the extraction of the metal. The mineral from which the metal is economically and conveniently extracted is called an ore.
Thus, all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores.

Gangue or Matrix
Impurities associated with ores are called gangue or matrix.
Metallurgy
The entire scientific and technological process used for isolation of the metal from its ores is known as metallurgy.
Types of Metallurgical Processes
- Pyrometallurgy Extraction of metals takes place at very high temperature. Cu, Fe, Zn, Sn, etc .. are extracted by this method.
- Bydrometallurgical process In this method, metals are extracted by the use of their aqueous solution. Ag and Au are extracted by this method.
- Electrometallurgical process Na, K, Li, Ca, etc., are extracted from their molten salt solution through electrolytic method.
Steps Involved in Metallurgy
Following steps are involved in the metallurgy :

Crushing of the Ore
The big lumps of ore are crushed into smaller pieces with the help of jaw-crushers. The process of grinding the crushed ore into fine powder with the help of the stamp mills is called pulverisation.
Concentration of Ores
Removel of unwanted materials (e.g., sand. clays, etc.) from the ore is known as ore concentration, ore dressing or ore benefaction. It can be carried out by various ways depending upon the nature of the ore.
Hydraulic Washing/Gravity Separation/Levigation
The process by which lighter earthy impurities are removed from the heavier ore particles by washing WIth water is called levigation. The lighter impurities are washed away. Thus. this method is based on the difference in the densities (specific gravities) of ore and gangue.
This method is commonly used for oxide ores such as haematite, tin stone and native orcs of Au, Ag, etc.
Froth Floatation
This method is used for the concentration of sulphide ores. This method is based on the preferential wetting of ore particles by oil and that of gangue by water .. As a result. the ore particles become light and rise to the top in the form of froth while the gangue particles become heavy and settle down. Thus. adsorption is involved in this method.
The froth can be stabilised by the addition of stabilisers (aniline or cresols).
Activator They activate the floating property of one of the component of the ore I and help in the separation of different minerals present in the same ore (CuSO4 is used as activator.
Depressants These are used to prevent certain types of particles from forming the froth with air bubbled, e.g., NaCN can be used as a depressant in the separation of ZnS and PbS ores. KCN is an another depressant.
Collectors It increasesthe non-wettability of ore particles by water, e.g., pine oils, xanthates and fatty acids.
Electromagnetic Separation
This method of concentration is employed when either the ore or the lmpurities associated with it are magnetic in nature. e.g., chromite, FeCr2O4, containing magnetic SiliCIOUS gangue and wolframite FeWO4, Containing cassiterite, 8nO4 (non-magnetic impurities) can be separated by this method.
Electrostatic Separation
This method is used for the separation of lead sulphide (good conductor) which is charged immediately in an electrostatic field and is thrown away from the roller from zinc sulphide (poor conductor) which is not charged and hence, drops vertically from the roller.
Chemical Method-Leaching
Leaching is the process in which the ore is concentrated by chemical reaction with a suitable reagent which dissolves the ore but not the impurities, e.g., bauxite is leached with a hot concentrated solution of NaOH which dissolves aluminium while other oxides (Fe2O3, TiO2, SiO2), remain undissolved and noble metals (Ag and Au) are leached with a dilute aqueous solution of NaCN or KCN in the presence of air.

Extraction of Crude Metals from Concentrated Ore
The concentrated ore is usually converted to oxide before reduction, as oxides are easier to reduce. Thus, isolation of crude metal from concentrated ore involves two major steps:
- Conversion to oxide.
- Reduction of the oxides to metal.
Conversion to Oxides
(i) Calcination It is the process of converting an ore into its oxides by heating it strongly, below its melting point in a limited supply of air or in absence of air.
During calcination, volatile impurities as well as organic matter and moisture are removed.

Calcination is used for metal carbonates and hydroxides and is carried out in reverberatory furnace.
(ii) Roasting It is the process of converting an ore into its metallic oxide by heating it strongly. below its melting point m excess of air. This process is commonly used for sulphide ores and is carried out in blast furnace or reverberatory furnace. Roasting helps to remove the non-metallic impurities and moisture.

The furnaces used in calcination and roasting employ refractory materials which resist high temperature and do not become soft.
- Acidic refractories : SiO2 and SiO2 + Al2O3
- Basic refractories : CaO and MgO
- Neutral refractories : Graphite, chromites. etc.
Heavy metals like Cu. Zn, Fe. So, etc., arc obtained by roasting and smelting.
Reduction of the Oxides to Metal
The roasted or the calcined ore is then converted to the free metal by reduction. Reduction method depends upon the activity of metal.
Metals which are low in the activity series (like Cu, Hg, Au) are obtained by heating their compounds lD air: metals which are in the middle of the activity “cries (like Fe. Zn, Ni, Sn) are obtained by heating their oxides with carbon while metals which are very high in the activity series (e.g., Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al) are obtained by electrolvtic reduction method.
(i) Smelting (reduction with carbon) The process of extracting the metal by fusion of its oxide ore with carbon (C) or CO is called smelting. It is carried out in a reverberatory furnace.

During smelting a substance. called flux is added which removes the non-fusible impurities as fusible slag. This slag is insoluble in the molten metal and is lighter than the molten metal. So, it floats over the molten metal and is skimmed off.
Acidic flux For basic impurities, acidic flux is added.
e.g., CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3

In the extraction of Cu and Fe, the slag obtained are respectively FeSiO3 and CaSiO3.
The obtained slag is used in road making as well as in the manufacturing of cement and fertilizers.
(ii) Reduction by hydrogen It is done for W or Mo oxide.

iii) Reduction by aluminium It is known as alumino thermic reduction or Gold Schmidt thermite process. Aluminium powder is used for this purpose.
e.g., Cr2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Cr
Mixture of the oxide and Al i.n the ratio of 3 : 1 is known as thermite and mixture of BaO2 + Mg powder acts as ignition powder.
(iv) Auto reduction This is used for reduction of sulphide ores of Pb, Hg, Cu, etc. The sulphide ore is heated in a supply of air at 770-970 K when the metal sulphide is partially oxidised to form its oxide or sulphate which then reacts with the remaining sulphide to give the metal.

(v) Reduction by Mg
TiCl4 + 2Mg → 2MgCl2 + Ti (Kroll’s process)
vi) Electrolytic reduction or electrometallurgy It is the process of extracting highly electropositive (active) metals such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al, etc by electrolysis of their oxides, hydroxides or chlorides in fused state, e.g., Mg is prepared by the electrolysis of fused salt of MgCl2 (Dow’s process).
Thermodynamic Principle in Extraction of Metals
The free energy change (ΔG) occurring during the reduction processes help in deciding the suitable method for reduction.
For the spontaneous reduction of an oxide, halide or sulphide by an element, the essential condition is that there is a decrease in the free energy of the system (-ve ΔG).
More the negative value of ΔG, the higher is the reducing power of an element. ΔG can be given as
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
- where, ΔH = enthalpy change;
- ΔG = Gibbs free energy
- T = temperature;
- ΔS = entropy change
For the reduction of a metal oxide with a reducing agent, the plot of ΔG° against temperature is studied, which is called Ellingbam diagram.
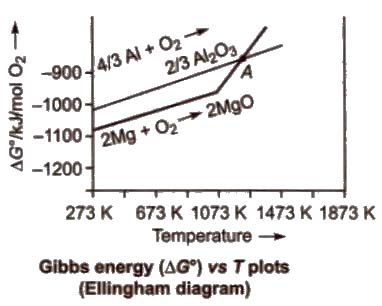
Characteristics of Ellingham Diagram
1. All the plots slope upwards since ΔG° becomes more positive when temperature increases, i.e., stability of oxides decreases.
2. A metal will reduce the oxide of other metals which lie above it in Ellingham diagram, i.e., the metals for which the free energy of formation (ΔG°f) of their oxides is more negative can reduce those metal oxides which has less negative ΔG°f
3. The decreasing order of the negative values of ΔG°f of metal oxides is Ca > Mg (below 1773 K) > AI > Ti > Cr > C > Fe > Ni> Hg > Ag
Thus, AI reduces FeO, CrO and NiO in thermite reduction but it will not reduce MgO at temperature below 1773 K.
Mg can reduce A12O3 below 162 K but above 1023 K, Al can reduce MgO.
4. CO is more effective reducing agent below 1073 K and above 1073 K. coke is more effective reducing agent, e.g., CO reduces F2O3 below 1073 K but above it, coke reduces Fe2O3.
Coke reduces ZnO above 1270 K.
Refining or Purification of Crude Metals
Physical Methods
(i) Liquation This method is used for refining the metals having low melting points (such as Sn. Pb, Hg, Bi) than the impurities, The impure metal is placed on the sloping hearth and is gently heated. The metal melts and flows down leaving behind the non-fusible impurrties.
(ii) Distillation This is useful for low boiling metals such as Zn, Hg. The impure liquid metal is evaporated to obtain the pure metal as distillate.
(iii) Cupellation
This method is used when impure metal contains impurities of other metals which form volatile oxides.
e.g., traces of lead ore removed from silver (as volatile PbO) by this process.
Chemical Methods
(i) Poling This method is used when the impure metal contains impurities of Its own oxide, e.g., CU2O in blister copper and SnO2 in impure Sn. The molten impure metal is stirred with green wood poles. At this high temperature. wood liberates gases such as CH4 which reduces any oxides present in the metal.
(ii) Electro-refining
In this method, impure metal forms the anode while the cathode is a rod or sheet of pure metal. The electrolytic solution consists of a soluble salt of the metal.
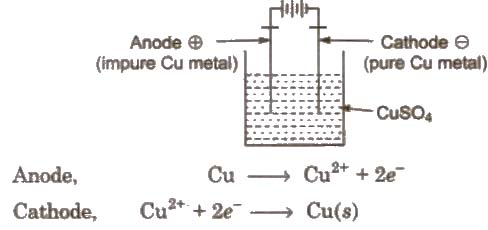
On passing electricity, the pure metal gets deposited on the cathode while the insoluble impurities settle down below the anode as anode mud or anode sludge. Metals like Cu, Ag, Au, Cr, Zn, Ni, etc are purified by this method.
(iii) Zone-refining This method is based upon the principle of fractional crystallisation, i.e., difference in solubilities of impurities in molten and solid state of metal. Semiconductors like silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide and indium antimonide are purified by this method. Elements of very high purity are obtained by this method.
(iv) Vapour phase refining In this method, crude metal is made free from impurities by first convertmg it Into its volatile compound by heating with a chemical reagent at low temperature. After this, the volatile compound is decomposed by heating to some higher temperature to give pure metal.
(a) van Arkel method This method is used for preparing ultra-pure metal used in space technology (e.g., Ti, Zr, etc.)
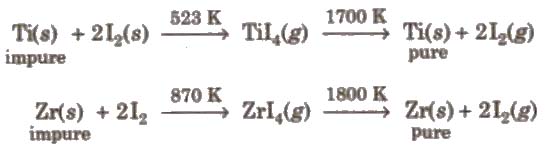
(b) Mond’s process It is used for refining of nickel.

(v) Chromatographic method Adsorption chromatography is generally used. The impure metal is dissolved in a suitable solvent and the solution is allowed to run slowly into an adsorbent column packed with alumina (Al2O3). The metal and the impurities present are adsorbed at different rates. These are then eluted with suitable eluent (solvent). In this method.
weakly adsorbed component is eluted first and the strongly adsorbed component is eluted afterwards.
Occurrence and Extraction of Some Metals
1. Metal Aluminium (AI)
Occurrence
- Bauxite – Al2O3.XH2O
- Cryolite – Na3AlF6
Common method of extraction Electrolysis of Al2O3 dissolved in molten Na3A1F6(neutral flux).
Neutral flux is the neutral compound added to the ore to decrease its melting point and to make it conducting, e.g., CaF2, cryolite (Na3AlF6) etc.
2. Metal Iron (Fe)
Occurrence
- Haematite – Fe2O3
- Magnetite – FE3O4
Common method of extraction Reduction of the oxide with CO and coke in blast furnace.
The iron obtained from blast furnace contains about 4% carbon and many impurities in smaller amount (e.g., S, P, Si, Mn) and is known as pig iron.
Cast iron is different from pig iron and is made by melting pig iron with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast. It has slightly lower carbon content (about 3%) and is extremely hard and brittle.
Wrought iron or malleable iron is the purest form of commercial iron and is prepared from cast iron by oxidising impurities in a reverberatory furnace lined with haematite. This haematite oxidises carbon to carbon monoxide.
Fe2O2 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
3. Metal Copper (Cu)
Occurrence
- Copper pyrites – CuFeS2
- Copper glance – Cu2S
Common method of extraction Roasting of sulphide partially and reduction.
Cu2S + FeS is called matte. Blister copper contains 96-98% copper with small amounts of Ag and Au as impurity.
4. Metal Zinc (Zn)
Occurrence
- Zinc blen de or sphalerite-ZnS
- Calamine – ZnCO3
- Zincite – ZnO
Common method of extraction Roasting followed by reduction with coke.
The metal may be purified by fractional distillation.
97-98% pure zinc is called spelter.
5. Metal Nickel (Ni)
Occurrence
- Penta landite – (Ni, Cu, Fe)S
- Kupfernickel – NiAs
- Smaltite – (Fe, Co. Ni) As
Common method of extraction Roasting followed by Refining is done by Mond’s Process.
Water gas is used as a reducing agent for nickel oxide.

Class 12 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 12 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 12 can also check Class 12 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 12th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 12 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 12 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 12 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 12 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 12 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 12 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 12.
Class 12 Chemistry Maths Notes Physics Notes Biology Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

