Class 11 Physics Surface Tension – Get here the Notes for Class 11 Physics Surface Tension. Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 11 with good score can check this article for Notes. This is possible only when you have the best CBSE Class 11 Physics study material and a smart preparation plan. To assist you with that, we are here with notes. Hope these notes will helps you understand the important topics and remember the key points for exam point of view. Below we provided the Notes of Class 11 Physics for topic Surface Tension.
- Class: 11th
- Subject: Physics
- Topic: Surface Tension
- Resource: Notes
CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Surface Tension
Candidates who are pursuing in Class 11 are advised to revise the notes from this post. With the help of Notes, candidates can plan their Strategy for particular weaker section of the subject and study hard. So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 11 Physics Surface Tension from this article.
Surface tension is the property of any liquid by virtue of which tries to minimize its free surface area.
Surface tension of a liquid is measured as the force acting per length on an imaginary line drawn tangentially on the free surface the liquid.
Surface tension S = Force/Length = F/l = Work done/Change in area
Its SI unit is Nm-1 or Jm-2 and its dimensional formula is [MT-2].
It is a scalar quantity. Surface tension is a molecular phenomenon which is due to cohesive force and root cause of the force is electrical in nature.
Surface tension of a liquid depends only on the nature of liquid and independent of the surface area of film or length of the line .
Small liquid drops are spherical due to the property of surface tension.
Adhesive Force
The force of attraction acting between the molecules of different substances is called adhesive force, e.g., the force of attracts acting between the molecules of paper and ink, water and glass, etc.
Cohesive Force
The force of attraction acting between the molecules of same substan is called cohesive force. e.g., the force of attraction acting between molecules of water, glass, etc.
Cohesive forces and adhesive forces are van der Waals’ forces.
These forces varies inversely as the seventh power of distance between the molecules.
Molecular Range
The maximum distance upto which a molecule can exert a force of attraction on other molecules is called molecular range.
Molecular range is different for different substances. In solids and liquids it is of the order of 10-9 m.
If the distance between the molecules is greater than 10-9 m, the force of attraction between them is negligible.
Surface Energy
If we increase the free surface area of a liquid then work has to be done against the force of surface tension. This work done is stored in liquid stu-face as potential energy,
This additional potential energy per unit area of free surface of liquid is called surface energy.
Surface energy (E) = S x &ΔM
where. S = surface tension and ΔA = increase in surface area.
(i) Work Done in Blowing a Liquid Drop If a liquid drop is blown up from a radius r1 to r2 then work done for that is
W = S . 4π (r22 – r12)
(ii) Work Done in Blowing a Soap Bubble As a soap bubble has two free surfaces, hence work done in blowing a soap bubble so as to increase its radius from r1 to r2 is given by
W = S.8π(r22 – r12)
(iii) Work Done in Splitting a Bigger Drop into n Smaller Droplets
If a liquid drop of radius R is split up into n smaller droplets, all of same size. then radius of each droplet
r = R. (n)-1/3
Work done, W = 4π(nr2 – R2)
= 4πSR2 (n1/3 – 1)
(iv) Coalescance of Drops If n small liquid drops of radius reach combine together so as to form a single bigger drop of radius R=n1/3.r, then in the process energy is released. Release of energy is given by
ΔU = S.4π(nr2 – R2)
= 4πSπn(1 – n1/3)
Angle of Contact
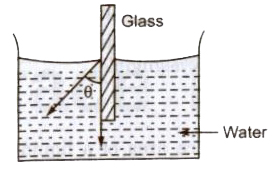
The angle subtended between the tangents drawn at liquid surface at solid surface inside the liquid at the point of contact, is called of contact (9).
Angle of contact depends upon the nature of the liquid and solid contact and the medium which exists above the free surface of liquid.
When wax is coated on a glass capillary tube, it becomes water-proof.
The angle of contact increases and becomes obtuse. Water does not in it. Rather it falls in the tube by virtue of obtuse angle of contact.
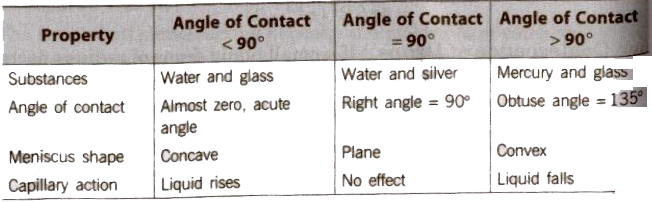
If θ is acute angle, i.e; θ <90°, then liquid meniscus will be concave upwards.
- If θ is 90°, then liquid meniscus will be plane.
- If θ is obtuse, i.e; θ >90°, then liquid meniscus will be convex upwards.
- If angle of contact is acute angle, i.e; θ <90°, then liquid will wet the surface.
- If angle of contact is obtuse angle, ie; θ > 90°, then liquid will not wet the surface.
Angle of contact increases with increase in temperature of Angle of contact decreases on adding soluble impurity to a liquid.
Angle of contact for pure water and glass is zero. For ordinary water and glass is 8°. For mercury and glass is 140°. For pure water silver is 90°. For alcohol and clean glass θ = 0°.
Angle of contact, meniscus, shape of liquid surface

Capillarity
The phenomenon called capillarity. of rise or fall of liquid column in a capillary tube is Ascent of a liquid column in a capillary tube is given by
h = (2S cos θ / rρg) – (r / 3)
If capillary is very narrow, then
h=2S cos θ / rρg
where, r = radius of capillary tube, p = density of the liquid, and
θ = angle of contact and S = surface tension of liquid.
- If θ < 90°, cos e is positive, so h is positive, i.e., liquid rises in a capillary tube.
- If θ > 90°, cos 9 is negative, so h is negative, i.e., liquid falls in a capillary tube.
- Rise of liquid in a capillary tube does not violate law of conservation of energy.
Some Practical Examples of Capillarity
- The kerosene oil in a lantern and the melted wax in a candle, rise in the capillaries formed in the cotton wick and burns.
- Coffee powder is easily soluble in water because water immediately wets the fine granules of coffee by the action of capillarity.
- The water given to the fields rises in the innumerable capillaries formed in the stems of plants and trees and reaches the leaves.
Zurin’s Law
If a capillary tube of insufficient length is placed vertically in a then liquid never come out from the tube its own, as
Rh = constant ⇒ R1h1 = R2h2
where, R = radius of curvature of liquid meniscus and
h = height of liquid column.
When a tube is kept in inclined position in a liquid the vertical height remains unchanged then length of liquid column.

Liquid rises (water in glass capillary) or falls (mercury in capillary) due to property of surface tension
T = Rρgh / 2 cos θ
where, R = radius of capillary tube, h = height of liquid, p = density of liquid, e = angle of contact,
T = surface tension of liquid and 9 = acceleration due to gravity.
Excess Pressure due to Surface Tension
(i) Excess pressure inside a liquid drop = 2S / R
(ii) Excess pressure inside an air bubble in a liquid = 2S / R
(iii) Excess pressure inside a soap bubble = 4S / R
where, S = surface tension and R = radius of drop/bubble.
(iv) Work done in spraying a liquid drop of radius R into n droplets of radius r = T x increase in surface area
= 4πTR3 (1/r – 1/R)
Fall in temperature
Δθ = 3T/J (1/r – 1/R)
where. J = 4.2 J/cal.
(v) When n small drops are combined into a bigger drop, then work done is given by
W = 4πR2T (n 1/3 – 1)
Temperature increase
Δθ = 3T/J (1/r – 1/R)
(vi) When two bubbles of radii r1 and r2 coalesce into a bubble of radius r isothermally, then
r2 = r12 + r22
(vii) When two soap bubbles of radii ‘1 and ‘2 are in contact with each other, then radius (r) of common interface.

Factors Affecting Surface Tension
- Surface tension of a liquid decreases with increase temperature and becomes zero at critical temperature.
- At boiling point, surface tension of a liquid becomes zero becomes maximum at freezing point.
- Surface tension decreases when partially soluble impurities such as soap, detergent, dettol, phenol, etc are added in water.
- Surface tension increases when highly soluble impurities such as salt is added in water.
- When dust particles or oil spreads over the surface of water, its surface tension decreases.
When charge is given to a soap bubble, its size increases surface tension of the liquid decreases due to electrification.
In weightlessness condition liquid does not rise in a capillary tube.
Some Phenomena Based on Surface Tension
- Medicines used for washing wounds, as detol, have a surface tension lower than water.
- Hot soup is more tasteful than the cold one because the surface tension of the hot soup is less than that of the cold and so spreads over a larger area of the tongue.
- Insects and mosquitoes swim on the surface of water in ponds and lakes due to surface tension. If kerosence oil is sprayed on the water surface, the surface tension of water is lowered and the insects and mosquitoes sink in water and are dead.
- If we deform a liquid drop by pushing it slightly, then due to surface tension it again becomes spherical.
Class 11 Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers
Hope these notes helped you in your schools exam preparation. Candidates can also check out the Key Points, Important Questions & Practice Papers for various Subjects for Class 11 in both Hindi and English language form the link below.
Class 11 NCERT Solutions
Candidates who are studying in Class 11 can also check Class 11 NCERT Solutions from here. This will help the candidates to know the solutions for all subjects covered in Class 11th. Candidates can click on the subject wise link to get the same. Class 11 Chapter-wise, detailed solutions to the questions of the NCERT textbooks are provided with the objective of helping students compare their answers with the sample answers.
Class 11 Mock Test / Practice
Mock test are the practice test or you can say the blue print of the main exam. Before appearing in the main examination, candidates must try mock test as it helps the students learn from their mistakes. With the help of Class 11 Mock Test / Practice, candidates can also get an idea about the pattern and marking scheme of that examination. For the sake of the candidates we are providing Class 11 Mock Test / Practice links below.
Class 11 Exemplar Questions
Exemplar Questions Class 11 is a very important resource for students preparing for the Examination. Here we have provided Exemplar Problems Solutions along with NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 11. Question from very important topics is covered by Exemplar Questions for Class 11.
CBSE Notes for Class 11 Physics Notes Biology Notes Maths Notes Chemistry Notes
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

