Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 9, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 is for Ray Optics and Optical Instruments. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 9. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
- A ray of light incident at an angle θ on a refracting face of a prism emerges from the other face normally. If the angle of the prism is 5° and the prism is made of a material of refractive index 1.5, the angle of incidence is
(a) 7.5°.
(b) 5°.
(c) 15°.
(d) 2.5°. - A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is
(a) blue.
(b) green.
(c) violet.
(d) red. - An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image
(a) moves away from the lens with an uniform speed 5 m/s.
(b) moves away from the lens with an uniform acceleration.
(c) moves away from the lens with a non-uniform acceleration.
(d) moves towards the lens with a non-uniform acceleration. - A passenger in an aeroplane shall
(a) never see a rainbow.
(b) may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric circles.
(c) may see a primary and a secondary rainbow as concentric arcs.
(d) shall never see a secondary rainbow. - You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
(a) The beam of red light would undergo total internal reflection.
(b) The beam of red light would bend towards normal while it gets refracted through the second medium.
(c) The beam of blue light would undergo total internal reflection.
(d) The beam of green light would bend away from the normal as it gets refracted through the second medium. - The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, it will
(a) act as a convex lens only for the objects that lie on its curved side.
(b) act as a concave lens for the objects that lie on its curved side.
(c) act as a convex lens irrespective of the side on which the object lies.
(d) act as a concave lens irrespective of side on which the object lies. - The phenomena involved in the reflection of radio waves by ionosphere is similar to
(a) reflection of light by a plane mirror.
(b) total internal reflection of light in air during a mirage.
(c) dispersion of light by water molecules during the formation of a rainbow.
(d) scattering of light by the particles of air. - The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ while directions in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 (Fig 9.1). Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4

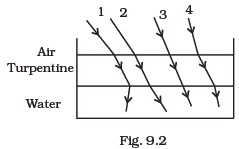
- The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Fig 9.2. shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in Fig 9.2, the path shown is correct?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
- A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h–1 on a straight road. Looking at the rear view mirror, the driver finds that the car following him is at a distance of 100 m and is approaching with a speed of 5 km h–1. In order to keep track of the car in the rear, the driver begins to glance alternatively at the rear and side mirror of his car after every 2 s till the other car overtakes. If the two cars were maintaining their speeds, which of the following statement (s) is/are correct?
(a) The speed of the car in the rear is 65 km h–1.
(b) In the side mirror the car in the rear would appear to approach with a speed of 5 km h–1 to the driver of the leading car.
(c) In the rear view mirror the speed of the approaching car would appear to decrease as the distance between the cars decreases.
(d) In the side mirror, the speed of the approaching car would appear to increase as the distance between the cars decreases. - There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Fig. 9.3). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because
(a) the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
(b) the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
(c) some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
(d) water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object. - A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB (Fig. 9.4). When observed from the face AD, the pin shall
(a) appear to be near A.
(b) appear to be near D.
(c) appear to be at the centre of AD.
(d) not be seen at all.

- Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known as Alexandar’s dark band. This is because
(a) light scattered into this region interfere destructively.
(b) there is no light scattered into this region.
(c) light is absorbed in this region.
(d) angle made at the eye by the scattered rays with respect to the incident light of the sun lies between approximately 42° and 50°. - A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought closer to the eye than the normal near point. This results in
(a) a larger angle to be subtended by the object at the eye and hence viewed in greater detail.
(b) the formation of a virtual erect image.
(c) increase in the field of view.
(d) infinite magnification at the near point. - An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20m and an eyepiece of focal length 2cm.
(a) The length of the telescope tube is 20.02m.
(b) The magnification is 1000.
(c) The image formed is inverted.
(d) An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light?
- The near vision of an average person is 25cm. To view an object with an angular magnification of 10, what should be the power of the microscope?
- An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
- Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices μ1 > μ2 > μ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is (h/3). A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
- For a glass prism (μ = √3) the angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of the prism. Find the angle of the prism.
Short Answer Type Questions
- A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror away from focus. The object distance is u. If the mirror has a focal length f, what will be the length of the image? You may take L <<|v – f|.
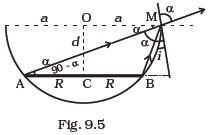
- A circular disc of radius ‘R’ is placed co-axially and horizontally inside an opaque hemispherical bowl of radius ‘a’ (Fig. 9.5). The far edge of the disc is just visible when viewed from the edge of the bowl. The bowl is filled with transparent liquid of refractive index μ and the near edge of the disc becomes just visible. How far below the top of the bowl is the disc placed?
- A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm above the principal axis. The top part is placed at (0,0) and an object placed at (–50 cm, 0). Find the coordinates of the image.
- In many experimental set-ups the source and screen are fixed at a distance say D and the lens is movable. Show that there are two positions for the lens for which an image is formed on the screen. Find the distance between these points and the ratio of the image sizes for these two points.
- A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index μ (Fig. 9.6). At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.

- A myopic adult has a far point at 0.1 m. His power of accommodation is 4 diopters. (i) What power lenses are required to see distant objects? (ii) What is his near point without glasses? (iii) What is his near point with glasses? (Take the image distance from the lens of the eye to the retina to be 2 cm.)
Long Answer Type Questions
- Show that for a material with refractive index μ ≥ √2 , light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
- The mixture a pure liquid and a solution in a long vertical column (i.e, horizontal dimensions << vertical dimensions) produces diffusion of solute particles and hence a refractive index gradient along the vertical dimension. A ray of light entering the column at right angles to the vertical is deviated from its original path. Find the deviation in travelling a horizontal distance d << h, the height of the column.
- If light passes near a massive object, the gravitational interaction causes a bending of the ray. This can be thought of as happening due to a change in the effective refractive index of the medium given by
n(r) = 1 + 2 GM/rc2
where r is the distance of the point of consideration from the centre of the mass of the massive body, G is the universal gravitational constant, M the mass of the body and c the speed of light in vacuum. Considering a spherical object find the deviation of the ray from the original path as it grazes the object. - An infinitely long cylinder of radius R is made of an unusual exotic material with refractive index –1 (Fig. 9.7). The cylinder is placed between two planes whose normals are along the y direction. The center of the cylinder O lies along the y-axis. A narrow laser beam is directed along the y direction from the lower plate. The laser source is at a horizontal distance x from the diameter in the y direction. Find the range of x such that light emitted from the lower plane does not reach the upper plane.

- i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (Fig. 9.8). Let the thickness of the lens vary as w(b) = w0 – (b2/α), where b is the vertical distance from the pole. w0 is a constant. Using Fermat’s principle i.e. the time of transit for a ray between the source and observer is an extremum, find the condition that all paraxial rays starting from the source will converge at a point O on the axis. Find the focal length.

(ii) A gravitational lens may be assumed to have a varying width of the form
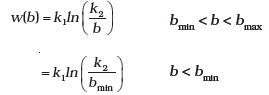
Show that an observer will see an image of a point object as a ring about the center of the lens with an angular radius
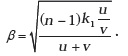
| « Previous | <Next » |
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions



















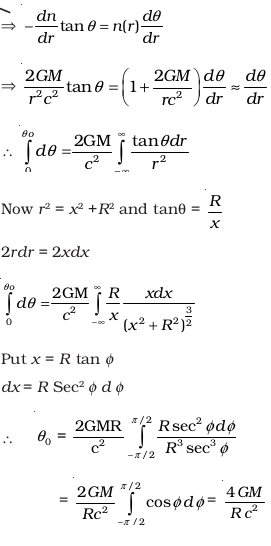




Physics Chemistry Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.




