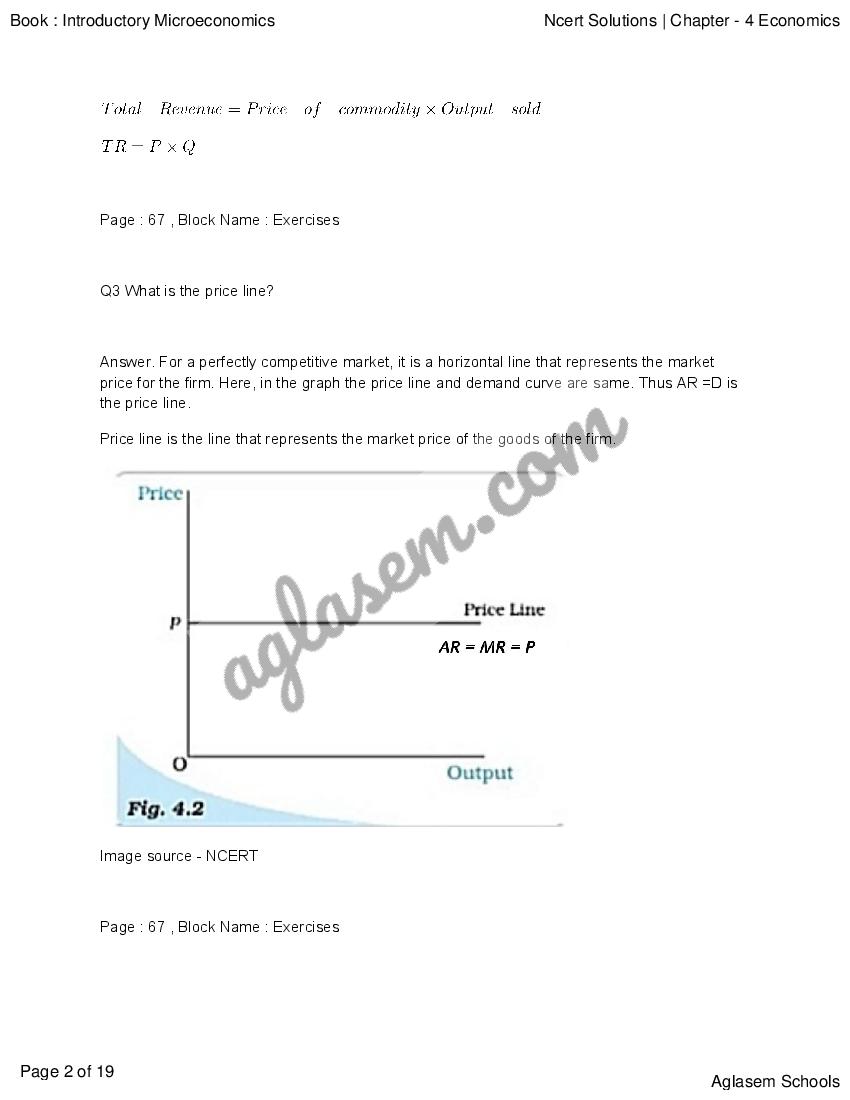
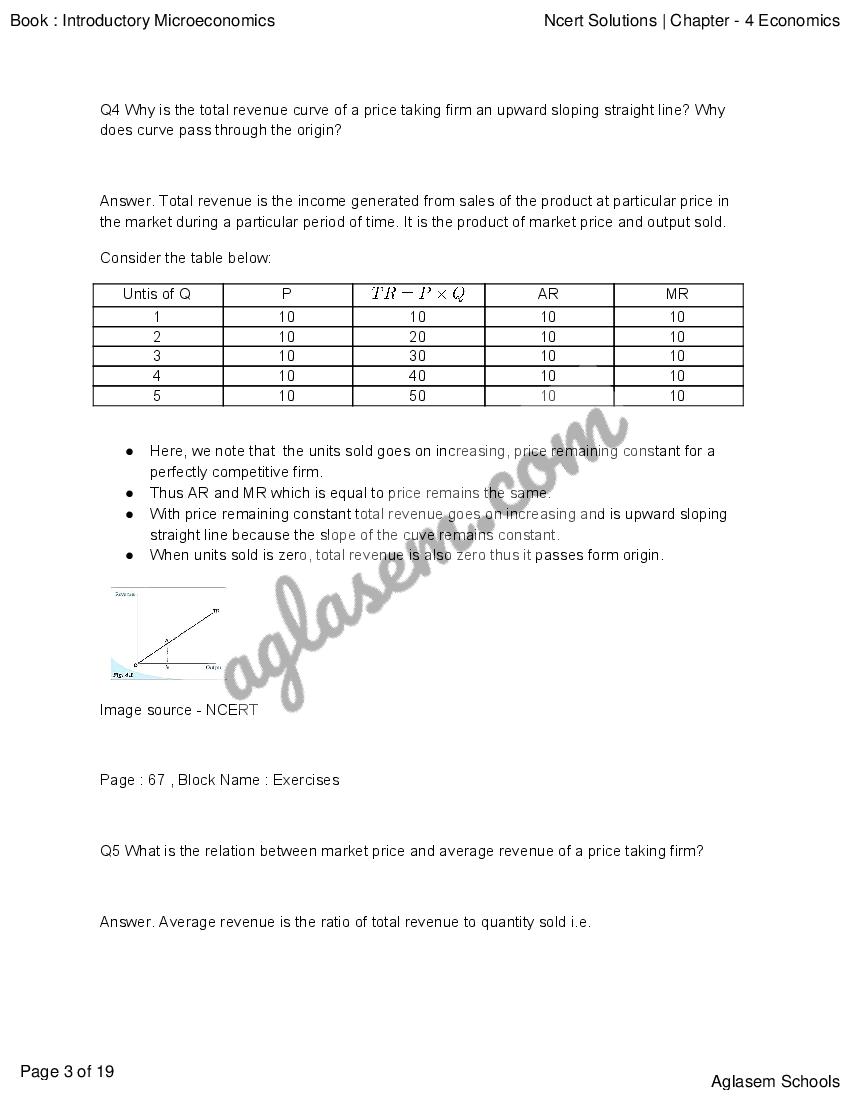
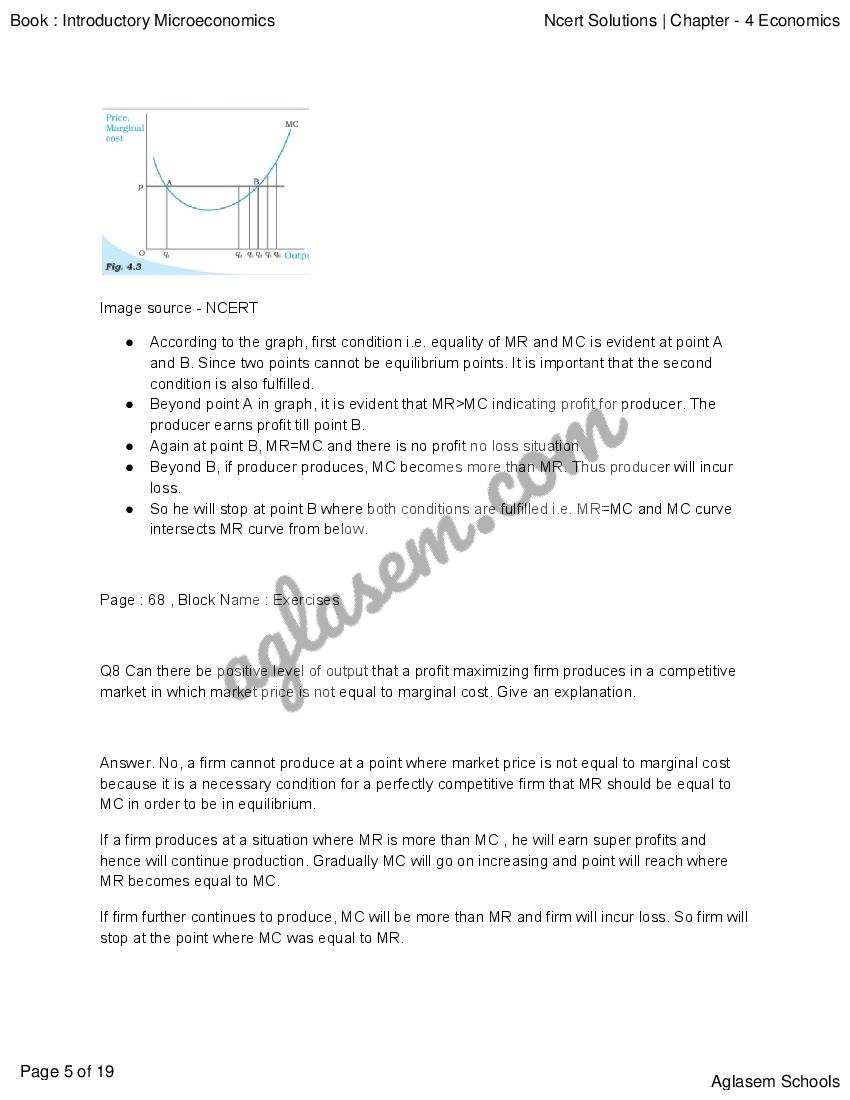
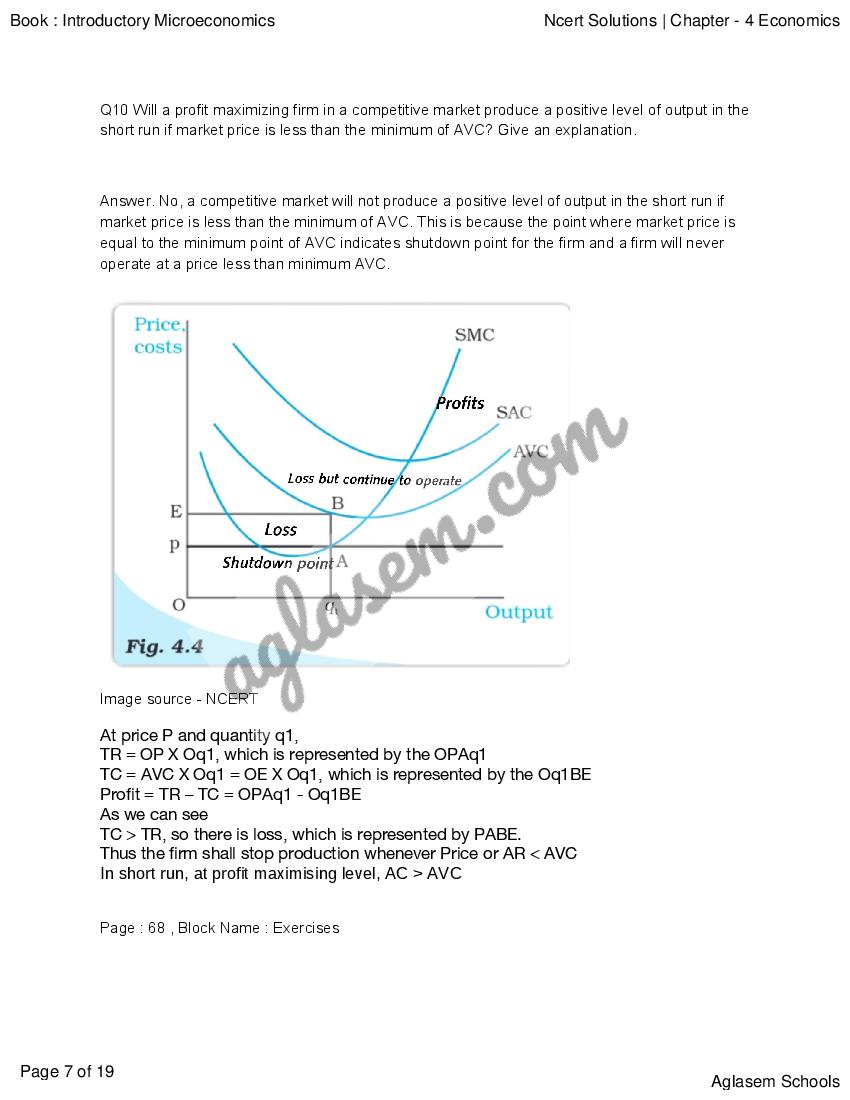
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition has been published by Aglasem. You can now download the Class 12 Economics Ch 4 Questions and Answers PDF here. This NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics contains answers of all questions asked in Chapter 4 in textbook, Introductory Microeconomics. Therefore you can refer it to solve The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition exercise questions and learn more about the topic.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition
Class – Class 12
Subject – Economics
Chapter – Ch 4
Chapter Name – The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition
Book – Introductory Microeconomics
Study Material – NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 PDF
While you can read NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Ch 4 for all exercises here on aglasem. You can also download this NCERT Solutions PDF to refer at anytime when you study The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition. Here it is.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 PDF Download Link – Click Here to Download Solutions PDF
How to download NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 PDF?
You can download the complete NCERT solutions for chapter 4 of this NCERT Book i.e. Introductory Microeconomics with following steps.
- First search NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Ch 4 PDF aglasem and come to this page.
- Now you will see the exercise questions answers of The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition and download pdf link on it.
- Click the Download PDF link to obtain the The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition questions with answers document.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
There are more chapters to study besides The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition in this subject. So here are NCERT solutions for all topics of Economics taught in 12th class here at aglasem.
Introductory Microeconomics
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 National Income Accounting
- Chapter 3 Money and Banking
- Chapter 4 Determination Of Income and Employment
- Chapter 5 Government Budget and The Economy
- Chapter 6 Open Economy Macroeconomics
Introductory Macroeconomics
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Theory Of Consumer Behaviour
- Chapter 3 Production and Costs
- Chapter 4 The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition
- Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium
NCERT Solutions for Class 12
Just like you got Economics Ch 4 solutions here. You can see exercise questions answers of other subjects and their topics too on aglasem. Here are NCERT solutions for all subjects of 12th standard NCERT books.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Geography
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 History
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Psychology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Sociology
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 – An Overview
The key highlights of this study material are as follows.
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Economics |
| Chapter Number | Ch 4 |
| Chapter Name | The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition |
| Book Name | Introductory Microeconomics |
| Book By | NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) |
| Educational Resource Here | NCERT Solutions of Class 12 Economics Ch 4 for All Exercise |
| More Questions Answers of This Subject | NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics |
| Download Book Chapter PDF | NCERT Book Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 |
| All Questions Answers For This Class | NCERT Solutions for Class 12 |
| Complete Solutions | NCERT Solutions |
If you have any queries on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition, then please ask in comments below.
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.