Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 10, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics
NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 is for Wave Optics. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 10. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
- Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in Fig. 10.1. A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid.
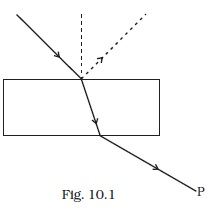
(a) For a particular orientation there shall be darkness as observed through the polaroid.
(b) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall be independent of the rotation.
(c) The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid.
(d) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go through a minimum for four orientations of the polaroid. - Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 104 A. The image seen through the slit shall
(a) be a fine sharp slit white in colour at the center.
(b) a bright slit white at the center diffusing to zero intensities at the edges.
(c) a bright slit white at the center diffusing to regions of different colours.
(d) only be a diffused slit white in colour. - Consider a ray of light incident from air onto a slab of glass (refractive index n) of width d, at an angle θ. The phase difference between the ray reflected by the top surface of the glass and the bottom surface is
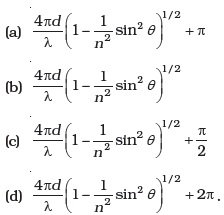
- In a Young’s double slit experiment, the source is white light. One of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case
(a) there shall be alternate interference patterns of red and blue.
(b) there shall be an interference pattern for red distinct from that for blue.
(c) there shall be no interference fringes.
(d) there shall be an interference pattern for red mixing with one for blue. - Figure 10.2 shows a standard two slit arrangement with slits S1, S2. P1, P2 are the two minima points on either side of P (Fig. 10.2). At P2 on the screen, there is a hole and behind P2 is a second 2- slit arrangement with slits S3, S4 and a second screen behind them.
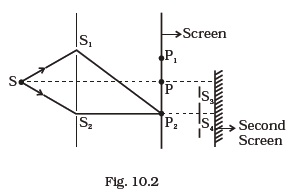
(a) There would be no interference pattern on the second screen but it would be lighted.
(b) The second screen would be totally dark.
(c) There would be a single bright point on the second screen.
(d) There would be a regular two slit pattern on the second screen.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- Two source S1 and S2 of intensity I1 and I2 are placed in front of a screen [Fig. 10.3 (a)]. The pattern of intensity distribution seen in the central portion is given by Fig. 10.3 (b). In this case which of the following statements are true.

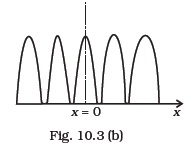
(a) S1 and S2 have the same intensities.
(b) S1 and S2 have a constant phase difference.
(c) S1 and S2 have the same phase.
(d) S1 and S2 have the same wavelength. - Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 103A. The image of the pinhole seen on a screen shall be
(a) a sharp white ring.
(b) different from a geometrical image.
(c) a diffused central spot, white in colour.
(d) diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot. - Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased
(a) the size decreases.
(b) the intensity increases.
(c) the size increases.
(d) the intensity decreases. - For light diverging from a point source
(a) the wavefront is spherical.
(b) the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
(c) the wavefront is parabolic.
(d) the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
- Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
- What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
- Why is the diffraction of sound waves more evident in daily experience than that of light wave?
- The human eye has an approximate angular resolution of φ = 5.8×10–4 rad and a typical photo printer prints a minimum of 300 dpi (dots per inch, 1 inch = 2.54 cm). At what minimal distance z should a printed page be held so that one does not see the individual dots.
- A polaroid (I) is placed in front of a monochromatic source. Another polaroid (II) is placed in front of this polaroid (I) and rotated till no light passes. A third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). In this case, will light emerge from (II). Explain.
Short Answer Type Questions
- Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
- For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000 Å and electrons accelerated through 100V used as the illuminating substance.
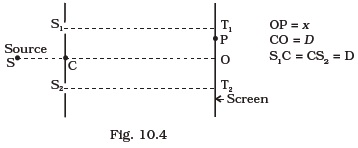
- Consider a two slit interference arrangements (Fig. 10.4) such that the distance of the screen from the slits is half the distance between the slits. Obtain the value of D in terms of λ such that the first minima on the screen falls at a distance D from the centre O.
Long Answer Type Questions
- Figure 10.5 shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.


AC = CO = D, S1C = S2C = d << D
A small transparent slab containing material of μ = 1.5 is placed along AS2 (Fig.10.6). What will be the distance from O of the principal maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab. .- Four identical monochromatic sources A,B,C,D as shown in the (Fig.10.7) produce waves of the same wavelength λ and are coherent. Two receiver R1 and R2 are at great but equal distances from B.
(i) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal?
(ii) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off?
(iii) Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when D is turned off?
(iv) Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off?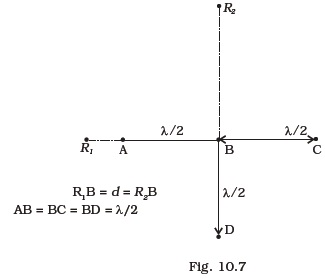
- The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permittivity ( εr) and relative permeability (μr). The refractive index is defined as √μr εr. For ordinary material εr > 0 and μr > 0 and the positive sign is taken for the square root. In 1964, a Russian scientist V. Veselago postulated the existence of material with εr < 0 and μr < 0. Since then such ‘metamaterials’ have been produced in the laboratories and their optical properties studied. For such materials n = – √μr εr. As light enters a medium of such refractive index the phases travel away from the direction of propagation.
(i) According to the description above show that if rays of light enter such a medium from air (refractive index =1) at an angle θ in 2nd quadrant, them the refracted beam is in the 3rd quadrant.
(ii) Prove that Snell’s law holds for such a medium. - To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions



















Physics Chemistry Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.
