Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 5, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter
NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 is for Magnetism and Matter. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 5. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
- A toroid of n turns, mean radius R and cross-sectional radius a carries current I. It is placed on a horizontal table taken as x-y plane. Its magnetic moment m
(a) is non-zero and points in the z-direction by symmetry.
(b) points along the axis of the toroid
(c) is zero, otherwise there would be a field falling as (1/r3) at large distances outside the toroid.
(d) is pointing radially outwards. - The magnetic field of Earth can be modelled by that of a point dipole placed at the centre of the Earth. The dipole axis makes an angle of 11.3° with the axis of Earth. At Mumbai, declination is nearly zero. Then,
(a) the declination varies between 11.3° W to 11.3° E.
(b) the least declination is 0°.
(c) the plane defined by dipole axis and Earth axis passes through Greenwich.
(d) declination averaged over Earth must be always negative. - In a permanent magnet at room temperature
(a) magnetic moment of each molecule is zero.
(b) the individual molecules have non-zero magnetic moment which are all perfectly aligned.
(c) domains are partially aligned.
(d) domains are all perfectly aligned. - Consider the two idealized systems: (i) a parallel plate capacitor with large plates and small separation and (ii) a long solenoid of length L >> R, radius of cross-section. In (i) E is ideally treated as a constant between plates and zero outside. In (ii) magnetic field is constant inside the solenoid and zero outside. These idealised assumptions, however, contradict fundamental laws as below:

- A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am–1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6T at a temperature of 4K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be
(a) (32/3) Am–1
(b) (2/3)Am–1
(c) 6 Am–1
(d) 2.4 Am–1
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
(a) Lines of B are necessarily continuous across S.
(b) Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S.
(c) Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S.
(d) Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S. - The primary origin(s) of magnetism lies in
(a) atomic currents.
(b) Pauli exclusion principle.
(c) polar nature of molecules.
(d) intrinsic spin of electron. - A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of μr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
(a) The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
(b) The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
(c) The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
(d) The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108. - Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding is due to
(a) electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free charges.
(b) lines of B can also end but conductors cannot end them.
(c) lines of B cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is not possible.
(d) shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert lines of B from the interior region. - Let the magnetic field on earth be modelled by that of a point magnetic dipole at the centre of earth. The angle of dip at a point on the geographical equator
(a) is always zero.
(b) can be zero at specific points.
(c) can be positive or negative.
(d) is bounded.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- A proton has spin and magnetic moment just like an electron. Why then its effect is neglected in magnetism of materials?
- A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
- Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 × 10-9) (at STP) and Cu (~10-5).
- From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
- A ball of superconducting material is dipped in liquid nitrogen and placed near a bar magnet.
(i) In which direction will it move?
(ii) What will be the direction of it’s magnetic moment?
Short Answer Type Questions
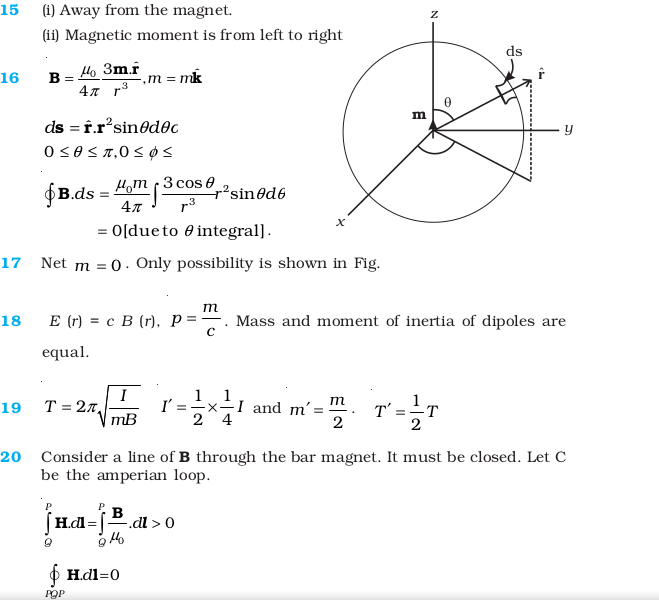
- Verify the Gauss’s law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole moment m at the origin for the surface which is a sphere of radius R.
- Three identical bar magnets are riveted together at centre in the same plane as shown in Fig. 5.1. This system is placed at rest in a slowly varying magnetic field. It is found that the system of magnets does not show any motion. The north-south poles of one magnet is shown in the Fig. 5.1. Determine the poles of the remaining two.

- Suppose we want to verify the analogy between electrostatic and magnetostatic by an explicit experiment. Consider the motion of (i) electric dipole p in an electrostatic field E and (ii) magnetic dipole m in a magnetic field B. Write down a set of conditions on E, B, p, m so that the two motions are verified to be identical. (Assume identical initial conditions.)
- A bar magnet of magnetic moment m and moment of inertia I (about centre, perpendicular to length) is cut into two equal pieces, perpendicular to length. Let T be the period of oscillations of the original magnet about an axis through the mid point, perpendicular to length, in a magnetic field B. What would be the similar period T′ for each piece?
- Use (i) the Ampere’s law for H and (ii) continuity of lines of B, to conclude that inside a bar magnet, (a) lines of H run from the N pole to S pole, while (b) lines of B must run from the S pole to N pole.
Long Answer Type Questions
- Verify the Ampere’s law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole moment m = mkˆ . Take C as the closed curve running clockwise along (i) the z-axis from z = a > 0 to z = R; (ii) along the quarter circle of radius R and centre at the origin, in the first quadrant of x-z plane; (iii) along the x-axis from x = R to x = a, and (iv) along the quarter circle of radius a and centre at the origin in the first quadrant of x-z plane.
- What are the dimensions of χ, the magnetic susceptibility? Consider an H-atom. Guess an expression for χ, upto a constant by constructing a quantity of dimensions of χ, out of parameters of the atom: e, m, v, R and μ0 . Here, m is the electronic mass, v is electronic velocity, R is Bohr radius. Estimate the number so obtained and compare with the value of |χ| ~10–5 for many solid materials.
- Assume the dipole model for earth’s magnetic field B which is given

- Consider the plane S formed by the dipole axis and the axis of earth. Let P be point on the magnetic equator and in S. Let Q be the point of intersection of the geographical and magnetic equators. Obtain the declination and dip angles at P and Q.
- There are two current carrying planar coils made each from identical wires of length L. C1 is circular (radius R ) and C2 is square (side a). They are so constructed that they have same frequency of oscillation when they are placed in the same uniform B and carry the same current. Find a in terms of R.
Click here to download the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter.
| « Previous | Next » |
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions







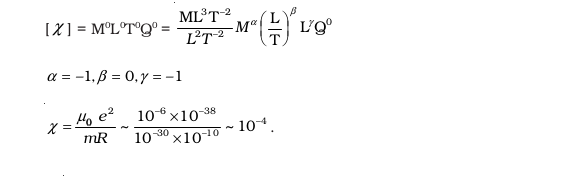




Physics Chemistry Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.

