Candidates can download NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 from this page. The exemplar has been provided by the National Council of Educational Research & Training (NCERT) and the candidates can check it from below for free of cost. It contains objective, very short answer type, short answer type, and long answer type questions. Along with it, the answer for each question has also been provided. From the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8, candidates can understand the level and type of questions that are asked in the exam.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 The d- and f- Block Elements
NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 is for The d- and f- Block Elements. The type of questions that will be asked from NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 are displayed in the below provided NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8. With the help of it, candidates can prepare well for the examination.
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
- Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d5. What is its atomic number?
(i) 25
(ii) 26
(iii) 27
(iv) 24 - The electronic configuration of Cu(II) is 3d9 whereas that of Cu(I) is 3d10. Which of the following is correct?
(i) Cu(II) is more stable
(ii) Cu(II) is less stable
(iii) Cu(I) and Cu(II) are equally stable
(iv) Stability of Cu(I) and Cu(II) depends on nature of copper salts - Metallic radii of some transition elements are given below. Which of these elements will have highest density?

(i) Fe
(ii) Ni
(iii) Co
(iv) Cu - Generally transition elements form coloured salts due to the presence of unpaired electrons. Which of the following compounds will be coloured in solid state?
(i) Ag2SO4
(ii) CuF2
(iii) ZnF2
(iv) Cu2Cl2 - On addition of small amount of KMnO4 to concentrated H2SO4, a green oily Compound is obtained which is highly explosive in nature. Identify the compound from the following.
(i) Mn2O7
(ii) MnO2
(iii) MnSO4
(iv) Mn2O3 - The magnetic nature of elements depends on the presence of unpaired electrons. Identify the configuration of transition element, which shows highest magnetic moment.
(i) 3d7
(ii) 3d5
(iii) 3d8
(iv) 3d2 - Which of the following oxidation state is common for all lanthanides?
(i) +2
(ii) +3
(iii) +4
(iv) +5 - Which of the following reactions are disproportionation reactions?
(a) Cu+ → Cu2+ + Cu
(b) 3MnO4– + 4H+ → 2MnO4– + MnO2 + 2H2O
(c) 2KMnO4 → K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
(d) 2MnO4– + 3Mn2+ + 2H2O → 5MnO2 + 4H+
(i) a, b
(ii) a, b, c
(iii) b, c, d
(iv) a, d - When KMnO4 solution is added to oxalic acid solution, the decolourisation is slow in the beginning but becomes instantaneous after some time because
(i) CO2 is formed as the product.
(ii) Reaction is exothermic.
(iii) MnO4– catalyses the reaction.
(iv) Mn2+ acts as autocatalyst - There are 14 elements in actinoid series. Which of the following elements does not belong to this series?
(i) U
(ii) Np
(iii) Tm
(iv) Fm - KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent in acidic medium. The number of moles of KMnO4 that will be needed to react with one mole of sulphide ions in acidic solution is
(i) 2 / 5
(ii) 3 / 5
(iii) 4 / 5
(iv) 1 / 5 - Which of the following is amphoteric oxide?
Mn2O7, CrO3, Cr2O3, CrO, V2O5, V2O4
(i) V2O5, Cr2O3
(ii) Mn2O7, CrO3
(iii) CrO, V2O5
(iv) V2O5, V2O4 - Gadolinium belongs to 4f series. It’s atomic number is 64. Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration of gadolinium?
(i) [Xe] 4f75d16s2
(ii) [Xe] 4f65d26s2
(iii) [Xe] 4f86d2
(iv) [Xe] 4f95s1 - Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are trapped inside the crystal lattice of metals. Which of the following is not the characteristic property of interstitial compounds?
(i) They have high melting points in comparison to pure metals.|
(ii) They are very hard.
(iii) They retain metallic conductivity.
(iv) They are chemically very reactive. - The magnetic moment is associated with its spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. Spin only magnetic moment value of Cr3+ ion is
(i) 2.87 B.M.
(ii) 3.87 B.M.
(iii) 3.47 B.M.
(iv) 3.57 B.M. - KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent in alkaline medium. When alkaline KMnO4 is treated with KI, iodide ion is oxidised to
(i) I2
(ii) IO–
(iii) IO3–
(iv) IO4– - Which of the following statements is not correct?
(i) Copper liberates hydrogen from acids.
(ii) In its higher oxidation states, manganese forms stable compounds with oxygen and fluorine.
(iii) Mn3+ and Co3+ are oxidising agents in aqueous solution.
(iv) Ti2+ and Cr2+ are reducing agents in aqueous solution - When acidified K2Cr2O7 solution is added to Sn2+ salts then Sn2+ changes to
(i) Sn
(ii) Sn3+
(iii) Sn4+
(iv) Sn+ - Highest oxidation state of manganese in fluoride is +4 (MnF4) but highest oxidation state in oxides is +7 (Mn2O7) because
(i) fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen.
(ii) fluorine does not possess d-orbitals.
(iii) fluorine stabilises lower oxidation state.
(iv) in covalent compounds fluorine can form single bond only while oxygen forms double bond. - Although Zirconium belongs to 4d transition series and Hafnium to 5d transition series even then they show similar physical and chemical properties because___________. .
(i) both belong to d-block.
(ii) both have same number of electrons.|
(iii) both have similar atomic radius.
(iv) both belong to the same group of the periodic table - Why is HCl not used to make the medium acidic in oxidation reactions of KMnO4 in acidic medium?
(i) Both HCl and KMnO4 act as oxidising agents.
(ii) KMnO4 oxidises HCl into Cl2 which is also an oxidising agent.
(iii) KMnO4 is a weaker oxidising agent than HCl.
(iv) KMnO4 acts as a reducing agent in the presence of HCl.
Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note : In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
- Generally transition elements and their salts are coloured due to the presence of unpaired electrons in metal ions. Which of the following compounds are coloured?
(i) KMnO4
(ii) Ce (SO4)2
(iii) TiCl4
(iv) Cu2Cl2 - Transition elements show magnetic moment due to spin and orbital motion of electrons. Which of the following metallic ions have almost same spin only magnetic moment?
(i) Co2+
(ii) Cr2+
(iii) Mn2+
(iv) Cr3+ - In the form of dichromate, Cr (VI) is a strong oxidising agent in acidic medium but Mo (VI) in MoO3 and W (VI) in WO3 are not because ___________.
(i) Cr (VI) is more stable than Mo(VI) and W(VI).
(ii) Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more stable than Cr(VI).
(iii) Higher oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable.
(iv) Lower oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable. - Which of the following actinides show oxidation states upto +7?
(i) Am
(ii) Pu
(iii) U
(iv) Np - General electronic configuration of actinides is (n–2)f1–14 (n-1)d0-2ns2.Which of the following actinides have one electron in 6d orbital?
(i) U (Atomic no. 92)
(ii) Np (Atomic no.93)
(iii) Pu (Atomic no. 94)
(iv) Am (Atomic no. 95) - Which of the following lanthanoids show +2 oxidation state besides the characteristic oxidation state +3 of lanthanoids?
(i) Ce
(ii) Eu
(iii) Yb
(iv) Ho - Which of the following ions show higher spin only magnetic moment value?
(i) Ti3+
(ii) Mn2+
(iii) Fe2+
(iv) Co3+ - Transition elements form binary compounds with halogens. Which of the following elements will form MF3 type compounds?
(i) Cr
(ii) Co
(iii) Cu
(iv) Ni - Which of the following will not act as oxidising agents?
(i) CrO3
(ii) MoO3
(iii) WO3
(iv) CrO42– - Although +3 is the characteristic oxidation state for lanthanides but cerium also shows +4 oxidation state because ___________.
(i) it has variable ionisation enthalpy
(ii) it has a tendency to attain noble gas configuration
(iii) it has a tendency to attain f0 configuration
(iv) it resembles Pb4+
Short Answer Type Questions
- Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
- Why E⊖ values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected?
- Why first ionisation enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn ?
- Transition elements show high melting points. Why?
- When Cu2+ ion is treated with KI, a white precipitate is formed. Explain the reaction with the help of chemical equation.
- Out of Cu2Cl2 and CuCl2, which is more stable and why?
- When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with HCl it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in excess, reacts with NH3 to give an explosive compound (C). Identify compounds A, B and C.
- Although fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen, but the ability of oxygen to stabilise higher oxidation states exceeds that of fluorine. Why?
- Although Cr3+ and Co2+ ions have same number of unpaired electrons but the magnetic moment of Cr3+ is 3.87 B.M. and that of Co2+ is 4.87 B.M. Why?
- Ionisation enthalpies of Ce, Pr and Nd are higher than Th, Pa and U. Why?
- Although Zr belongs to 4d and Hf belongs to 5d transition series but it is quite difficult to separate them. Why?
- Although +3 oxidation states is the characteristic oxidation state of lanthanides but cerium shows +4 oxidation state also. Why?
- Explain why does colour of KMnO4 disappear when oxalic acid is added to its solution in acidic medium.
- When orange solution containing Cr2O72– ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when H+ ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
- A solution of KMnO4 on reduction yields either a colourless solution or a brown precipitate or a green solution depending on pH of the solution. What different stages of the reduction do these represent and how are they carried out?
- The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain why?
- E⊖ of Cu is + 0.34V while that of Zn is – 0.76V. Explain.
- The halides of transition elements become more covalent with increasing oxidation state of the metal. Why?
- While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital but reverse happens during the ionisation of the atom. Explain why?
- Reactivity of transition elements decreases almost regularly from Sc to Cu. Explain.
Matching Type Questions
Note : Match the items of Column I and Column II in the following questions
- Match the catalysts given in Column I with the processes given in Column II.
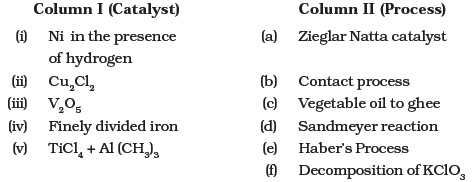
- Match the compounds/elements given in Column I with uses given in Column II.

- Match the properties given in Column I with the metals given in Column II.

- Match the statements given in Column I with the oxidation states given in Column II.

- Match the solutions given in Column I and the colours given in Column II.

- Match the property given in Column I with the element given in Column II.

- Match the properties given in Column I with the metals given in Column II.

Assertion and Reason Type Questions
Note : In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(i) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(iii) Assertion is not true but reason is true.
(iv) Both assertion and reason are false.
- Assertion : Cu2+ iodide is not known.
Reason : Cu2+ oxidises I– to iodine. - Assertion : Separation of Zr and Hf is difficult.
Reason : Because Zr and Hf lie in the same group of the periodic table. - Assertion : Actinides form relatively less stable complexes as compared to lanthanoids.
Reason : Actinides can utilise their 5f orbitals along with 6d orbitals in bonding but lanthanoids do not use their 4f orbital for bonding. - Assertion : Cu cannot liberate hydrogen from acids.
Reason : Because it has positive electrode potential. - Assertion : The highest oxidation state of osmium is +8.
Reason : Osmium is a 5d-block element
Long Answer Type Questions
- Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
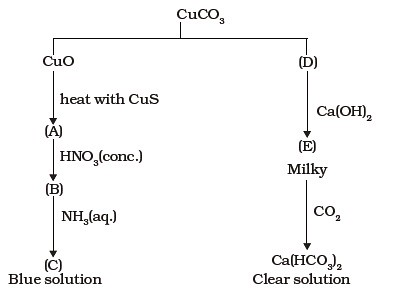
- When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water, a yellow solution of compound (B) is obtained. After treatment of this yellow solution with sulphuric acid, compound (C) can be crystallised from the solution. When compound (C) is treated with KCl, orange crystals of compound (D) crystallise out. Identify A to D and also explain the reactions.
- When an oxide of manganese (A) is fused with KOH in the presence of an oxidising agent and dissolved in water, it gives a dark green solution of
compound (B). Compound (B) disproportionates in neutral or acidic solution to give purple compound (C). An alkaline solution of compound (C) oxidises potassium iodide solution to a compound (D) and compound (A) is also formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved. - On the basis of Lanthanoid contraction, explain the following :
(i) Nature of bonding in La2O3 and Lu2O3.
(ii) Trends in the stability of oxo salts of lanthanides from La to Lu.
(iii) Stability of the complexes of lanthanides.
(iv) Radii of 4d and 5d block elements.
(v) Trends in acidic character of lanthanide oxides. - (a) Answer the following questions :
(i) Which element of the first transition series has highest second ionisation enthalpy?
(ii) Which element of the first transition series has highest third ionisation enthalpy?
(iii) Which element of the first transition series has lowest enthalpy of atomisation?
(b) Identify the metal and justify your answer.
(i) Carbonyl M (CO)5
(ii) MO3F - Mention the type of compounds formed when small atoms like H, C and N get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals. Also give physical and Chemical characteristics of these compounds.
- (a) Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state. How does Fe(III) catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions?
(b) Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts. - A violet compound of manganese (A) decomposes on heating to liberate oxygen and compounds (B) and (C) of manganese are formed. Compound (C) reacts with KOH in the presence of potassium nitrate to give compound (B). On heating compound (C) with conc. H2SO4 and NaCl, chlorine gas is liberated and a compound (D) of manganese along with other products is formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved.
| « Previous | Next » |
Answers







Chemistry Physics Maths Biology
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel.
